使用 epsilon 实施 NFA 的计划迁移到 DFA 转换
非确定性有限自动机(NFA): NFA 是一种有限自动机,在某些情况下,当单个输入被赋予单个状态时,机器会进入多个状态,即某些动作不能由当前唯一确定状态和当前输入符号。
An NFA can be represented as M = { Q, ∑, ∂, q0, F}Q → Finite non-empty set of states.
∑ → Finite non-empty set of input symbols.
∂ → Transitional Function.
q0 → Beginning state.
F → Final State
NFA 带有 (null) 或 ∈ move :如果任何有限自动机包含 ε (null) move 或 transaction,则该有限自动机称为带有 &in 的 NFA;移动
例子 :
考虑带有 ∈ 的 NFA 的下图;移动 :
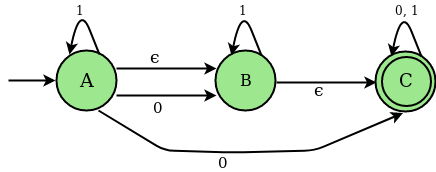
上述 NFA 的过渡状态表
| STATES | 0 | 1 | epsilon |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | B, C | A | B |
| B | – | B | C |
| C | C | C | – |
Epsilon (∈) – 闭包:给定状态 X 的 Epsilon 闭包是一组状态,可以从状态 X 到达,只有 (null) 或 ε 移动,包括状态 X 本身。换句话说,一个状态的ε-闭包可以通过一个状态的ε-闭包的联合运算来获得,该状态的ε-闭包可以通过单个ε移动以递归方式从X到达。
对于上面的例子 ∈关闭如下:
∈ closure(A) : {A, B, C}
∈ closure(B) : {B, C}
∈ closure(C) : {C}
Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA): DFA 是一种有限自动机,在所有情况下,当将单个输入提供给单个状态时,机器会进入单个状态,即机器的所有移动都可以由下式唯一确定当前状态和当前输入符号。
使用 ε-move 将 NFA 转换为 DFA 的步骤:
Step 1 : Take ∈ closure for the beginning state of NFA as beginning state of DFA.
Step 2 : Find the states that can be traversed from the present for each input symbol
(union of transition value and their closures for each states of NFA present in current state of DFA).
Step 3 : If any new state is found take it as current state and repeat step 2.
Step 4 : Do repeat Step 2 and Step 3 until no new state present in DFA transition table.
Step 5 : Mark the states of DFA which contains final state of NFA as final states of DFA.
对应于上述 NFA 的 DFA 的转移状态表
| STATES | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| A, B, C | B, C | A, B, C |
| B, C | C | B, C |
| C | C | C |
DFA 状态图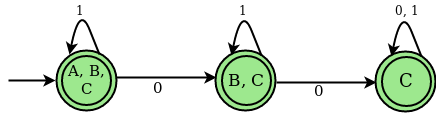
例子 :
Input : 6
2
FC - BF
- C -
- - D
E A -
A - BF
- - -
Output :
STATES OF NFA : A, B, C, D, E, F,
GIVEN SYMBOLS FOR NFA: 0, 1, eps
NFA STATE TRANSITION TABLE
STATES |0 |1 eps
--------+------------------------------------
A |FC |- |BF
B |- |C |-
C |- |- |D
D |E |A |-
E |A |- |BF
F |- |- |-
e-Closure (A) : ABF
e-Closure (B) : B
e-Closure (C) : CD
e-Closure (D) : D
e-Closure (E) : BEF
e-Closure (F) : F
********************************************************
DFA TRANSITION STATE TABLE
STATES OF DFA : ABF, CDF, CD, BEF,
GIVEN SYMBOLS FOR DFA: 0, 1,
STATES |0 |1
--------+-----------------------
ABF |CDF |CD
CDF |BEF |ABF
CD |BEF |ABF
BEF |ABF |CD
Input :
9
2
- - BH
- - CE
D - -
- - G
- F -
- - G
- - BH
I - -
- - -
Output :
STATES OF NFA : A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I,
GIVEN SYMBOLS FOR NFA: 0, 1, eps
NFA STATE TRANSITION TABLE
STATES |0 |1 eps
--------+------------------------------------
A |- |- |BH
B |- |- |CE
C |D |- |-
D |- |- |G
E |- |F |-
F |- |- |G
G |- |- |BH
H |I |- |-
I |- |- |-
e-Closure (A) : ABCEH
e-Closure (B) : BCE
e-Closure (C) : C
e-Closure (D) : BCDEGH
e-Closure (E) : E
e-Closure (F) : BCEFGH
e-Closure (G) : BCEGH
e-Closure (H) : H
e-Closure (I) : I
********************************************************
DFA TRANSITION STATE TABLE
STATES OF DFA : ABCEH, BCDEGHI, BCEFGH,
GIVEN SYMBOLS FOR DFA: 0, 1,
STATES |0 |1
--------+-----------------------
ABCEH |BCDEGHI |BCEFGH
BCDEGHI |BCDEGHI |BCEFGH
BCEFGH |BCDEGHI |BCEFGH
解释 :
输入的第一行包含 NFA 的状态数 ( N )。输入的第二行表示输入符号 ( S ) 的数量。在示例1 中,NFA 的状态数为 6,即( A、B、C、D、E、F )和 2 个输入符号,即(0、1 )。由于我们正在与 ∈ 合作开发 NFA;移动, ∈将作为额外的输入符号添加。接下来的N行包含 NFA 的每个状态的转换值。第 i 行第 j 列的值表示第 j 个输入符号上第 i 个状态的转换值。在 example1 transition(A, 0) 中: FC 。
输出包含 NFA,∈通过转换输入 NFA 获得相应 NFA 和 DFA 的每个状态的闭包。还指定了 DFA 的状态和输入符号。
以下是上述方法的实现:
// C Program to illustrate how to convert e-nfa to DFA
#include
#include
#include
#define MAX_LEN 100
char NFA_FILE[MAX_LEN];
char buffer[MAX_LEN];
int zz = 0;
// Structure to store DFA states and their
// status ( i.e new entry or already present)
struct DFA {
char *states;
int count;
} dfa;
int last_index = 0;
FILE *fp;
int symbols;
/* reset the hash map*/
void reset(int ar[], int size) {
int i;
// reset all the values of
// the mapping array to zero
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
ar[i] = 0;
}
}
// Check which States are present in the e-closure
/* map the states of NFA to a hash set*/
void check(int ar[], char S[]) {
int i, j;
// To parse the individual states of NFA
int len = strlen(S);
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// Set hash map for the position
// of the states which is found
j = ((int)(S[i]) - 65);
ar[j]++;
}
}
// To find new Closure States
void state(int ar[], int size, char S[]) {
int j, k = 0;
// Combine multiple states of NFA
// to create new states of DFA
for (j = 0; j < size; j++) {
if (ar[j] != 0)
S[k++] = (char)(65 + j);
}
// mark the end of the state
S[k] = '\0';
}
// To pick the next closure from closure set
int closure(int ar[], int size) {
int i;
// check new closure is present or not
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (ar[i] == 1)
return i;
}
return (100);
}
// Check new DFA states can be
// entered in DFA table or not
int indexing(struct DFA *dfa) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < last_index; i++) {
if (dfa[i].count == 0)
return 1;
}
return -1;
}
/* To Display epsilon closure*/
void Display_closure(int states, int closure_ar[],
char *closure_table[],
char *NFA_TABLE[][symbols + 1],
char *DFA_TABLE[][symbols]) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < states; i++) {
reset(closure_ar, states);
closure_ar[i] = 2;
// to neglect blank entry
if (strcmp(&NFA_TABLE[i][symbols], "-") != 0) {
// copy the NFA transition state to buffer
strcpy(buffer, &NFA_TABLE[i][symbols]);
check(closure_ar, buffer);
int z = closure(closure_ar, states);
// till closure get completely saturated
while (z != 100)
{
if (strcmp(&NFA_TABLE[z][symbols], "-") != 0) {
strcpy(buffer, &NFA_TABLE[z][symbols]);
// call the check function
check(closure_ar, buffer);
}
closure_ar[z]++;
z = closure(closure_ar, states);
}
}
// print the e closure for every states of NFA
printf("\n e-Closure (%c) :\t", (char)(65 + i));
bzero((void *)buffer, MAX_LEN);
state(closure_ar, states, buffer);
strcpy(&closure_table[i], buffer);
printf("%s\n", &closure_table[i]);
}
}
/* To check New States in DFA */
int new_states(struct DFA *dfa, char S[]) {
int i;
// To check the current state is already
// being used as a DFA state or not in
// DFA transition table
for (i = 0; i < last_index; i++) {
if (strcmp(&dfa[i].states, S) == 0)
return 0;
}
// push the new
strcpy(&dfa[last_index++].states, S);
// set the count for new states entered
// to zero
dfa[last_index - 1].count = 0;
return 1;
}
// Transition function from NFA to DFA
// (generally union of closure operation )
void trans(char S[], int M, char *clsr_t[], int st,
char *NFT[][symbols + 1], char TB[]) {
int len = strlen(S);
int i, j, k, g;
int arr[st];
int sz;
reset(arr, st);
char temp[MAX_LEN], temp2[MAX_LEN];
char *buff;
// Transition function from NFA to DFA
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
j = ((int)(S[i] - 65));
strcpy(temp, &NFT[j][M]);
if (strcmp(temp, "-") != 0) {
sz = strlen(temp);
g = 0;
while (g < sz) {
k = ((int)(temp[g] - 65));
strcpy(temp2, &clsr_t[k]);
check(arr, temp2);
g++;
}
}
}
bzero((void *)temp, MAX_LEN);
state(arr, st, temp);
if (temp[0] != '\0') {
strcpy(TB, temp);
} else
strcpy(TB, "-");
}
/* Display DFA transition state table*/
void Display_DFA(int last_index, struct DFA *dfa_states,
char *DFA_TABLE[][symbols]) {
int i, j;
printf("\n\n********************************************************\n\n");
printf("\t\t DFA TRANSITION STATE TABLE \t\t \n\n");
printf("\n STATES OF DFA :\t\t");
for (i = 1; i < last_index; i++)
printf("%s, ", &dfa_states[i].states);
printf("\n");
printf("\n GIVEN SYMBOLS FOR DFA: \t");
for (i = 0; i < symbols; i++)
printf("%d, ", i);
printf("\n\n");
printf("STATES\t");
for (i = 0; i < symbols; i++)
printf("|%d\t", i);
printf("\n");
// display the DFA transition state table
printf("--------+-----------------------\n");
for (i = 0; i < zz; i++) {
printf("%s\t", &dfa_states[i + 1].states);
for (j = 0; j < symbols; j++) {
printf("|%s \t", &DFA_TABLE[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
// Driver Code
int main() {
int i, j, states;
char T_buf[MAX_LEN];
// creating an array dfa structures
struct DFA *dfa_states = malloc(MAX_LEN * (sizeof(dfa)));
states = 6, symbols = 2;
printf("\n STATES OF NFA :\t\t");
for (i = 0; i < states; i++)
printf("%c, ", (char)(65 + i));
printf("\n");
printf("\n GIVEN SYMBOLS FOR NFA: \t");
for (i = 0; i < symbols; i++)
printf("%d, ", i);
printf("eps");
printf("\n\n");
char *NFA_TABLE[states][symbols + 1];
// Hard coded input for NFA table
char *DFA_TABLE[MAX_LEN][symbols];
strcpy(&NFA_TABLE[0][0], "FC");
strcpy(&NFA_TABLE[0][1], "-");
strcpy(&NFA_TABLE[0][2], "BF");
strcpy(&NFA_TABLE[1][0], "-");
strcpy(&NFA_TABLE[1][1], "C");
strcpy(&NFA_TABLE[1][2], "-");
strcpy(&NFA_TABLE[2][0], "-");
strcpy(&NFA_TABLE[2][1], "-");
strcpy(&NFA_TABLE[2][2], "D");
strcpy(&NFA_TABLE[3][0], "E");
strcpy(&NFA_TABLE[3][1], "A");
strcpy(&NFA_TABLE[3][2], "-");
strcpy(&NFA_TABLE[4][0], "A");
strcpy(&NFA_TABLE[4][1], "-");
strcpy(&NFA_TABLE[4][2], "BF");
strcpy(&NFA_TABLE[5][0], "-");
strcpy(&NFA_TABLE[5][1], "-");
strcpy(&NFA_TABLE[5][2], "-");
printf("\n NFA STATE TRANSITION TABLE \n\n\n");
printf("STATES\t");
for (i = 0; i < symbols; i++)
printf("|%d\t", i);
printf("eps\n");
// Displaying the matrix of NFA transition table
printf("--------+------------------------------------\n");
for (i = 0; i < states; i++) {
printf("%c\t", (char)(65 + i));
for (j = 0; j <= symbols; j++) {
printf("|%s \t", &NFA_TABLE[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int closure_ar[states];
char *closure_table[states];
Display_closure(states, closure_ar, closure_table, NFA_TABLE, DFA_TABLE);
strcpy(&dfa_states[last_index++].states, "-");
dfa_states[last_index - 1].count = 1;
bzero((void *)buffer, MAX_LEN);
strcpy(buffer, &closure_table[0]);
strcpy(&dfa_states[last_index++].states, buffer);
int Sm = 1, ind = 1;
int start_index = 1;
// Filling up the DFA table with transition values
// Till new states can be entered in DFA table
while (ind != -1) {
dfa_states[start_index].count = 1;
Sm = 0;
for (i = 0; i < symbols; i++) {
trans(buffer, i, closure_table, states, NFA_TABLE, T_buf);
// storing the new DFA state in buffer
strcpy(&DFA_TABLE[zz][i], T_buf);
// parameter to control new states
Sm = Sm + new_states(dfa_states, T_buf);
}
ind = indexing(dfa_states);
if (ind != -1)
strcpy(buffer, &dfa_states[++start_index].states);
zz++;
}
// display the DFA TABLE
Display_DFA(last_index, dfa_states, DFA_TABLE);
return 0;
}
在 ∈ 中使用 NFA move :如果我们想构造一个接受一种语言的 FA,有时会变得非常困难,或者似乎不可能构造一个直接的 NFA 或 DFA。但是如果 NFA 带有 ∈使用moves,则可以轻松构建和描述过渡图。