给定二叉树的中序和层序遍历,构造二叉树。下面是一个例子来说明这个问题。
例子:
Input: Two arrays that represent Inorder
and level order traversals of a
Binary Tree
in[] = {4, 8, 10, 12, 14, 20, 22};
level[] = {20, 8, 22, 4, 12, 10, 14};
Output: Construct the tree represented
by the two arrays.
For the above two arrays, the
constructed tree is shown.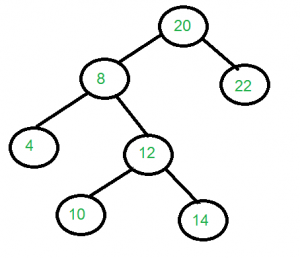
我们在下面的帖子中讨论了一个解决方案,该解决方案适用于 O(N^3)
从中序和水平顺序遍历构造一棵树 |设置 1
方法:以下算法使用O(N^2)时间复杂度解决上述问题,使用c++中的unordered_set数据结构(基本上是做一个hash表)把当前根的左子树的值放在后面,我们会检查以 O(1) 复杂度来查找当前 levelOrder 节点是否是左子树的一部分。
如果它是左子树的一部分,则为左添加一个 lLevel 数组,否则将其添加到右子树的 rLevel 数组中。
下面是上述想法的c++实现
C++
/* program to construct tree using inorder
and levelorder traversals */
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node */
struct Node
{
int key;
struct Node* left, *right;
};
Node* makeNode(int data){
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->key = data;
newNode->right = newNode->right = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// Function to build tree from given
// levelorder and inorder
Node* buildTree(int inorder[], int levelOrder[],
int iStart, int iEnd, int n)
{
if (n <= 0)
return NULL;
// First node of level order is root
Node* root = makeNode(levelOrder[0]);
// Search root in inorder
int index = -1;
for (int i=iStart; i<=iEnd; i++){
if (levelOrder[0] == inorder[i]){
index = i;
break;
}
}
// Insert all left nodes in hash table
unordered_set s;
for (int i=iStart;ileft = buildTree(inorder, lLevel,
iStart, index-1, index-iStart);
root->right = buildTree(inorder, rLevel,
index+1, iEnd, iEnd-index);
return root;
}
/* Utility function to print inorder
traversal of binary tree */
void printInorder(Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
printInorder(node->left);
cout << node->key << " ";
printInorder(node->right);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int in[] = {4, 8, 10, 12, 14, 20, 22};
int level[] = {20, 8, 22, 4, 12, 10, 14};
int n = sizeof(in)/sizeof(in[0]);
Node *root = buildTree(in, level, 0,
n - 1, n);
/* Let us test the built tree by
printing Inorder traversal */
cout << "Inorder traversal of the "
"constructed tree is \n";
printInorder(root);
return 0;
} Java
/*
* program to construct tree using inorder
* and levelorder traversals
*/
import java.util.HashSet;
class GFG
{
/* A binary tree node */
static class Node {
int key;
Node left, right;
};
static Node makeNode(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.key = data;
newNode.right = newNode.right = null;
return newNode;
}
// Function to build tree from given
// levelorder and inorder
static Node buildTree(int inorder[], int levelOrder[], int iStart, int iEnd, int n) {
if (n <= 0)
return null;
// First node of level order is root
Node root = makeNode(levelOrder[0]);
// Search root in inorder
int index = -1;
for (int i = iStart; i <= iEnd; i++) {
if (levelOrder[0] == inorder[i]) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
// Insert all left nodes in hash table
HashSet s = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = iStart; i < index; i++)
s.add(inorder[i]);
// Separate level order traversals
// of left and right subtrees.
int[] lLevel = new int[s.size()]; // Left
int[] rLevel = new int[iEnd - iStart - s.size()]; // Right
int li = 0, ri = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (s.contains(levelOrder[i]))
lLevel[li++] = levelOrder[i];
else
rLevel[ri++] = levelOrder[i];
}
// Recursively build left and right
// subtrees and return root.
root.left = buildTree(inorder, lLevel, iStart, index - 1, index - iStart);
root.right = buildTree(inorder, rLevel, index + 1, iEnd, iEnd - index);
return root;
}
/*
* Utility function to print inorder
* traversal of binary tree
*/
static void printInorder(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
printInorder(node.left);
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
printInorder(node.right);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args) {
int in[] = { 4, 8, 10, 12, 14, 20, 22 };
int level[] = { 20, 8, 22, 4, 12, 10, 14 };
int n = in.length;
Node root = buildTree(in, level, 0, n - 1, n);
/*
* Let us test the built tree by
* printing Inorder traversal
*/
System.out.println("Inorder traversal of the constructed tree is ");
printInorder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjeev2552 Javascript
Java
import java.util.HashMap;
//class Node
class Node{
int data;
Node left,right;
Node(int data){
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class ConstructTree {
//hashmap to store the indices of levelorder array
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
//function to construct hashmap
void constructMap(int level[]) {
for(int i=0;i end)
return null;
int min_index = start;
//In the range of start & end from inorder, search the element
//with least index from level order map
for(int i=start+1;i<=end;i++) {
int temp = in[i];
//if current element from inorder have least index in
//levelorder map, update min_index
if(map.get(in[min_index]) > map.get(temp))
min_index = i;
}
//create a node with current element
Node root = new Node(in[min_index]);
//if start is equal to end, then return root
if(start == end)
return root;
//construct left and right subtrees
root.left = construct(in,level,start,min_index-1);
root.right = construct(in,level,min_index+1,end);
return root;
}
//function to print inorder
void printInorder(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
printInorder(node.left);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
printInorder(node.right);
}
//Driver function
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConstructTree tree = new ConstructTree();
int in[] = {4, 8, 10, 12, 14, 20, 22};
int level[] = {20, 8, 22, 4, 12, 10, 14};
//function calls
tree.constructMap(level);
int n = level.length;
Node root = tree.construct(in, level, 0, n-1);
tree.printInorder(root);
}
}
//This method is contributed by Likhita AVL 输出
Inorder traversal of the constructed tree is
4 8 10 12 14 20 22 时间复杂度:O(N^2)
优化:没有单独的左子树和右子树的级别顺序遍历数组。
方法:使用哈希。
使用HashMap来存储层序遍历的索引。在inorder的start&end范围内,从层序图中搜索索引最少的元素。递归创建左右子树。
index -> the least index
for left subtree: start to index-1
for right subtree: index+1 to end执行:
Java
import java.util.HashMap;
//class Node
class Node{
int data;
Node left,right;
Node(int data){
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class ConstructTree {
//hashmap to store the indices of levelorder array
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
//function to construct hashmap
void constructMap(int level[]) {
for(int i=0;i end)
return null;
int min_index = start;
//In the range of start & end from inorder, search the element
//with least index from level order map
for(int i=start+1;i<=end;i++) {
int temp = in[i];
//if current element from inorder have least index in
//levelorder map, update min_index
if(map.get(in[min_index]) > map.get(temp))
min_index = i;
}
//create a node with current element
Node root = new Node(in[min_index]);
//if start is equal to end, then return root
if(start == end)
return root;
//construct left and right subtrees
root.left = construct(in,level,start,min_index-1);
root.right = construct(in,level,min_index+1,end);
return root;
}
//function to print inorder
void printInorder(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
printInorder(node.left);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
printInorder(node.right);
}
//Driver function
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConstructTree tree = new ConstructTree();
int in[] = {4, 8, 10, 12, 14, 20, 22};
int level[] = {20, 8, 22, 4, 12, 10, 14};
//function calls
tree.constructMap(level);
int n = level.length;
Node root = tree.construct(in, level, 0, n-1);
tree.printInorder(root);
}
}
//This method is contributed by Likhita AVL
输出
4 8 10 12 14 20 22 时间复杂度: O(n^2)。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。