理想气体方程和绝对温度
一端带有充满液体的灯泡的温度计,最常用的液体是水银、甲苯、酒精、戊烷、杂酚油,由于其不同的膨胀特性,除了固定读数外,它们显示不同的温度读数。另一方面,使用气体的温度计显示相同的温度读数。使用哪种类型的气体并不重要。实验表明,所有气体在低密度下都以相同的方式膨胀。
压力 (P)、体积 (V) 和温度 (T) 其中 T = t + 273.15 和 t 是以°C 为单位的温度是解释给定数量(质量)气体行为的变量。理想气体定律,也称为通用气体方程,是一种假设理想气体的方程状态。尽管存在缺陷,但理想气体定律很好地近似了许多气体在各种情况下的行为。 Benoit Paul Émile Clapeyron 在 1834 年提出了理想气体定律,它是经验查尔斯定律、波义耳定律、阿伏伽德罗定律和盖伊定律的混合体。吕萨克的。
理想气体方程
理想气体定律是 17 世纪 Boyle 和 18 世纪 Charles 的观测工作的结合。
波义耳定律:对于保持在固定温度下的给定量气体,气体压力与气体体积成反比,即在恒定温度下,一定量气体的压力和体积之间的关系可以写为,
P ∝ 1 / V
or
PV = Constant
where P is the pressure and V is the volume.
查尔斯定律:对于保持在恒定压力下的给定固定数量的气体,气体体积与气体温度成正比,即在恒定温度下,一定量气体的体积和温度之间的关系可以写为,
V ∝ T
or
V / T = Constant
where T is the Temperature.
这两个定律适用于低密度气体,可以归为一个关系。值得注意的是,
PV = 常数
和
V/T = 常数
对于特定数量的气体,则
因此PV/T也应该是一个常数。
它可以以更一般的形式表述,适用于任何数量的任何低密度气体,而不仅仅是特定数量的该气体。这种关系描述了理想气体定律,称为理想气体方程。
It can be expressed as,
PV / T = nR
or
PV = nRT
where, n is the number of moles in the sample of gas and R is the universal gas constant.
Note: The universal gas constant (R) has a value of 8.314 kJ/mole in the SI system.
它也可以以更一般的形式表述,适用于任何数量的任何低密度气体,而不仅仅是特定数量的该气体。
理想气体方程的推导
Let P is the pressure exerted by the gas, V is the volume f the gas, T is the Temperature.
According to Boyle’s Law,
P ∝ 1/V
or
V ∝ 1/P ……(1)
According to Charles’ Law,
V ∝ T ……..(2)
According to Avogadro’s Law,
When P and T are both constant, the volume of a gas is proportional to the number of moles of gas.i.e.
V ∝ n …….(3)
Compare equation (1), (2) and (3) as,
V ∝ nT/P
or
PV = nRT
where R is the Universal gas constant and it is value of 8.314 J/mol-K
绝对温度
Thermodynamic temperature is another name for absolute temperature. The thermodynamic energy of a system is lowest at this temperature. Absolute temperature equals zero Kelvin or -273 °C, commonly known as absolute zero. The velocity of the gas particles stops at absolute zero temperature. This signifies that the particles of the gas really aren’t moving. At absolute zero, the volume of the gas is zero. As a result, the volume of a gas is measured by its absolute zero.
温度与压力和体积有直接关系,即
PV ∝ T
这种关系使气体能够用于确定具有恒定体积的气体温度计中的温度。
因此,在恒定体积下,该关系可以写为,
P ∝ T ,并且温度是用定容气体温度计根据压力读取的。
一条直线从压力与温度的关系图中出现。
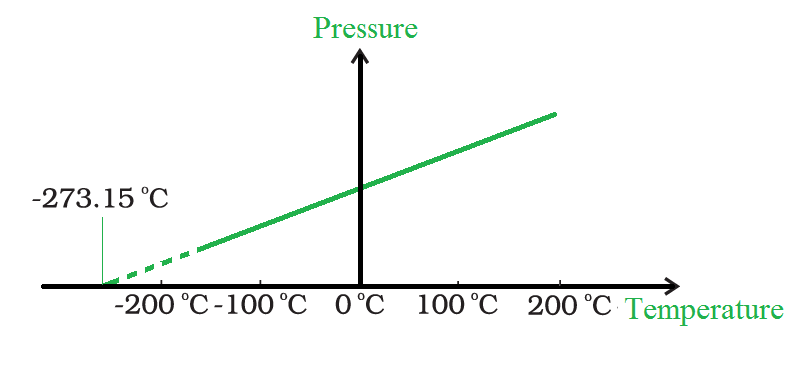
在恒定体积下,低密度气体的压力与温度的关系图
对真实气体的观察与低温下理想气体定律的预期值不同。然而,这种关系在很宽的温度范围内是线性的,如果气体仍然是气体,压力会随着温度的降低而下降到零。将直线外推到轴产生理想气体的绝对最低温度。绝对零定义为 - 273.15 摄氏度的温度。开尔文温标,通常称为绝对标度温度,建立在绝对零上。
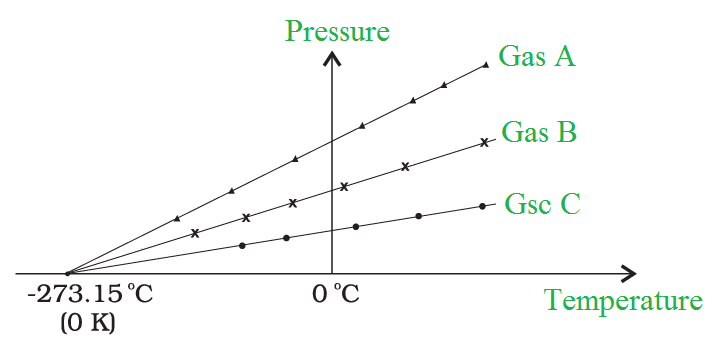
压力与温度的关系图中相同的绝对零温度以及低密度气体的线外推。
在开尔文温标上,以– 273.15 °C 作为零点,即0 K。在开尔文和摄氏温度系统中,单位大小是相同的。因此,它们之间的关系可以表示为
T = t + 273.15
其中 t 是以°C 为单位的温度
示例问题
问题1:STP 2.34 克二氧化碳气体所占的体积是多少?
解决方案:
Given,
Weight (m) of the carbon dioxide is 2.34 grams.
At STP, Temperature is 273.0 K.
Pressure is 1.00 atm.
The universal gas constant (R) has a value of 0.08206 L atm mol¯1 K¯1.
The expression for the number of mole is,
n = m/M
where, n is the number of moles, m is the weight and M is the molar mass of the substance.
Molar mass of the carbon dioxide is 44.0 g mol¯1.
So, the value of n can be calculated as,
n = 2.34 g / 44.0 g mol¯1
= 0.0532 mol
According to the ideal gas equation,
PV = nRT
Rearranging the equation,
V = nRT / P
Substituting all the values,
V = [0.0532 mol) (0.08206 L atm mol¯1 K¯1) (273.0 K)] / 1.00 atm
= 1.19 L
问题 2:STP 的氩气样品占 56.2 升。确定样品中氩的摩尔数和氩的质量。
解决方案:
Given,
Volume (V) of the argon gas is 56.2 liters.
At STP, Temperature is 273.0 K.
Pressure is 1.00 atm.
Molar mass of the argon gas is 39.948 g/mol.
According to the ideal gas equation,
PV = nRT
Rearranging the equation,
n = PV / RT
Subtitituting all the values in the above equation,
n = [(1.00 atm) (56.2 L) ] / [ (0.08206 L atm mol¯1 K¯1) (273.0 K)]
= 2.50866 mol
The expression for the number of mole is
n = m/M
Rearranging the equation,
m = nM
Subtitituting all the values in the above equation,
m = (2.50866 mol)×(39.948 g/mol)
= 100 g
问题 3:在什么温度下,0.654 摩尔氖气在 1.95 个大气压下会占据 12.30 升?
解决方案:
Given,
The Volume (V) of the neon gas is 12.30 liters.
The Pressure is 1.95 atm.
The Number of moles is 0.654 moles.
According to the ideal gas equation,
PV = nRT
Rearranging the equation,
T = PV / nR
Subtitituting all the values in the above equation,
T = [(1.95 atm) ×(12.30 L)] / [(0.654 mol)×(0.08206 L atm mol¯1 K¯1)]
= 447 K
问题 4:推导理想气体方程?
解决方案:
Let P is the pressure exerted by the gas, V is the volume f the gas, T is the Temperature.
According to Boyle’s Law,
P ∝ 1/V
or
V ∝ 1/P ……(1)
According to Charles’ Law,
V ∝ T ……..(2)
According to Avogadro’s Law,
When P and T are both constant, the volume of a gas is proportional to the number of moles of gas.i.e.
V ∝ n …….(3)
Compare equation (1), (2) and (3) as,
V ∝ nT/P
or
PV = nRT
where R is the Universal gas constant and it is value of 8.314 J/mol-K
问题 5:将 5.600 g 固体 CO2 放入一个 4.00 L 的空密封容器中,温度为 300 K。当所有固体 CO2 变成气体时,容器中的压力是多少?
解决方案:
Given,
The Weight (m) of the carbon dioxide is 5.600 g.
The Volume (V) of the carbon dioxide is 4.00 L.
The Temperature is 300 K.
Molar mass of the carbon dioxide is 44.0 g mol¯1
The expression for the number of mole is
n = m/M
Subtitituting all the values in the above equation,
n = (5.600 g) / (44.009 g/mol)
= 0.1272467 mol
According to the ideal gas equation,
PV = nRT
Rearranging the equation,
P = nRT/V
Subtitituting all the values in the above equation,
P = (0.1272467 mol)× (0.08206 L atm mol¯1 K¯1)× (300 K)/ (4.00 L)
= 0.7831 atm