给定一个带有某些项的序列,我们需要计算该序列的下一个K项。假定序列是由某个多项式生成的,但是该多项式可能是复杂的。注意多项式是以下形式的表达式:
P(x)= a0 + a1 x + a2 x ^ 2 + a3 x ^ 3…….. +一个x ^ n
给定的序列始终可以由多个多项式来描述,在这些多项式中,我们需要找到最低阶的多项式并仅使用该多项式生成下一项。
例子:
If given sequence is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 then its next term will be 6, 7, 8, etc
and this correspond to a trivial polynomial.
If given sequence is 1, 4, 7, 10 then its next term will be 13, 16, etc.我们可以使用一种称为差分法的技术来解决此问题,该技术可从拉格朗日多项式推导而来。
该技术很简单,我们取连续项之间的差,如果差相等,则停止并建立序列的下一项,否则我们再次取这些差之间的差,直到它们变为常数。
下图以示例说明了该技术,给定序列为8、11、16、23,我们假设找到该序列的下3个项。
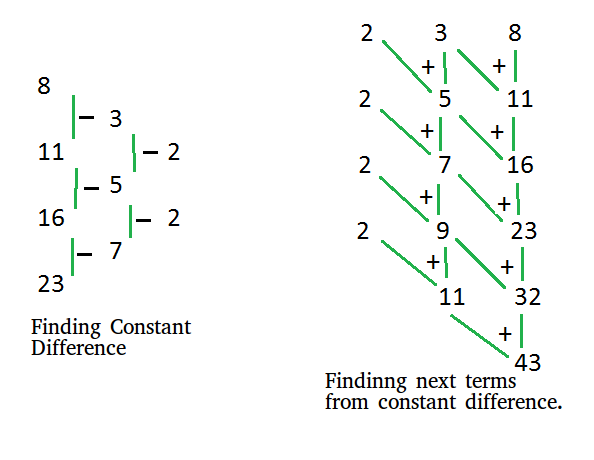
在下面的代码中,实现了相同的技术,首先循环,直到获得恒定的差,将每个差序列的第一个数保留在单独的向量中,以再次重建该序列。然后,将具有相同常数差的K实例添加到数组中,以生成新的K序列项,并按照相反的顺序执行相同的过程来重建序列。
请参阅下面的代码以获得更好的理解。
C++
// C++ code to generate next terms of a given polynomial
// sequence
#include
using namespace std;
// method to print next terms term of sequence
void nextTermsInSequence(int sequence[], int N, int terms)
{
int diff[N + terms];
// first copy the sequence itself into diff array
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
diff[i] = sequence[i];
bool more = false;
vector first;
int len = N;
// loop untill one difference remains or all
// difference become constant
while (len > 1)
{
// keeping the first term of sequence for
// later rebuilding
first.push_back(diff[0]);
len--;
// converting the difference to difference
// of differences
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
diff[i] = diff[i + 1] - diff[i];
// checking if all difference values are
// same or not
int i;
for (i = 1; i < len; i++)
if (diff[i] != diff[i - 1])
break;
// If some difference values were not same
if (i != len)
break;
}
int iteration = N - len;
// padding terms instance of constant difference
// at the end of array
for (int i = len; i < len + terms; i++)
diff[i] = diff[i - 1];
len += terms;
// iterating to get actual sequence back
for (int i = 0; i < iteration; i++)
{
len++;
// shifting all difference by one place
for (int j = len - 1; j > 0; j--)
diff[j] = diff[j - 1];
// copying actual first element
diff[0] = first[first.size() - i - 1];
// converting difference of differences to
// difference array
for (int j = 1; j < len; j++)
diff[j] = diff[j - 1] + diff[j];
}
// printing the result
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
cout << diff[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// Driver code to test above method
int main()
{
int sequence[] = {8, 11, 16, 23};
int N = sizeof(sequence) / sizeof(int);
int terms = 3;
nextTermsInSequence(sequence, N, terms);
return 0;
} Java
// Java code to generate next terms
// of a given polynomial sequence
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Method to print next terms term of sequence
static void nextTermsInSequence(int []sequence,
int N, int terms)
{
int []diff = new int[N + terms];
// First copy the sequence itself
// into diff array
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
diff[i] = sequence[i];
//bool more = false;
ArrayListPython3
# Python3 code to generate next terms
# of a given polynomial sequence
# Method to print next terms term of sequence
def nextTermsInSequence(sequence, N, terms):
diff = [0] * (N + terms)
# First copy the sequence itself
# into diff array
for i in range(N):
diff[i] = sequence[i]
more = False
first = []
length = N
# Loop untill one difference remains
# or all difference become constant
while (length > 1):
# Keeping the first term of sequence
# for later rebuilding
first.append(diff[0])
length -= 1
# Converting the difference to difference
# of differences
for i in range(length):
diff[i] = diff[i + 1] - diff[i]
# Checking if all difference values are
# same or not
for i in range(1, length):
if (diff[i] != diff[i - 1]):
break
# If some difference values
# were not same
if (i != length):
break
iteration = N - length
# Padding terms instance of constant
# difference at the end of array
for i in range(length, length + terms):
diff[i] = diff[i - 1]
length += terms
# Iterating to get actual sequence back
for i in range(iteration):
length += 1
# Shifting all difference by one place
for j in range(length - 1, -1, -1):
diff[j] = diff[j - 1]
# Copying actual first element
diff[0] = first[len(first) - i - 1]
# Converting difference of differences to
# difference array
for j in range(1, length):
diff[j] = diff[j - 1] + diff[j]
# Printing the result
for i in range(length):
print(diff[i], end = " ")
print ()
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
sequence = [ 8, 11, 16, 23 ]
N = len(sequence)
terms = 3
nextTermsInSequence(sequence, N, terms)
# This code is contributed by chitranayalC#
// C# code to generate next terms
// of a given polynomial sequence
using System;
using System.Collections;
class GFG{
// Method to print next terms term of sequence
static void nextTermsInSequence(int []sequence,
int N, int terms)
{
int []diff = new int[N + terms];
// First copy the sequence itself
// into diff array
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
diff[i] = sequence[i];
//bool more = false;
ArrayList first = new ArrayList();
int len = N;
// Loop untill one difference remains
// or all difference become constant
while (len > 1)
{
// Keeping the first term of
// sequence for later rebuilding
first.Add(diff[0]);
len--;
// Converting the difference to
// difference of differences
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
diff[i] = diff[i + 1] - diff[i];
// Checking if all difference values
// are same or not
int j;
for(j = 1; j < len; j++)
if (diff[j] != diff[j - 1])
break;
// If some difference values
// were not same
if (j != len)
break;
}
int iteration = N - len;
// Padding terms instance of constant
// difference at the end of array
for(int i = len; i < len + terms; i++)
diff[i] = diff[i - 1];
len += terms;
// Iterating to get actual sequence back
for(int i = 0; i < iteration; i++)
{
len++;
// Shifting all difference by one place
for(int j = len - 1; j > 0; j--)
diff[j] = diff[j - 1];
// Copying actual first element
diff[0] = (int)first[first.Count - i - 1];
// Converting difference of differences
// to difference array
for(int j = 1; j < len; j++)
diff[j] = diff[j - 1] + diff[j];
}
// Printing the result
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
Console.Write(diff[i] + " ");
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int []sequence = { 8, 11, 16, 23 };
int N = sequence.Length;
int terms = 3;
nextTermsInSequence(sequence, N, terms);
}
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56Javascript
输出:
8 11 16 23 30 37 44