运动方程的样题
速度、距离、时间的关系学了很久,知道一个很简单的公式,S = D/T(速度=距离/时间),这个公式是求速度的最基本公式、距离或物体/物体的时间。但是,这个公式只对恒定速度有效,当物体的速度发生变化(无论是增加还是减少)时,已知该物体分别处于某种加速或减速状态。
加速
物体中的加速度定义为速度相对于时间的变化率。当物体没有加速度时,它有恒定的速度,当物体有一些正或负的加速度值时,物体有变化的速度,在这种情况下,引入了初速度和终速度的概念。运动方程适用于经历恒定加速度的物体。虽然在现实生活中要找到一个具有恒定加速度的物体并不容易,但还是有一些实际的例子。例如,当一个球落下时(假设没有空气阻力),它会因重力而经历恒定的加速度。
运动方程
运动方程由牛顿给出。引入运动方程来定义运动中物体的所有未知可能参数,该运动经历一些恒定加速度。如果所有三个方程都已知,则可以解决所有类型的问题,因为这三个方程涵盖了所有参数。
牛顿第一运动方程
设初速度为 u,终速度为 v,物体的加速度为 a,时间为 t。第一个运动方程将是,
v = u + 在
证明:
a = (v-u)/t
at = v-u
v = u+ at
牛顿第二运动方程
设物体的初速度为u,物体的加速度为a,物体覆盖的位移为S,第二个方程为,
S = ut + 1/2(在2处)
证明:
The average velocity is given as- v+u/2
![]()
Putting the value of v from first equation of motion here,
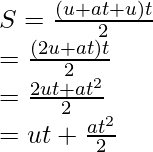
牛顿第三运动方程
设物体的初速度和终速度分别为 u 和 v,物体的加速度为 a,物体覆盖的位移为 S。 那么,第三运动方程为:
v 2 = u 2 + 2as
证明:
The average velocity of an object is ⇢ v+u/2
![]()
The acceleration of the object can be written as,
a= (v-u)/t
Multiply S and a,
示例问题
问题 1:定义平均速度和平均速度?
回答:
Average Speed
It is defined as the total path covered in total time.
Average Speed= Total Distance/Total Time= D/T
Average Velocity
It is defined as the Total displacement by total time taken.
Average Velocity (v)= S2– S1/ T2– T1 = S/T
问题 2:一个静止的物体被加速,它行进了 5 分钟。提供给身体的恒定加速度是2m/sec 2 。求物体在停止前的最终速度。另外,请回答用于找出最终速度的运动方程。
解决方案:
The first equation of motion is the best suitable here to find out the final velocity.
First equation of motion, v=u +at
Initial velocity= 0 m/sec
Time for which object was in motion= 5 minute = 5× 60sec= 300 seconds
The constant acceleration provided to the object= 2 m/sec2
v= u+ at
v= 0+ 2× 300
v= 600m/sec
问题3:一个球从某个高度落下。球花了15秒才到达地面。球最初的高度是多少,还要回答使用哪个运动方程来回答这个问题? [取g=10m/sec 2 ]
回答:
The second equation of motion is the best suitable for answering this type of question,
Second equation of motion, S= ut + 1/2(at2)
The height at which ball is dropped= h
As the ball is dropped, u= 0 m/sec
a=g (acceleration due to gravity), g= 10m/sec2
h= 0+ 1/2(gt2)
h= 1/2(10× 15×15)
h= 1125meters
The height at which ball was present initially was 1.125kms.
问题4:这句话告诉“物体的平均速度等于瞬时速度”是什么意思?
回答:
The statement “The average velocity of a body is equal to its instantaneous velocity” means that there is no variation in the velocity of the object whatsoever throughout its motion.
Hence, it can be concluded from the statement that the body has a constant velocity.
问题5:一辆初速为1m/sec的汽车运动了10分钟,然后停了下来,停前的速度是5m/sec。汽车的恒定加速度是多少?
解决方案:
Initial Velocity= 1 m/sec
Final Velocity= 5 m/sec
Time for which the car was in motion = 10 mint
Acceleration = ?
Using First equation of motion,
v = u+ at
5 = 1+ a× (10×60)
a × 600 = 4
a = 4/600
a = 0.0066 m/sec2
问题 6:一个循环在 8 分钟内跑了 2 公里,循环的初速度为 1 米/秒。找出循环在其运动中的加速度。
解决方案:
Displacement covered= 2km
Total Time Taken = 8minutes= 8× 60= 480 seconds.
Initial Velocity= 1 m/sec
Using Second equation of motion to find the acceleration of the cycle,
Second Equation of motion, S= ut + 1/2(at2)
2000= 1× 480 + 1/2(a×4802)
2000= 480+ 115200a
1520= 115200a
a= 0.0139m/sec2
问题 7:一个玩具不小心从屋顶上掉下来了。玩具落地前的最终速度为 8m/sec。求建筑物的高度。
解决方案:
Acceleration of the toy is equal to the acceleration due to gravity.
a = g = 9.8m/sec2
Final velocity= 8m/sec
Initial velocity= 0m/sec
Applying Third equation of motion, v2= u2+ 2aS
82 = 0+ 2×9.8 × S
S = 64/9.8×2
S = 3.26 meters
Hence, the height of the building is 3.26 meters.
问题 8:一个具有不同加速度的物体可以被认为是运动方程的一个很好的例子吗?
回答:
No. The equations of motion are applicable only for the body undergoing constant acceleration. Acceleration changing with respect to time is called as jerk and a body undergoing jerk will not be suitable in the equations of motion.
问题 9:求一个物体以 2m/sec 的初速度和 0.5m/sec 2的加速度运动了 500 米的物体的最终速度。
解决方案:
The third equation of motion is suitable for this example,
Third equation of motion, v2= u2+2aS
v= ?, u=2m/sec, a=0.5m/sec2, S= 500m
v2= 25+2× 0.5 × 500
v2= 504
v= 22.4m/sec
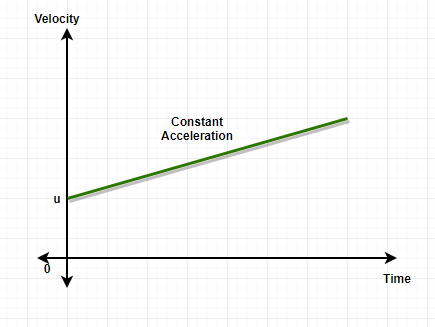
问题 10:画出零加速度和恒加速度的速度-时间图。
回答:
The slope for zero acceleration on velocity time graph is zero and hence the graph is parallel to x-axis.
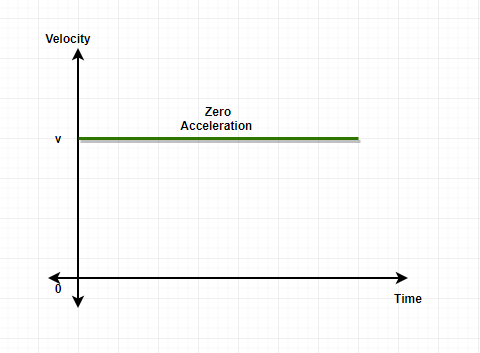
The slope for constant acceleration will have a constant value on velocity time graph and hence, the graph will be a straight line.