要绘制一条直线,我们需要至少两个位于该直线上的点。从给定直线的斜率截距形式,我们可以使用公式中的信息非常容易地计算直线上的两个点。考虑斜率为m且y轴为c的直线。我们知道该直线方程的斜率截距形式为: y = mx + c 。此处,y轴截距c表示该线已将Y轴切割为距原点c的距离,这进一步意味着切割点为(0,c) 。现在,我们可以在图中绘制直线上的固定点。使用该点和直线的斜率,我们可以绘制直线图。
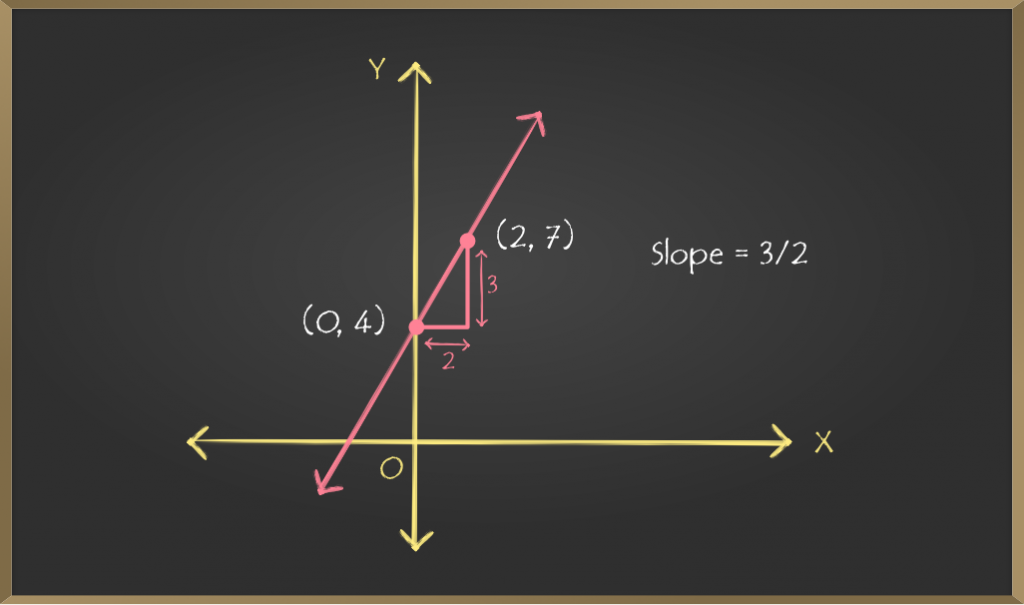
绘制斜率截距形式
现在,我们在直线上有一个固定点,它是坐标为(0,c)的切割点。为了确定第二点,我们需要使用直线的斜率m作为所考虑的直线。
我们知道,
Slope = change in y/change in x
令斜率m = p / q
如果m为分数形式,则p为分子,q为分母。如果m是整数,那么我们总是可以将m作为分子(p),将1作为分母(q)(因为m / 1 = m)。
p/q = change in y/change in x
这进一步意味着q坐标在x坐标上的变化将导致p单位在y坐标上的变化。因此,如果点(x,y)位于该直线上,则点(x + q,y + p)也将位于该直线上。对于所考虑的直线,我们知道(0,c)位于直线上,而p / q (m = p / q)是直线的斜率。如上所述,点(0 + q,c + p)或点(q,c + p)也将位于该线上。现在,我们可以在图形上绘制这两个点,并将它们连接起来将为我们提供所需的直线。为了进一步说明,请参见上图,其中m = p / q = 3/2和c = 4。
图上的样例问题
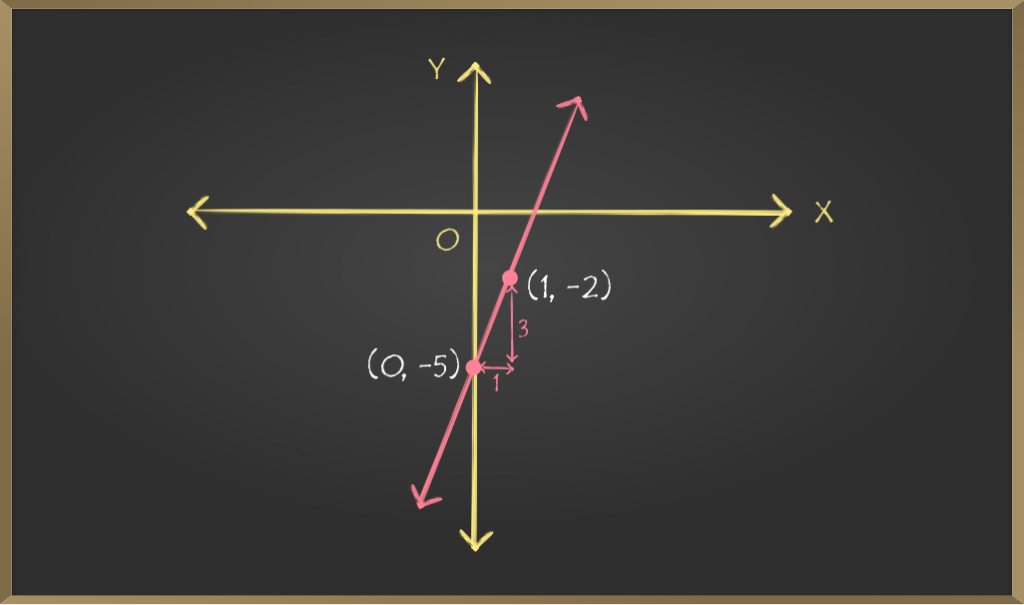
问题1:为斜率截距方程绘制一个图,y = 3x – 5。
解决方案:
Comparing given equation with y = mx + c we get,
m = 3 ⇒ p/q = 3/1 ⇒ p = 3, q = 1 and c = -5
c = -5 implies that y-intercept of the line is -5, i.e.
the line cuts the Y-axis on the point (0, -5)
m = 3 or p/q = 3/1 implies that slope of the line is 3,
i.e. 1 unit change in x-coordinate will result 3 units
change in y-coordinate. Thus, if point (x, y) lies on
the given straight line then point (x +1, y +3) will also
lie on that line.
⇒ Point (0, -5) and point (0+1, -5+3) ⇒(1, -2)
lies on the given straight line. Joining these two
points will give us the required line.
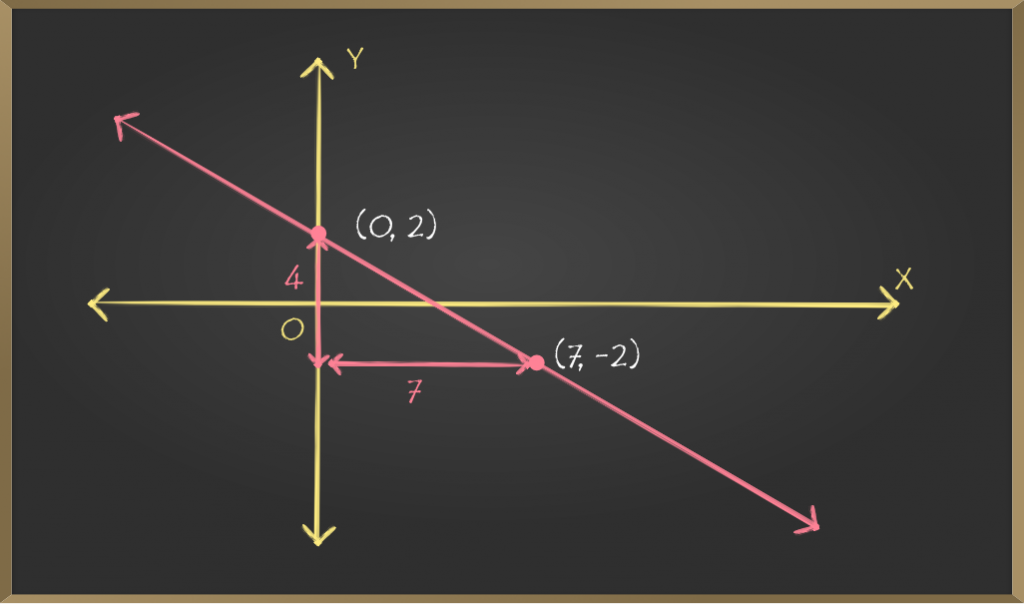
问题2:绘制坡度截距方程y =-(4/7)x + 2的图。
解决方案:
Comparing given equation with y = mx + c we get,
m = -(4/7) ⇒ p/q ⇒ -(4/7) ⇒ p = -4, q = 7 and c = 2
⇒ Point (0, 2) and point (0 + 7, 2 – 4) ⇒(7, -2)
lies on the given straight line. Joining these two
points will give us the required line.
问题3:绘制坡度截距方程y =(5/3)x + 4的图。
解决方案:
Comparing given equation with y = mx + c we get,
m = 5/3 ⇒ p/q ⇒ 5/3 ⇒ p = 5, q = 3 and c = 4
⇒ Point (0, 4) and point (0+3, 4+5) ⇒(3, 9)
lies on the given straight line. Joining these two
points will give us the required line.

概括
- 直线的斜率截距形式为: y = mx + c ,其中m为斜率, c为y截距。
- 斜率截距形式可用于绘制直线。
- 从斜率截距形式y = mx + c,我们可以确定直线上的两个点,分别是(0,c)和(q,c + p) ,其中p / q = m 。连接这些点将为我们提供所需的直线。