序列和系列在人类活动的多个领域中都有几个重要的应用。当序列遵循某些特定模式时,通常称为渐进。算术和几何级数是常见进程的一些示例。让我们看看这些进展中的一些问题,以便更好地理解它们。
成长模式
这种类型的数字序列问题首先描述了如何生成数字序列。给出了序列的一些术语,我们需要弄清楚序列中的模式,然后是序列的下一个术语。
解决这样的序列:
- 寻找给定数字之间的模式。
- 确定是否使用+,-,×或÷
- 使用模式来解决顺序。
增长模式
顾名思义,增加模式本质上将一直在增加。下一项和紧接其前的一项都将通过操作(×,-,+)进行类似的关联。
问题: 6,13,27,55,…..在给定的顺序中,下一项的值是多少?
回答:
On looking carefully into the pattern, one can see that
13 = 6 × 2 + 1
27 = 13 × 2 + 1
55 = 27 × 2 + 1
This shows that every term is twice the preceding term plus one. So, let the next term be “a”.
a = 55 × 2 + 1
= 110 + 1
= 111
Hence, the next term is 111.
递减模式
在递减模式中,下一个将小于上一项,并且两个连续项将遵循某个模式。
问题:该系列的下一个术语是什么:220,100,40,…。
回答:
The series follow the pattern: 100 = (220×0.5)-10
40 = (100×0.5)-10
Therefore, the next term will be (40×0.5)-10 = 10
算术级数
在算术级数中,连续项将具有相同的差异,并表示为“ d”,第一个项称为“ a”,而项数则表示为“ n”。
The formula for nth term is:
Tn= a+ (n-1)d
问题1、2、5、8、11…。查找序列的下一项。
回答:
It can be noticed by carefully studying the terms of the sequence that the difference between each consecutive term remains the same. For example:
5 – 2 = 3
8 – 5 = 3
11 – 8 = 3
So, the next will be at a difference of three from the last term. Since the last term of the sequence is 11. The next terms will be 14.
OR
The formula for nth term in Arithmetic progression can also be used here, 5th term is required here:
a = 2
d = (3)
T5 = 2+(5-1)(3)
= 2+12
= 14
问题2:15、12、9,…__。查找下一个学期。
回答:
In this problem also, all the terms have a difference of three between them. The difference is that the sequence in decreasing in nature. Since the last term is 9, the next term will be 3 less than the last term. So, the last term will be 6.
斐波那契数列
有时有些序列的图案不可见,斐波那契序列就是这种序列的一个例子。在数学和计算机科学领域中,这是一个非常普遍的序列。
该数字排列为1、1、2、3、5、8…。在此模式是不可见的,此序列以取决于其历史的方式进行。
令n为序列的第n个项。在此序列中, n = a n-1 + a n-2 。
例如,
a2 = a1 + a0 i.e 2 = 1 + 1,
a3 = a1 + a2 i.e 3 = 2 + 1,
a4 = a3 + a2 i.e 5 = 2 + 3 and,
a5 = a4 + a3 i.e 8 = 5 + 3.
问题:斐波那契数列的下一个术语是什么:1,1,2,3,5,8,13,……
回答:
In Fibonacci Series, the next term is the sum of the last two terms.
Therefore, the next term will be (8+13)= 21
几何系列
在开始讨论与几何级数有关的问题之前。让我们快速回顾一下GP的总和和n项的公式。
几何级数的一般形式是a,ar,ar 2 ,ar 3 ……其中a =第一项,r =公共比率,而n是第n个项。
- 级数的第n个项:a n = ar n-1 。
- GP的n个项之和:
![由QuickLaTeX.com渲染 S_{n} = a[\frac{r^{n}-1}{r-1}] \text{ where } r \ne 1](https://mangdo-1254073825.cos.ap-chengdu.myqcloud.com//front_eng_imgs/geeksforgeeks2021/Sequence%20and%20Series%20Word%20Problems%20%7C%20Class%2011%20Maths_0.jpg)
- 无限GP的总和:

有限的GP问题
这些类型的问题包括存在有限数量项的几何级数。
问题1:某种文化中的细菌数量每小时增加一倍。如果最初在培养物中存在30种细菌,那么在第2小时,第4小时和第n小时的末尾将存在多少细菌?
回答:
The growth of the bacteria makes a GP, 30, 60, 120,….. and so on.
In this GP, a = 30, r = 2. Let the number of bacteria at nth hour be an.
At n = 2, a2 = ar2-1
= (30)(2)2-1 = 30 × 2 = 60
At n = 4, a4 = ar4-1
= (30)(2)4-1 = 30 × 23 = 240
At nth step an = ar(n-1) = 30 × 2n-1
问题2:一个人有2个父母,4个祖父母,8个曾祖父母,依此类推。找出他祖先十代中祖先的数量。
回答:
This is a problem of finite GP. The sequence can be thought like this,
2, 4, 8, 16, …..
So, the total number of ancestors in 10 generation of his family.
2, 4, 8, 16, 32, …..10 terms.
Here, a = 2, r = 2 and n = 10
S10 = a ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com S_{n} = a[\frac{r^{n}-1}{r-1}] \\ = 2[\frac{2^{10} - 1}{2 - 1}] \\ = 2[1023] = 2046](https://mangdo-1254073825.cos.ap-chengdu.myqcloud.com//front_eng_imgs/geeksforgeeks2021/Sequence%20and%20Series%20Word%20Problems%20%7C%20Class%2011%20Maths_2.jpg)
无限GP问题
无限几何级数是无限几何序列的总和。这个系列没有最后学期
问题1:猴子从树上摆动。在第一个秋千上,她经过24m弧线。每次挥杆,她都会经过24m的弧线。每次挥杆时,她都会经过一个弧度,该弧度是前一个挥杆长度的一半。猴子完成第100000次挥杆后,走过的总距离是多少?
回答:
Now this movement represents a GP with a = 24 and r = 1/2. Now, since the GP is decreasing and the question asks for the sum till 100000th term. To save the calculation , we can consider it an infinite GP and round of the answer we get.
Sum of an infinite GP = ![]()
Here, a = 24 and r = 1/2. Let the sum be S
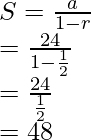
So the monkey travels almost 24m in these many swings.
问题2:一个球从24英寸高的桌子上掉下来。球反弹并始终达到落下距离的四分之三。球最终停在地面上之前经过的大致距离是多少?
回答:
It should be noticed that this problem actually involves two infinte geometric series. The first series involves ball falling and the other series involves ball rising after rebounding from the ground.
Falling: a1 = 24 , r = 3/4
Rising: a2 = 24(3/4) = 18 ,r = 3/4
Using the formula for infinite geometric series,
S = ![]()
Let S be the total distance travelled:
S = Srising + Sfalling
Srising =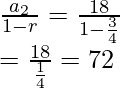
Sfalling = 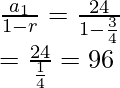
Now, S = Srising + Sfalling = 72 + 96 = 168