问题1.解决
解决方案:
Using the property of modulus operator, we know
|x| > a ⇒ x < -a or x > a
Therefore, ![]() or
or ![]()
⇒ x < ![]() or x >
or x > ![]()
⇒ x < -3 or x > ![]()
Hence, we can conclude x lies in the range ( -∞, -3) ∪ ( ![]() ,∞ )
,∞ )
问题2.解决| 4 – x | +1 <3
解决方案:
We have, | 4 – x | + 1 < 3
⇒ | 4 – x | < 2
Using the property of modulus operator, we know
|x| < a ⇒ -a < x < a
⇒ -2 < 4 – x < 2
⇒ -6 < -x < -2
⇒ 6 > x > 2
⇒ 2 < x < 6
Hence, we can conclude x lies in the range (2, 6)
问题3:解决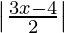 ≤
≤ 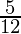
解决方案:
Using the property of modulus operator, we know
|x| ≤ a ⇒ -a ≤ x ≤ a
⇒ – ![]() ≤
≤ ![]() ≤
≤ ![]()
⇒ – ![]() ≤ 3x – 4 ≤
≤ 3x – 4 ≤ ![]()
⇒ – ![]() + 4 ≤ 3x ≤
+ 4 ≤ 3x ≤ ![]() + 4
+ 4
⇒ ![]() ≤ 3x ≤
≤ 3x ≤ ![]()
⇒ ![]() ≤ x ≤
≤ x ≤ ![]()
Hence, we can conclude x lies in the range [ ![]() ,
, ![]() ]
]
问题4:解决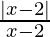 > 0
> 0
解决方案:
Using the property of modulus operator, we have
| x -2 | = x-2 when x ≥ 2 or 2-x when x < 2
since, ![]() > 0 for x > 2
> 0 for x > 2
Hence, we can conclude x lies in the range ( 2, ∞)
问题5:解决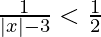
解决方案:
We are given, ![]()
⇒ ![]() < 0
< 0
⇒ ![]() < 0
< 0
⇒ ![]() < 0
< 0
⇒ ![]() < 0
< 0
Now, we have two cases:
Case 1: When x ≥ 0, then |x| = x
![]() < 0
< 0
⇒ (5 – x < 0 and x – 3 > 0) or ( 5 – x > 0 and x – 3 < 0)
⇒ (x >5 and x > 3) or ( x < 5 and x < 3)
⇒ x > 5 and x < 3
Therefore, we can conclude, from case 1 that x lies in the range [ 0,3) U (5,∞)
Case 2: When x ≤ 0 then |x| = -x
![]() < 0
< 0
⇒ ![]() > 0
> 0
⇒ (x + 5 > 0 and x + 3 > 0) or ( x + 5 <0 and x + 3 < 0)
⇒ ( x > -5 and x > -3 ) or ( x < -5 and x < -3 )
⇒ x > -3 or x < -5
Therefore, we can conclude, from case 2 that x lies in the range [ -∞, -5) U (-3,0)
Now, taking the union of above two cases we can conclude x lies in the range (-∞, -5) U ( -3,3) U (5, ∞)
问题6:解决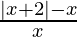 <2
<2
解决方案:
We have ![]() < 2
< 2
⇒ ![]() – 2 < 0
– 2 < 0
⇒ ![]() < 0
< 0
⇒ ![]() < 0
< 0
Now, we have two cases:
Case 1: When x ≥ -2, then |x+2| = x+2,
![]() < 0
< 0
⇒ ![]() < 0
< 0
⇒ ![]() < 0
< 0
⇒ ![]() > 0
> 0
⇒ (x – 1 > 0 and x > 0) or ( x – 1 < 0 and x < 0)
⇒ (x > 1 and x > 0) or ( x < 1 and x < 0)
⇒ x > 1 or x < 0
Therefore, we can conclude, from case 1 that x lies in the range [ -2,0) U (1,∞)
Case 1: When x ≤ -2, then |x+2| = -(x+2),
![]() < 0
< 0
⇒ ![]() < 0
< 0
⇒ ![]() < 0
< 0
⇒ ![]() > 0
> 0
⇒ (2x -+ 1 > 0 and x > 0) or ( 2x + 1 < 0 and x < 0)
⇒ (x > -1/2 and x > 0) or ( x < -1/2 and x < 0)
⇒ x > 0 or x < -1/2
Therefore, we can conclude, from case 2 that x lies in the range ( -∞,-2 ] U (0,∞)
Now, taking the union of above two cases we can conclude x lies in the range [ -2,0 ) U (1,∞) U (-∞, -2] U ( 0, ∞) i.e., x belongs to (-∞,0) U (1,∞)
问题7:解决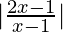 > 2
> 2
解决方案:
We have ![]() > 2
> 2
⇒ ![]() – 2 > 0
– 2 > 0
⇒ ![]() > 0 or
> 0 or ![]() +2 < 0
+2 < 0
⇒ ![]() > 0 or
> 0 or ![]() < 0
< 0
⇒ x-1 >0 or ![]() < 0
< 0
⇒ x-1 > 0 or [ (4x-3 > 0 and x-1 < 0) or ( 4x-3 < 0 and x-1 > 0) ]
⇒ x > 1 or [ (x > 3/4 and x < 1) or ( x < 3/4 and x > 1) ]
⇒ x > 1 or [ 3/4 < x < 1 or ∅]
⇒ 3/4 < x < 1 or x > 1
Hence, we can conclude x lies in the range ( 3/4, 1) U (1, ∞ )
问题8.解决| x-1 | + | x-2 | + | x-3 | ≥6
解决方案:
We have, |x-1| + |x-2| + |x-3| ≥ 6 ———————let this be equation (1)
As, | x-1 | = ( x-1, when x ≥ 1 and 1-x when x < 1 )
similarly, | x-2 | = ( x-2, when x ≥ 2 and 2-x when x < 2 )
and | x-3 | = ( x-3, when x ≥ 3 and 3-x when x < 3 )
Now, we have four cases:
Case 1: When x < 1
1 – x + 2 – x + 3 – x ≥ 6
⇒ 6 -3x ≥ 6
⇒ x ≤ 0
So, we see x lies in the range (-∞ ,0]
Case 2: when 1 ≤ x < 2
x – 1 + 2 – x + 3 – x ≥ 6
⇒ 4 – x ≥ 6
⇒ x ≤ -2
using case 2 , we see x has no values so x ∈ ∅
Case 3: when 2 ≤ x < 3
x – 1 + x – 2 + 3 – x ≥ 6
⇒ x ≥ 6
using case 3 , we see x has no values so x ∈ ∅
Case 4: when x ≥ 3
x – 1 + x – 2 + x – 3 ≥ 6
⇒ 3x – 6 ≥ 6
⇒ x ≥ 4
using case 4 , we see x has no values so x ∈ [ 4, ∞ )
Combining all the cases, we get to know x lies in the range ( -∞, 0 ] U [ 4, ∞)
问题9:解决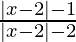 ≤0
≤0
解决方案:
We have, ![]() ≤ 0
≤ 0
Case 1: when x ≥ 2, then | x -2 | = x – 2
![]() ≤ 0
≤ 0
⇒ ![]() ≤ 0
≤ 0
⇒ ( x – 3 ≤ 0 and x – 4 > 0 ) or ( x – 3 ≥ 0 and x – 4 < 0)
⇒ ( x ≤ 3 and x > 4 ) or ( x ≥ 3 and x < 4)
⇒ ∅ or ( 3 ≤ x < 4)
⇒ 3 ≤ x < 4
using case 1 , we see x lies in the range [ 3, 4 )
Case 2: when x ≤ 2, then | x – 2| = 2 – x,
![]() ≤ 0
≤ 0
⇒ ![]() ≤ 0
≤ 0
⇒ ![]() ≤ 0
≤ 0
⇒ ( x – 1 ≤ 0 and x > 0 ) or ( x – 1 ≥ 0 and x< 0)
⇒ ( x ≤ 1 and x > 0 ) or ( x ≥ 1 and x< 0)
⇒ ( 0 < x ≤ 1) or ∅
⇒ 0 < x ≤ 1
using case 2 , we see x lies in the range ( 0, 1 ]
Combining all the cases, we get to know x lies in the range ( 0, 1 ] U [ 3, 4)
问题10:解决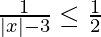
解决方案:
We have, ![]()
⇒ ![]() ≤ 0
≤ 0
⇒ ![]() ≤ 0
≤ 0
⇒ ![]() ≤ 0
≤ 0
Case 1: when x ≥ 0 then |x| =x
⇒ ![]() ≤ 0
≤ 0
⇒ ( 5 – x ≤ 0 and x – 3 > 0 ) or ( 5 – x ≥ 0 and x – 3 < 0)
⇒ ( x ≥ 5 and x > 3 ) or ( x ≤ 5 and x < 3)
⇒ x ≥ 5 or x < 3
using case 1, we see x lies in the range ( 0, 3 ) U [5, ∞ )
Case 2: when x < 0 then |x| = -x
⇒ ![]() ≤ 0
≤ 0
⇒ ![]() ≥ 0
≥ 0
⇒ ( x + 5 > 0 and x + 3 > 0 ) or ( x + 5 < 0 and x + 3 < 0)
⇒ ( x > -5 and x > -3 ) or ( x < -5 and x < -3)
⇒ x > -3 or x < -5
using case 2, we see x lies in the range ( -∞, -5 ) U (-3, ∞ )
Combining both the cases, we get to know x lies in the range ( -∞, -5 ) U (-3, ∞ ) U ( 0, 3 ) U [5, ∞ )
问题11.解决| x + 1 | + | x | > 3
解决方案:
We have, |x + 1| + |x| > 3
⇒ |x + 1| = ( x + 1 when x ≥ -1 and -(x + 1) when x < -1 )
similarly, |x| = (x when x ≥ 0 and -x when x < 0)
Case 1: When x < -1
|x + 1| + |x| > 3
⇒ – (x+1) -x > 3
⇒ -2x -1 > 3
⇒ x < -2
using case `1, we see x lies in the range ( -∞, -2 )
Case 2: When -1 ≤ x < 0
|x + 1| + |x| > 3
⇒ (x+1) + x > 3
⇒ 2x > 2
⇒ x > 1
using case `2, we see x lies in the range ( 1, ∞ )
Combining both the cases, we get to know x lies in the range ( -∞, -2 ) U ( 1, ∞ )
问题12.解决1≤| x – 2 | ≤3
解决方案:
We have, 1 ≤ |x – 2| ≤ 3
Case 1: |x – 2| ≥ 1
⇒ ((x – 2) ≤ -1 or (x-2) ≥ 1)
⇒ ( x ≤ 1 or x ≥ 3)
using case `1, we see x lies in the range ( -∞,1 ] U [3,∞)
Case 2: |x – 2| ≤ 3
⇒ ( -3 ≤ (x-2) ≤ 3)
⇒ (-1 ≤ x ≤ 5)
using case `2, we see x lies in the range [-1, 5]
Combining both the cases, we get to know x lies in the range [-1, 1 ] U [ 3, 5 ]
问题13.解决| 3-4x | ≥9
解决方案:
We have, |3-4x| ≥ 9
therefore, by using property of modulus we know, |x| ≥ a ⇒ x ≤ -a or x ≥ a
⇒ (3-4x) ≤ -9 or (3-4x) ≥ 9
⇒ -4x ≤ -12 or -4x ≥ 6
⇒ x ≥ 3 or x ≤ -3/2
Hence, we can conclude x lies in the range ( -∞, -3/2] U [ 3, ∞ )