均匀电场中电偶极子上的转矩
科学是一门奇怪的学科,随着新学科的出现,它永远不会停止给你带来惊喜。我们都知道,电荷无处不在,它的存在会引发各种自然事件。此外,正电荷和负电荷以多种形式存在,在刺激场的存在下表现出各种特征。
你遇到过“电偶极子”这个词吗?这种不寻常的电荷配置,即正电荷和负电荷,创造了一个有趣的物理概念。更具体地说,电偶极子是正电荷和负电荷的分离。
考虑一对符号相反但大小相等的电荷,它们之间的距离要小得多。电偶极子在存在外部场的情况下的行为现在是我们的主要关注点。在继续讨论在均匀电场中作用在电偶极子上的转矩特性之前,让我们回顾一下在均匀电场中作用在电偶极子上的转矩特性。
扭矩
Torque is the measurement of the force that causes an item to rotate around an axis.
扭矩是一个向量,其方向由作用在轴上的力决定。扭矩矢量的大小确定如下:
τ = F r sinθ
在哪里
- F 是作用在轴上的力,
- r 是力臂的长度,
- θ 是力矢量和力臂之间的角度,&
- τ 是扭矩矢量
电偶极子
An electric dipole is a pair of equal and opposite electric charges separated by a distance d.
这些电荷的大小和它们之间的距离的乘积就是电偶极矩。电偶极矩是具有从负电荷到正电荷的明确方向的矢量。
电偶极矩,
p = qd
在哪里
- q 是电荷的大小 &
- d 是分离距离。
电偶极子上的扭矩
考虑放置在均匀外场“E”中的偶极子,以计算偶极子放置在外场中时所经历的扭矩。正电荷将在向上方向受到“qE”大小的电力,而负电荷将在向下方向受到“qE”大小的电力。
因为合力为零,可以观察到偶极子处于过渡平衡状态。然而,什么是旋转平衡?在这种情况下,偶极子可能保持固定但以一定的角速度旋转。这一事实已通过实验证明,它表明两个静电力 (qE) 表现为顺时针扭矩。结果,当偶极子置于均匀的外部电场中时,它会旋转。永远记住,扭矩总是成对起作用。此外,它的大小是力和它的手臂的结果。臂可以被认为是施加力的点和偶极子发生旋转的点之间的距离。
扭矩的推导
考虑一个带有电荷 +q 和 -q 的偶极子,它们形成一个偶极子,因为它们之间的距离为 d。将其置于强度为 E 的均匀电场中,偶极子的轴与电场形成角度 θ。
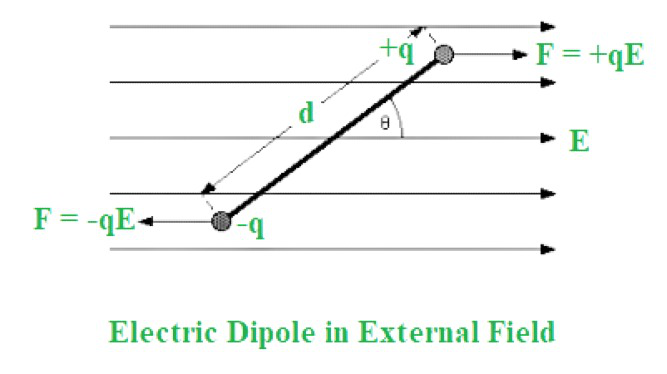
电荷上的力, F = ± q E
垂直于偶极子的力的分量, F = ± q E sinθ
由于这些分量相等且相隔距离 d,因此偶极子上的扭矩为:
Torque = Force × distance between forces
τ = (q E sinθ) d = q d E sinθ
由于'qd'是偶极矩(p)的大小,偶极矩的方向是从正电荷到负电荷;扭矩是偶极矩和电场的叉积。如果电场的方向为正,则上图中的转矩为顺时针方向(因此为负)。
因此,
τ = – p E sinθ
负号表示扭矩为顺时针方向。
示例问题
问题 1:电偶极子以 30° 角放置,电场强度为 3 × 10 4 N ⁄ C。它承受的扭矩为 5 Nm。如果偶极子长度为 5 cm,则计算偶极子上的电荷。
解决方案:
Given:
Electric field, E = 3 × 104 N ⁄ C
Angle between dipole and electric field, θ = 30°
Dipole length, d = 5 cm = 0.05 m
Torque, τ = 5 N m
The torque on a dipole in electric field is given by:
τ = q d E sin θ
q = τ ⁄ d E sin θ
= 5 ⁄ (0.05 × 3 × 104 × sin30°) C
= 6.7 mC
Hence, the torque on a dipole in an electric field is 6.7 mC.
问题 2:两个微小的电偶极子 AB 和 CD,每个偶极矩为 p,保持 120° 的角度。结果是什么偶极矩?如果 E 指向 +x 方向,则在该系统上运行的扭矩的大小和方向是多少?
解决方案:
Effective dipole moment of AB and CD, pe = √(p2 + p2 + 2 p p cos120°)
= √(2 p2 + 2 p2(−1 ⁄ 2))
= p
The resultant vector makes 30° angle with x-axis, so the torque experienced by the effective dipole,
τ = p E sin 30°
= (1 ⁄ 2) p E
It acts along the z-direction.
Hence, the effective dipole moment is p; the torque operating on the system is (1 ⁄ 2) p E along the +z-direction.
问题 3:一个 0.5 C m 大小的电偶极子平行于强度为 30 N⁄C 的电场放置。计算作用在偶极子上的扭矩。
解决方案:
Given:
Electric field, E = 30 N⁄C
Angle between dipole and electric field, θ = 0°
Electric dipole moment, p = 0.5 C m
The torque acting on a dipole is given as:
τ = p E sinθ
= p E sin0°
= 0
Hence, the torque acting on the dipole is 0.
问题 4:为什么偶极子放置在非均匀电场中时会同时受到力和扭矩?
解决方案:
Each charge of a dipole receives a force when it is put in an uniform electric field and the dipole vector direction is not parallel to the field direction. The magnitude of both forces is identical, yet they are moving in opposing directions. A pair is formed by these equal and opposing parallel forces. This pair applies a torque on the dipole, causing it to spin and align in the field direction. The force, however, is always zero in uniform field.
There will be a torque when a dipole is put in a non-uniform field, as stated above. The forces acting on the charges are not the same after the dipole is aligned to the field direction. As a result, the dipole will be subjected to a net force in the direction of increasing field. As a result, the electric dipole experiences both torque and force in a non-uniform field.
问题5:外电场中的偶极子在什么角度承受最大扭矩?
解决方案:
The torque acting on a dipole is given as:
τ = p E sinθ
The value of sine function is maximum at an angle of 90°, i.e., sin90° = 1, so the dipole experiences the maximum torque at an angle of 90° with the field, or we can say that the dipole experiences the maximum torque when it is held perpendicular to the electric field.