切线和法线方程
导数用于求函数相对于变量的变化率。要找到函数相对于变量的变化率,需要将函数相对于该变量进行微分。函数y = f(x)相对于 x 的变化率由 dy/dx 或 f'(x) 定义。例如 y = x 2 + x 那么,dy/dx = f'(x) = d(x 2 + x)/dx = 2x + 1。
当两个变量(让 x = f(t) 和 y = g(t))相对于另一个变量 t 变化时,变化率由链式法则计算。 y 相对于 x 的变化率为:dy/dx = (dy/dt) × (dt/dx)。例如,x = t 和 y = 2t ,则 dy/dx 计算为:dx/dt = 1 或 dt/dx = 1 和 dy/dt = 2。因此,dy/dx = (dy/dt) × ( dt/dx) = 2 × 1 = 2。因此,y 相对于 x 的变化率计算为 y 相对于 t 的变化率和 t 相对于 x 的变化率。
衍生品的应用
导数主要用于数学中,以找出任何变量的值相对于另一个变量的变化。在现实生活中,也会看到和讨论衍生品。比如速度这个词被提到很多,但很少有人知道速度也是一个导数,速度是距离相对于时间的变化。让我们看看衍生品的一些重要应用,
- 求函数相对于变量的变化率。
- 找到切线和法线曲线。
- 求函数的最大值和最小值。
- 查找函数是增加还是减少以及函数增加或减少的区间。
- 求函数的凹度(函数是上凹还是下凹)。
- 从位移计算速度,从速度计算加速度(速度是位移相对于时间的变化,加速度是速度相对于时间的变化)。
- 找出某些数量的近似值(例如平方根、一个数字的立方根)。
切线和法线
在给定点与曲线相切是在给定点接触曲线的直线(不与曲线相交,仅在给定点接触曲线)。而法线是垂直于切线的直线。
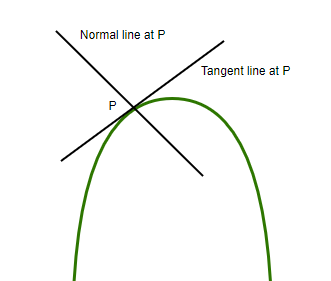
因此,切线斜率和法线斜率的乘积为-1 。令切线和法线的表示斜率为m T 和m N 分别。然后,
mT × mN = -1.
If tangent makes angle Θ with x-axis then slope of tangent = mT = tan Θ.
Since, mT × mN = -1 So, tan Θ × mN = -1.
Hence, the slope of normal is -1/tan Θ or -cot Θ.
正切方程和法线方程
方程为y = f(x)在点a的曲线的切线斜率为f'(a) ( f(x)在点a 的导数)。因此,点斜率形式的切线方程为
(y – f(a))/(x – a) = f'(a),
并使用方程m T × m N = -1 ,
法线方程为:
(y – f(a))/(x – a) = -1/f'(a).
示例问题
问题1:y = x 2是一个曲线方程,求切线方程,法线在点(1, 1)。
解决方案:
First differentiate y = x2, y’ = 2x .
Slope of tangent at point (1, 1) is 2 × 1 = 2 and slope of normal is -1/2 .
Hence, equation of tangent at point (1, 1) is: (y – 1)/(x – 1) = 2 => y = 2x – 1
And equation of normal at point (1, 1) is: (y – 1)/(x – 1) = -1/2 = 2y = -x + 3 .
问题2:y = x 4 + x 2是一个曲线方程,求点(1, 2)的切线方程和法线方程
解决方案:
First differentiate y = x4 + x2 , we get y’ = 4x3 + 2x .
Slope of tangent at point (1, 2) is 4 × (1)3 + 2 × 1 = 6 and slope of normal is -1/6.
Hence, equation of tangent at point (1, 2) is: (y – 2)/(x – 1) = 6 => y = 6x – 4
And equation of normal at point (1, 2) is: (y – 2)/(x – 1) = -1/6 => 6y = -x + 13.
问题3:y = x 是曲线方程,求(1, 1) 点的切线方程和法线方程。
解决方案:
First differentiate y = x , we get y’ = 1 .
The slope of the tangent at point (1, 1) is 1, and the slope of normal is -1.
Hence, equation of tangent at point (1, 1) is: (y – 1)/(x – 1) = 1 => y = x
And equation of normal at point (1, 1) is: (y – 1)/(x – 1) = -1 => 2y = -x + 2.
问题 4:x = t 和 y = t 是曲线方程,求点 t = 2 处的切线方程和法线方程。
解决方案:
First differentiate x = t, we get dx/dt = 1 or dt/dx = 1.
And differentiate y = t, dy/dt = 1.
Hence, dy/dx = (dy/dt) × (dt/dx) = 1 × 1 = 1.
The slope of the tangent at point t = 2 is 1 and slope of normal is -1.
Hence, equation of tangent at point at point t = 2 is: (y – 2)/(x – 2) = 1 => y = x
And equation of normal at point at point t = 2 is (y – 2)/(x – 2) = -1 => y = -x + 4.
问题 5:x = t 和 y = t 2是曲线方程,求 t = 1 处的切线方程和法线方程。
解决方案:
First, differentiate x = t, dx/dt = 1 or dt/dx = 1.
And differentiate y = t2, dy/dt = 2t = 2 × 1 = 2.
Hence, dy/dx = (dy/dt) × (dt/dx) = 2 × 1 = 2.
The slope of the tangent at point t = 1 is 2 and the slope of normal is -1/2.
Hence, equation of tangent at point at point t = 1 is (y – 1)/(x – 1) = 2 => y = 2x – 1.
And equation of normal at point at point t = 1 is (y – 1)/(x – 1) = -1/2 => 2y = -x + 3.