如果 tan A = 4/3,则求 cos A 的值
三角学是数学的一个重要分支,它处理直角三角形中边与角的关系。三角学在物理学中也很重要,它用于查找塔的高度、恒星之间的距离,或用于导航系统。三角学的原理是“如果两个三角形有一组相等的角,那么它们的边在相同的比率内” 。边长通常不同,但边长比相同。
三角函数
三角函数或圆函数或三角比显示角度和边的关系。这些三角比是通过取边的比来获得的。我们有六个三角比 Sin、Cos、Tan、Cosec、Sec、Cot。
- sin A = 垂直 / 斜边
- cos A = 底边 / 斜边
- tan A = 垂直 / 底
- 婴儿床 A = 底座 / 垂直
- sec A = 斜边 / 底边
- cosec A = 斜边 / 垂直
这里,A 是与垂直边相对的角度。
让我们看看直角三角形的垂直、底边和斜边是什么,
- 垂直:角的前面是垂直的。在这种情况下,30 度前面的一侧称为垂直。
- 底:底是包含角的边之一,斜边除外。
- 斜边:与90°相对的一侧。这是最大的一面。
Note: Perpendicular and base changes as angle changes. During a triangle, a side is perpendicular for an angle, but an equivalent side may be a base for an additional angle, but the hypotenuse remains an equivalent because it’s a side opposite to angle 90°.
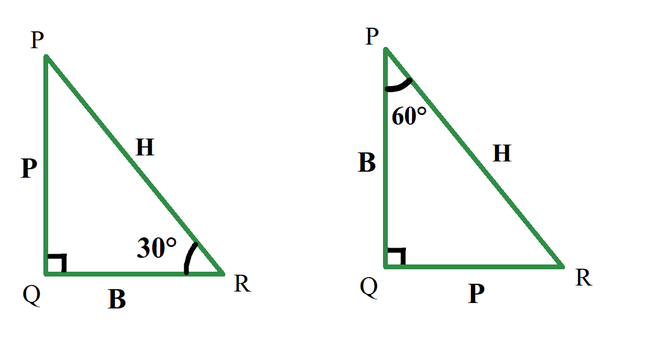
在上面的等效三角形图中,如果考虑角度 30°,则垂线是边 PQ,但如果考虑角度 60°,则垂线是边 QR。
如果 tan A = 4/3,则求 cos A 的值
解决方案:
Tan – The tan of an angle A is the ratio of lengths of perpendicular to the base.
Tan A = Perpendicular / Base
Cos – The cos of an angle A is the ratio of lengths of the base to the hypotenuse.
Cos A = Base / Hypotenuse
In a right triangle if tan A is 4/3 it looks as follows.
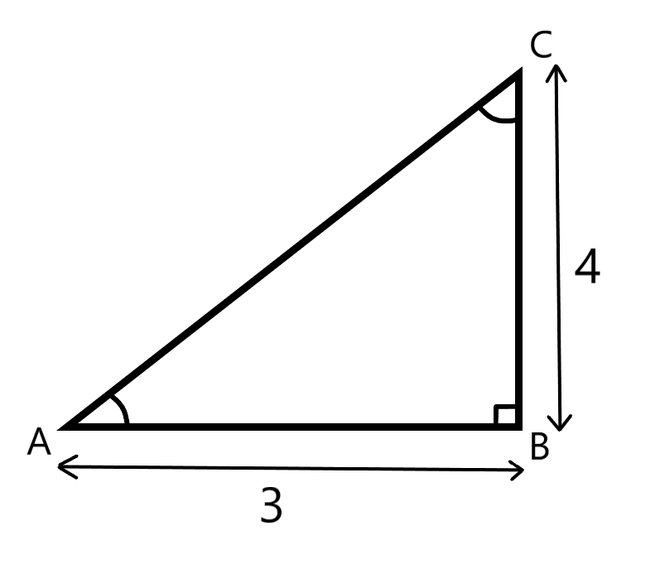
tan A = 4/3
perpendicular / base = 4/3
Calculating hypotenuse –
H2 = P2 + B2
H2 = 42 + 32
H2 = 16 + 9
H2 = 25
H =5
Cos A = Base / hypotenuse
Cos A = 3/5
示例问题
问题1:在一个直角三角形中,角A为60°,底边为3m。求斜边的长度。
解决方案:
Given: Base = 3m
Cos 60 = 1/2
B/H = 1/2
3/H = 1/2
H = 6
问题2:直角三角形中,角A为30°,斜边为3m。求基地的长度。
解决方案:
Given: Hypotenuse = 3m
Cos 30° = √3/2
B/H = √3/2
B/3 = √3/2
B = 3√3/2
问题3:在一个直角三角形中,角A,垂线是9√3m,底边是9m,求角A。
解决方案:
Given: perpendicular = 9√3m, Base = 9m.
Tan A = 9√3 / 9
Tan A = √3
Tan (60°) = √3
Angle A = 60°