坐标几何定义为使用平面上任意尺寸的坐标点对几何进行的研究。使用坐标几何,可以找到两点之间的距离,以比例划分线,找到线的中点,计算笛卡尔平面中三角形的面积,等等。
根据给定的参数,有多种方法可以找到三角形的面积,例如三角形的底边和高度,顶点的坐标,边的长度等。以下是找到三角形面积的3种方法。
方法1:使用三角形的底和高
当给出三角形的底数和高度时,我们将使用此方法,该方法是所有方法中最简单的。对于给定的三角形,如果三角形的高度为“ h ”且三角形的底数为“ b ”,则三角形的面积为:
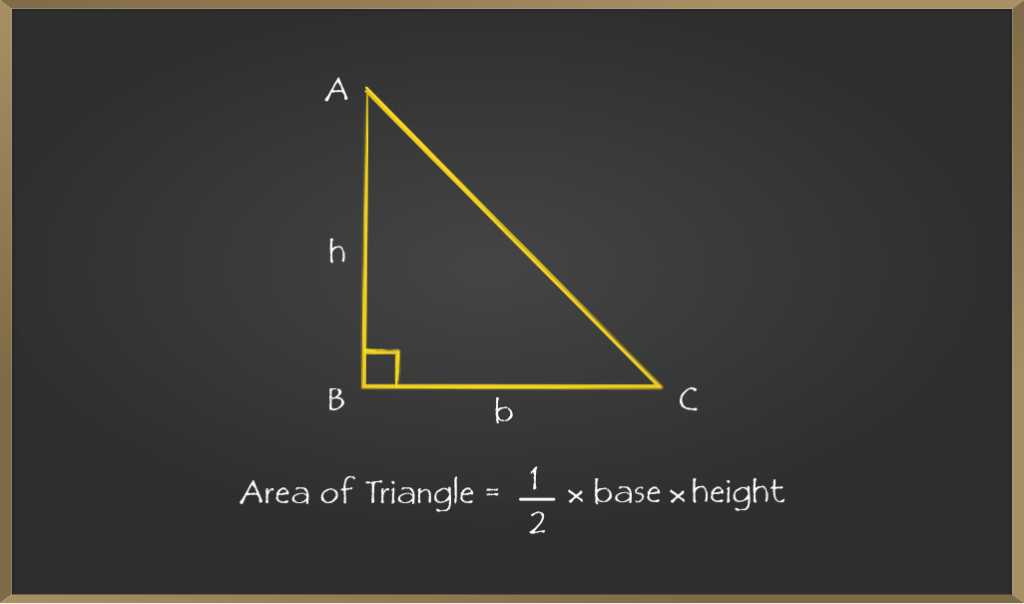
公式的推导
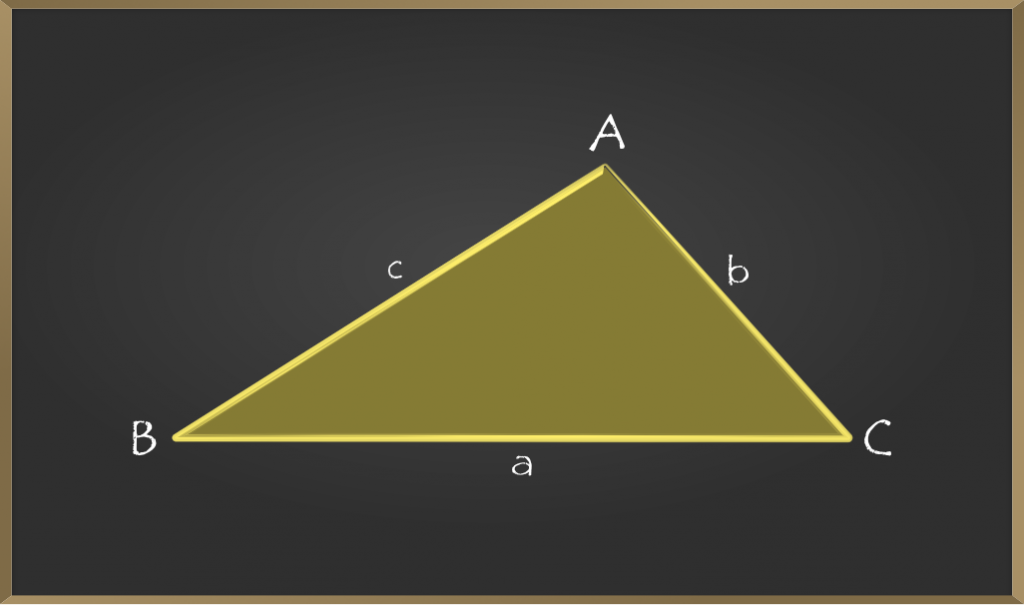
步骤1:考虑直角三角形ABC。
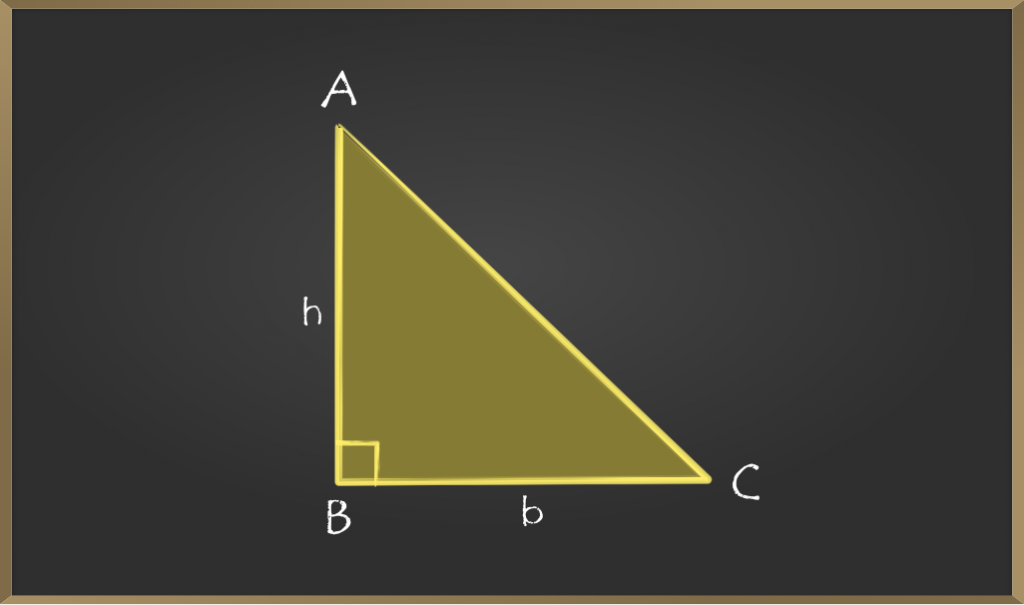
步骤2:现在从点A画一条水平线,从点C画一条垂直线。让点D成为两条线相交的点。
第3步:图形将看起来像一个矩形,即,如果我们添加2个相似的三角形,则会生成一个矩形。
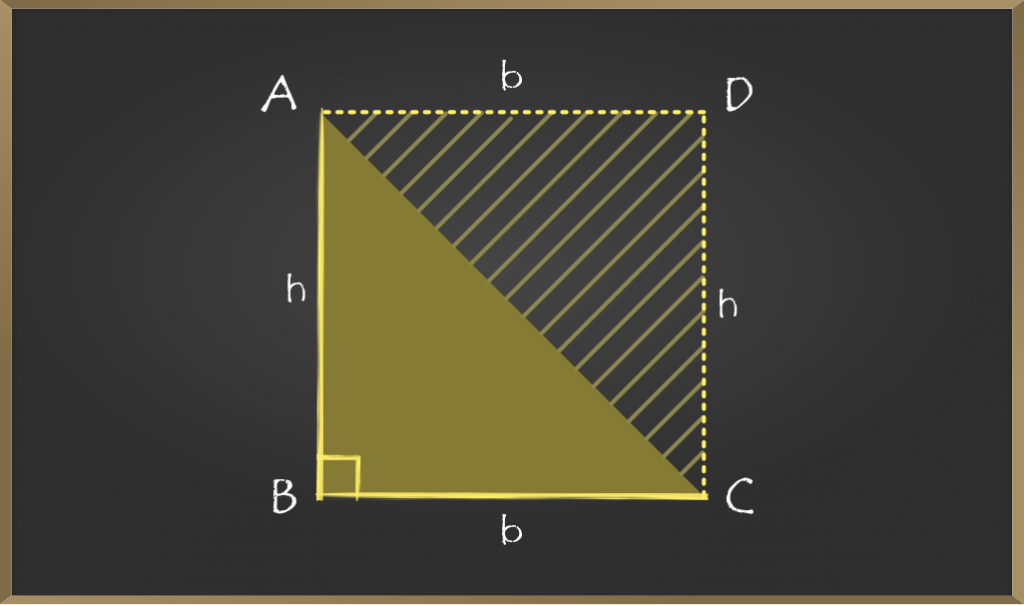
步骤4:由于我们需要三角形ABC的面积,因此我们可以将其写为(矩形ABCD / 2的面积)。
步骤5:继续执行第4步:
=> Area of ABC = (area of rectangle ABCD / 2)
=> Area of ABC = (b × h) / 2
Hence, proved that area of the triangle is (1 / 2) × b × h
公式中的样本问题
示例1:找到高度和底边分别为6厘米和5厘米的三角形的面积?
解决方案:在问题中,明确提到高度和底数是:
Given, h = 6 and b = 5
Area of triangle is given as = (1 / 2) × b × h
=> (1 / 2) × 6 × 5
=> 3 × 5 = 15
Hence, the area of the given triangle is 15 cm2
示例2:找到面积为12 cm 2且底边为6 cm的三角形的高度?
解决方案:
Given, area = 12 and b = 6
Area of triangle is = (1 / 2) × b × h
=> 12 = (1 / 2) × 6 × h
=> h = 12 / 3 = 4
Hence, the height of the given triangle is 4 cm.
方法2:使用苍鹭公式
如果未给出三角形的底边和高度,则如果给出三角形的边,则可以使用Heron公式。
如果a,b,c是三角形的边,则三角形的面积为:
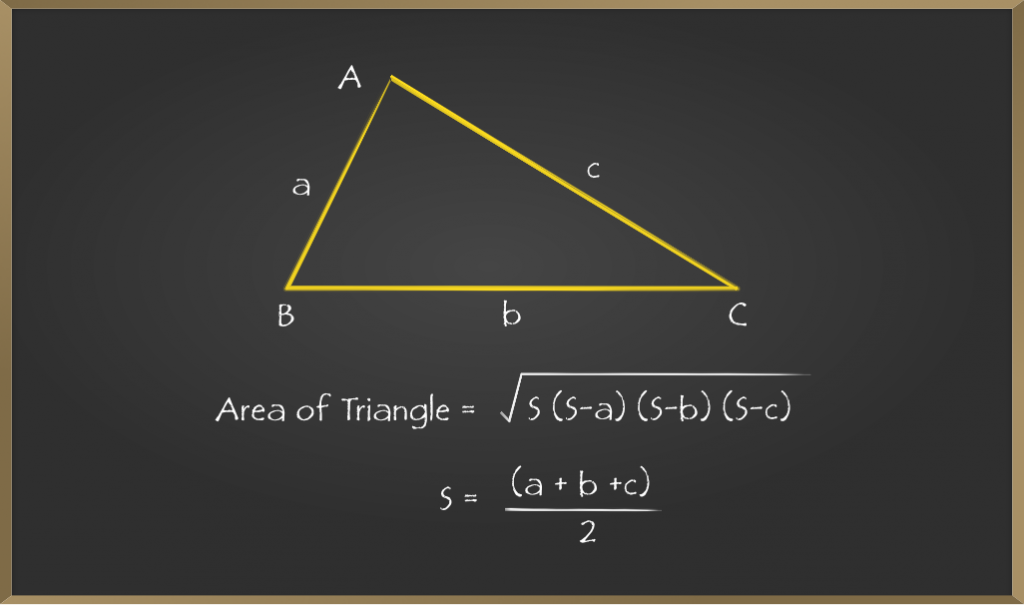
公式的推导
步骤1:众所周知,半周长s =(a + b + c)/ 2
=> 2s = a + b + c
=> 2s – 2a = a + b + c – 2a [subtracting both sides 2a]
=> 2(s – a) = b + c – a —————1
Similarly,
=> 2(s – b) = c + a – b —————2
=> 2(s – c) = a + b – c —————3
We will be using these relations later in the derivation.
第2步:现在,让我们看一下侧面a,b,c的斜角三角形
步骤3:由于我们没有三角形的高度或高度,因此从BC的A垂直于D绘制一个垂直线,其底数为’a’。
步骤4:现在,如果我们清楚地观察到,形成了两个三角形,分别为ΔABD和 ∆ ADC 。如果BD的长度是d,则DC的长度将是– d。
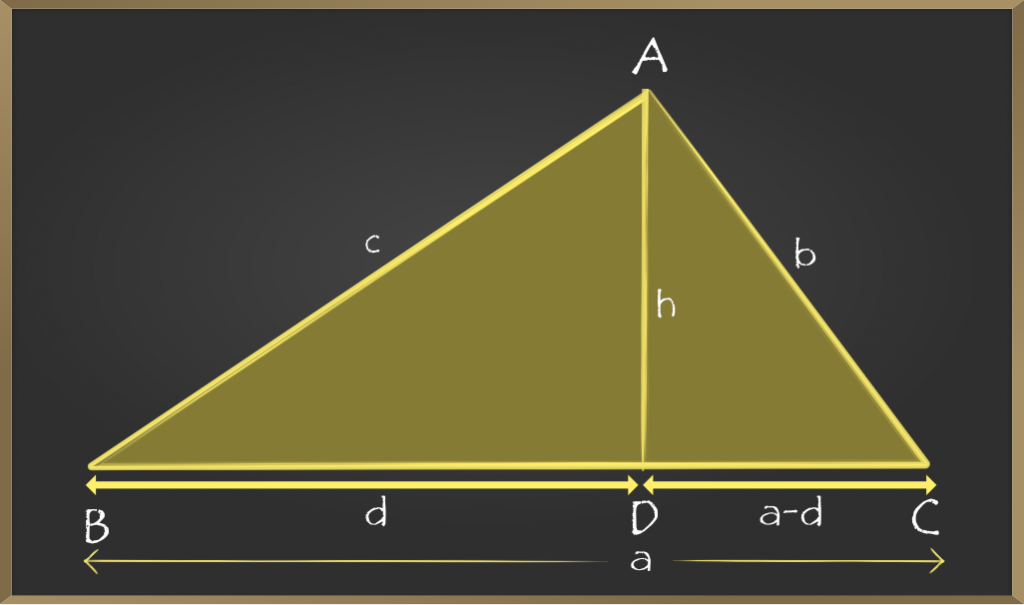
步骤5:现在,在毕达哥拉斯定理的三角形ABD中
=> h2 = c2 – d2 ——————–4
Similarly in ∆ADC
=> h2 = b2 – (a – d)2
From equation 4 substitute value of h2
=> c2 – d2 = b2 – (a – d)2
=> c2 – d2 = b2 – (a2 + d2 – 2ad)
After simplification of the equation we will get,
d = (c2 + a2 + b2) / 2a
Now substitute above value in the equation 4
=> h2 = c2 – [(c2 + a2 + b2) / 2a]2
=> h2 = (c – {(c2 + a2 + b2) / 2a})(c + {(c2 + a2 + b2) / 2a}) because [a2 – b2 = (a + b)(a – b)]
=> h2 = (1 / 4a2)[ b2 – (a – c)2][(a + c)2 – b2]
=> h2 = (1 / 4a2)[(b – a + c)(b + a – c)(a + c – b)(a + b + c)] because [a2 – b2 = (a + b)(a – b)]
From equation 1, 2 and 3 substitutes into above equation
=> h2 = (1 / 4a2) [2(s – a) × 2(s – b) × 2(s – c) × 2s]
=> h2 = (4 / a2) [s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)]
=> h = (2 / a) √[s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)] ————–5
步骤6:从方法1中我们知道是否给定了三角形的底边和高度,那么三角形的面积为(底边×高度)/ 2。现在用此公式替换高度
=> area of ABC = (1 / 2) × a × (2 / a) √[s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)]
After simplification
=> area of ABC = √[s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)]
因此,证明了三角形面积的苍鹭公式。
苍鹭公式的样本问题
示例1:如果三角形的边分别为3 cm,4 cm和5 cm,则找到三角形的面积。
解决方案:
Let a = 3, b = 4, and c = 5
First, we have to find semi perimeter
=> s = (a + b + c) / 2
=> s = (3 + 4 + 5) / 2
=> s = 12 / 2 = 6
As we know heron’s formula is √[s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)], so substituting values in it
=> √[s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)]
=> √[6(6 – 3)(6 – 4)(6 – 5)]
=> √[6 × 3 × 2 × 1]
=> √36 = 6
The area of the triangle is 6 cm2
示例2:使用苍鹭公式推导公式,以求出边为a的等边三角形的面积
解决方案:
To find semi perimeter
=> s = (a + b + c) / 2
=> s = (a + a + a ) / 2
=> s = 3a / 2
Now using heron’s formula
=> √[s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)]
=> √[(3a / 2)((3a / 2) – a)((3a / 2) – a)((3a / 2) – a)]
=> √[(3a / 2)(a / 2)(a / 2)(a / 2)]
=> √(3a4 / 16)
=> √3(a2) / 4
Hence area of a equilateral triangle is √3(a2) / 4
方法3:使用顶点的坐标
在前面的方法中,我们看到了不同的条件,在方法3中,如果给出了三角形的坐标,则将看到如何找到三角形的面积。
如果三角形的坐标为(x1,y1),(x2,y2)和(x3,y3),则三角形的面积为
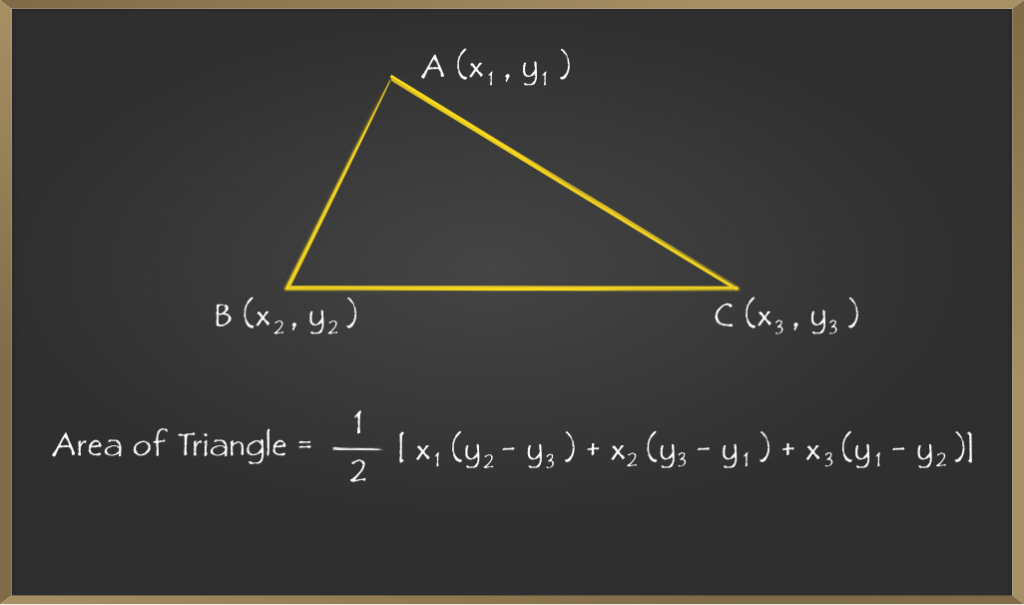
公式的推导
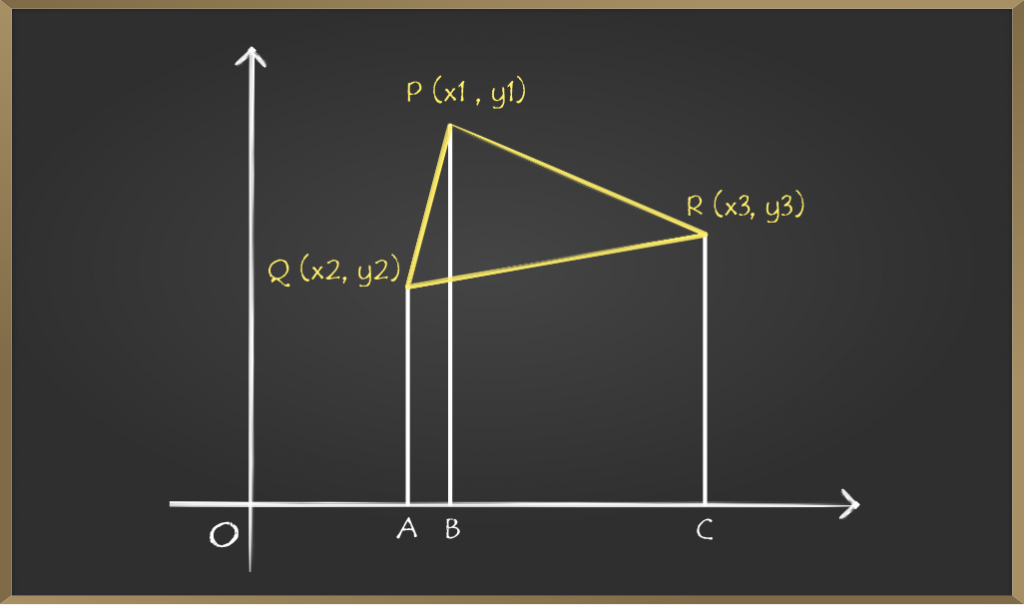
步骤1:分别在A,B和C处绘制从坐标P,Q和R到X轴的垂直线。
步骤2:现在,如果我们仔细看一下图,会在坐标平面中形成三个不同的梯形,例如PQAB,PBCR和QACR。
步骤3:因此, ΔQPR的面积计算为
Area of ∆PQR = [Area of trapezium PQAB + Area of trapezium PBCR] – [Area of trapezium QACR] —-(1)
步骤4:现在计算所有3个梯形的面积。
Since Area of a trapezium = (1 / 2) (sum of the parallel sides) × (distance between sides)
梯形PQAB的发现区域
=> Area of trapezium PQAB = (1 / 2)(QA + PB) × AB
=> QA = y2
=> PB = y1
=> AB = OB – OA = x1 – x2
=> Area of trapezium PQAB = (1 / 2)(y1 + y2)(x1 – x2 ) —-(2)
梯形PBCR的发现区域
=>Area of trapezium PBCR =(1 / 2) (PB + CR) × BC
=>PB = y1
=>CR = y3
=>BC = OC – OB = x3 – x1
=>Area of trapezium PBCR =(1 / 2) (y1 + y3 )(x3 – x1) —-(3)
梯形QACR的发现区域
=>Area of trapezium QACR = (1 / 2) (QA + CR) × AC
=>QA = y2
=>CR = y3
=>AC = OC – OA = x3 – x2
=>Area of trapezium QACR =(1 / 2)(y2 + y3 ) (x3 – x2 )—-(4)
步骤5:将(2),(3)和(4)替换为(1),
=> Area of ∆PQR = (1 / 2)[(y1 + y2)(x1 – x2 ) + (y1 + y3 )(x3 – x1) – (y2 + y3 ) (x3 – x2 )]
=> Area of ∆PQR = (1 / 2) |[x1 (y2 – y3 ) + x2 (y3 – y1 ) + x3(y1 – y2)]|
因此,这是在给出坐标的情况下找到三角形面积的公式。
Note: Observe that there is a mod, which indicates that, if we got a negative value we should only consider the numerical value as the area can’t be negative.
公式中的样本问题
示例1:顶点为A(1,2),B(4,2)和C(3,5)的∆ABC面积是多少?
解决方案:
首先,让我们画一个图以更好地理解。
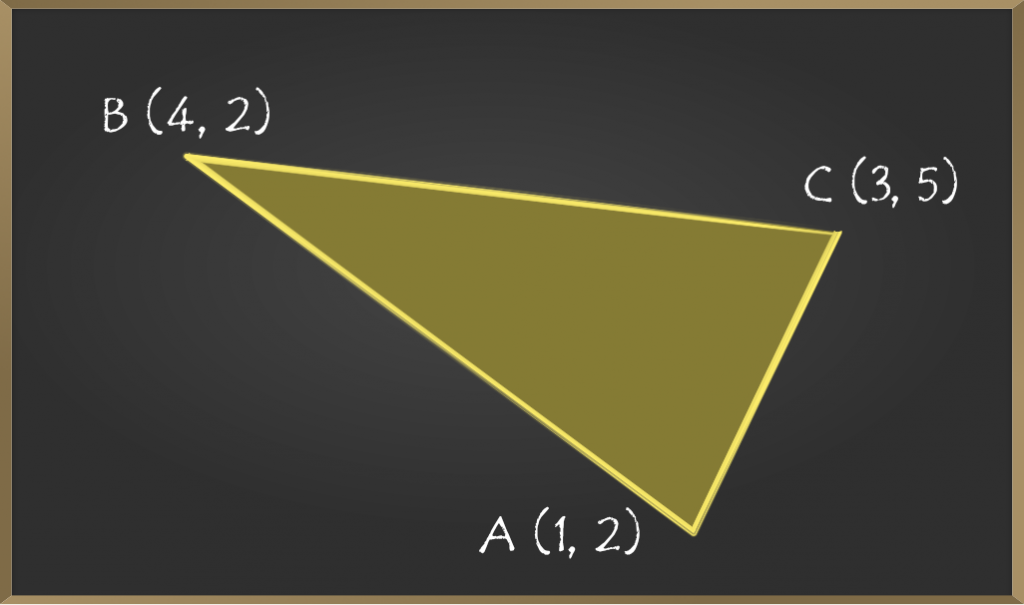
现在将给定坐标与(x1,y1),(x2,y2)和(x3,y3)进行比较。
Let, (x1, y1) = (1, 2)
=> (x2, y2) = (4, 2)
=> (x3, y3) = (3, 5)
现在我们必须替换(1/2)[x1(y2-y3)+ x2(y3-y1)+ x3(y1-y2)]中的值
=> (1 / 2) [1 (2 – 5 ) + 4 (5 – 2 ) + 3(2 – 2)]
=> (1 / 2) [(- 3) + 12 + 0]
=> (1 / 2) [9] = 4.5
Hence the area of the triangle is 4.5 sq units
示例2:三角形的面积为坐标(x1、1),(2、3)和(4、5)的1的x1的值是多少?
解决方案:
首先,让我们画一个图以更好地理解。
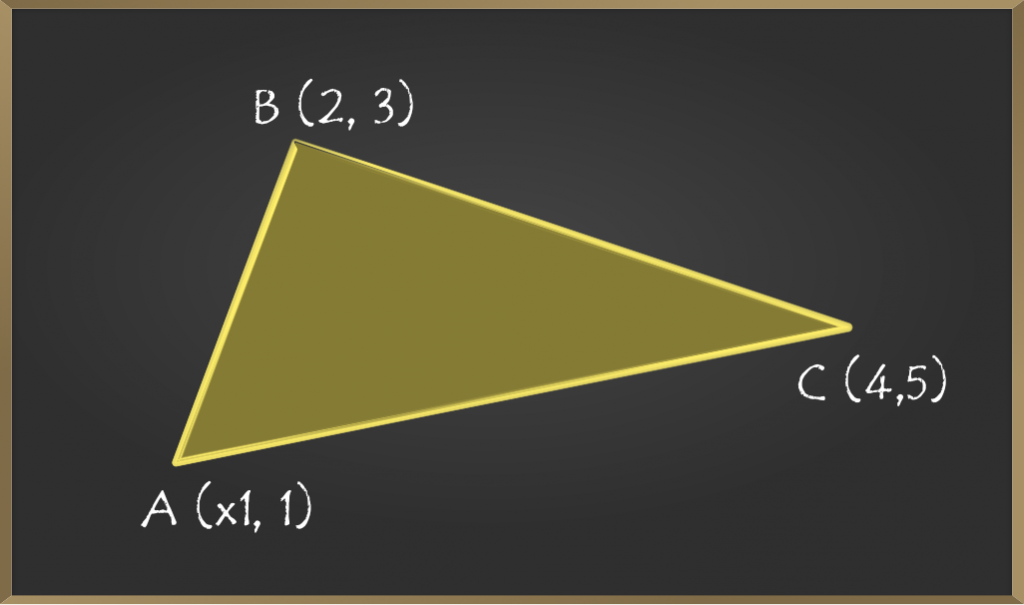
在这个问题中,我们必须找到值“ x1”,它是点A的X坐标。
假定三角形的面积为1。
现在将给定坐标与(x1,y1),(x2,y2)和(x3,y3)进行比较。
Let, (x1, y1) = (x1, 1)
=> (x2, y2) = (2, 3)
=> (x3, y3) = (4, 5)
现在我们必须替换(1/2)[x1(y2-y3)+ x2(y3-y1)+ x3(y1-y2)]中的值
=> (1 / 2) [x1(3 – 5 ) + 2(5 – 1 ) + 4(1 – 3)] = 1
=> (1 / 2) [x1(- 2) + 8 + -8] = 1
=> -x1 = 1
=> x1 = ±1 square units.
Hence, the value of x1 can be both -1 and 1