距离公式是坐标几何中被广泛使用的重要概念之一。通过使用距离公式,我们可以找到最短的距离,即在点之间绘制一条直线。有两种方法可以找到点之间的距离:
- 勾股定理
- 距离公式
勾股定理
该定理与毕达哥拉斯定理相似,但此处的用法略有不同。通常根据毕达哥拉斯定理,我们会在直角三角形中找到缺失的长度。这里我们也做同样的事情,但是在此之前,我们必须找到三角形的坐标。
假设男孩从一个点向西走了4 m,向南转弯,走了3 m。现在,要计算从起点到终点的最短距离,将是所形成三角形的斜边,如下所示。
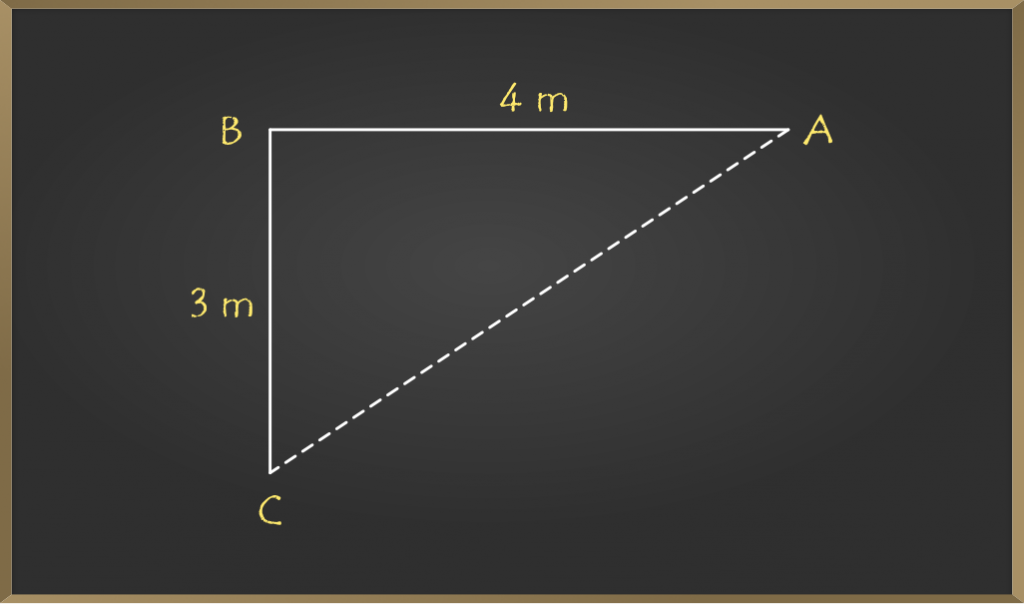
在上图中,您可以看到起点和终点分别是A和C。给定点A,B之间的距离为4 m,而点B,C之间的距离为3 m。为了找到最短的距离,除了AC以外什么都没有,我们将使用勾股定理。
这是使用毕达哥拉斯(Pythagoras)定理计算的,如下所示:
=> AC2 = AB2 + BC2
=> AC = √(16 + 9)
=> AC = √25 = 5 m
Hence the shortest distance is 5 m.
勾股定理的样本问题
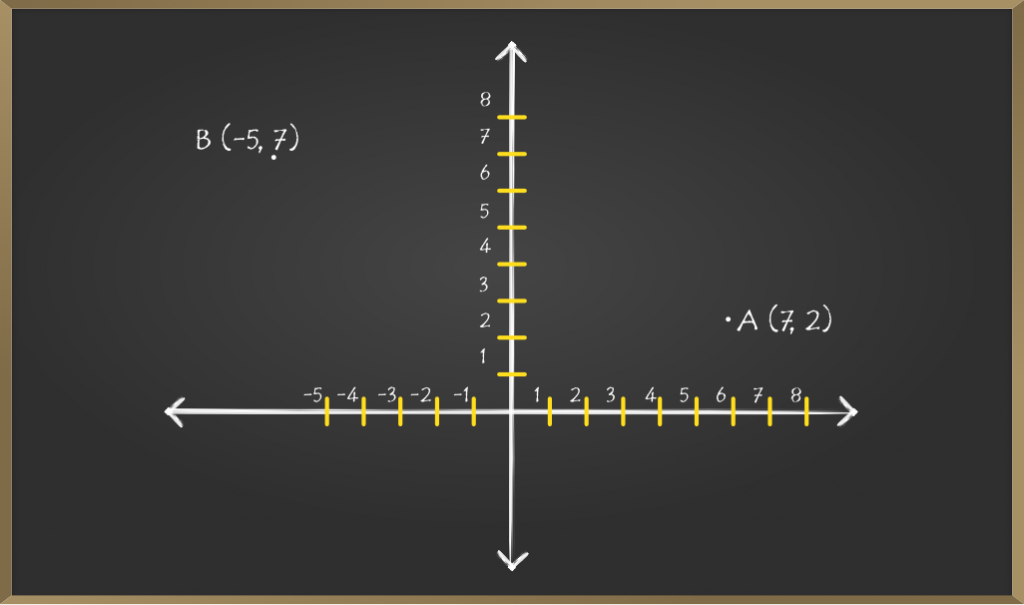
问题1:使用勾股定理,找到点(-5,2)和(7,2)之间的距离?
解决方案:让我们尝试可视化图形上的坐标
现在,让我们用直线将点A和B连接起来,并分别从点A和B绘制水平线和垂直线。
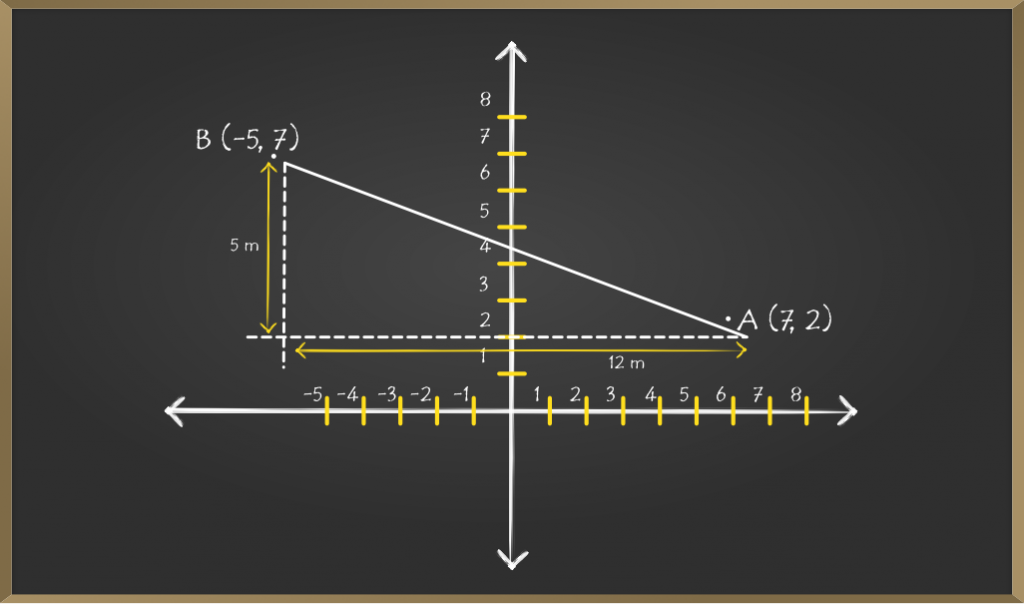
水平线和垂直线在C点重合。现在我们必须找到水平线和垂直线的距离,即AC和BC的长度。
=> AC = (x2 – x1) = (7 – (-5)) = 12
=> BC = (y2 – y1) = (2 – 7) = -5 [As distance can’t be negative, we have to only consider numerical value]
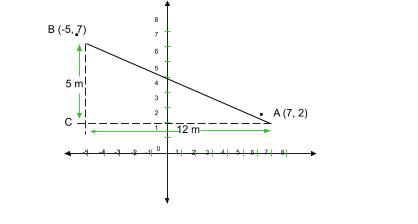
如上图所示,现在问题变成了毕达哥拉斯基本定理
=> AB2 = AC2 + BC2
=> AB2 = 52 + 122
=> AB = √(25 + 144)
=> AB = √169 = 13 square units
Therefore, the distance between the given points is 13 sq units.
问题2 :使用勾股定理,找到点(4,8)和(6,4)之间的距离?
解决方案:看到问题后,您要做的第一件事就是绘制图表。有时绘图使问题变得简单。
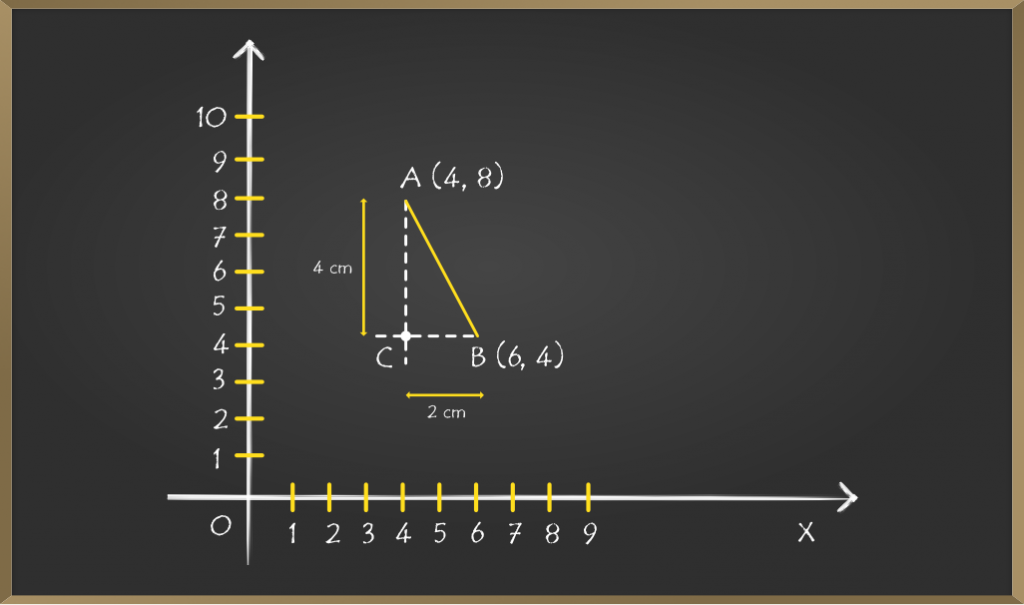
由于我们必须找到点A和B之间的距离,因此首先将这些点连接起来,然后从点A画一条垂直线,从点B画一条水平线,让两条延长线相交的点为C。
现在找到点C的坐标,我们应该敏锐地观察到点C与点B处于同一水平,即Y坐标将相同,并且类似地,点A和点C将具有相同的X坐标。
So coordinates of AC will become (4, 4)
Length of line BC will be (6 – 4) = 2 cm
Length of line AC will be (8 – 4) = 4 cm
Now by using Pythagoras theorem,
=> AB2 = AC2 + BC2
=> AB2 = 42 + 22
=> AB = √(16 + 4)
=> AB = √20 = 4.47 (approx)
Hence the distance between point A and B is 4.47 cm
问题3:给定点M(x,2)和N(2,5)之间的距离为5 cm。找出x的值?
解决方案:第一步是绘制图表以清楚地了解问题。
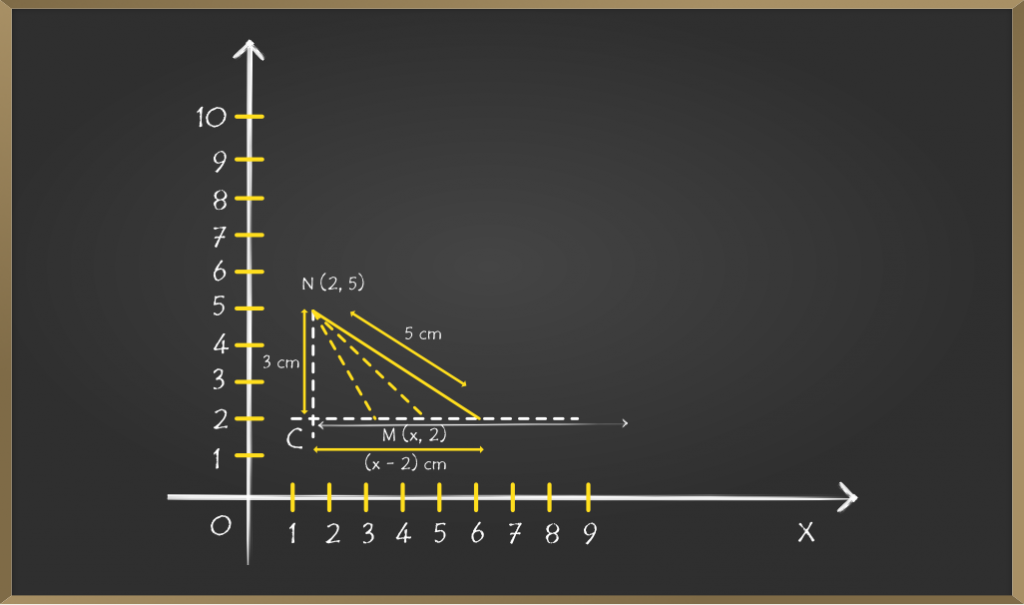
这个问题与以前的问题不同,因为在这里我们必须找到点M的x坐标,其中点MN之间的距离已给定
点N是固定的,但M不是固定的。但是我们知道点M的y坐标。
因此,我们将在y = 2处绘制水平线。但是我们不知道x坐标会有几种可能性。
现在从点N和点C画一条垂直线,两条线相交。
Length of NC = (5 – 2) = 3 cm
Length of MC = (x – 2) cm
And it is already given NM = 5 cm
Applying Pythagoras theorem,
=> NM2 = NC2 + MC2
=> 52 = 32 + (x – 2)2
=> 25 – 9 = (x – 2)2
=> 16 = (4)2 = (x – 2)2
After cancelling squares on both sides
=> x – 2 = 4
=> x = 6
Therefore value of x is 6 and point M is (6, 2)
距离公式
距离公式用于查找任意两个给定点之间的距离。根据毕达哥拉斯定理,我们可以得出距离公式。使用距离公式比勾股定理容易得多。
AB = √[(x2 - x1)² + (y2 - y1)²]
where points are A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2)
让我们看看这个公式是如何得出的
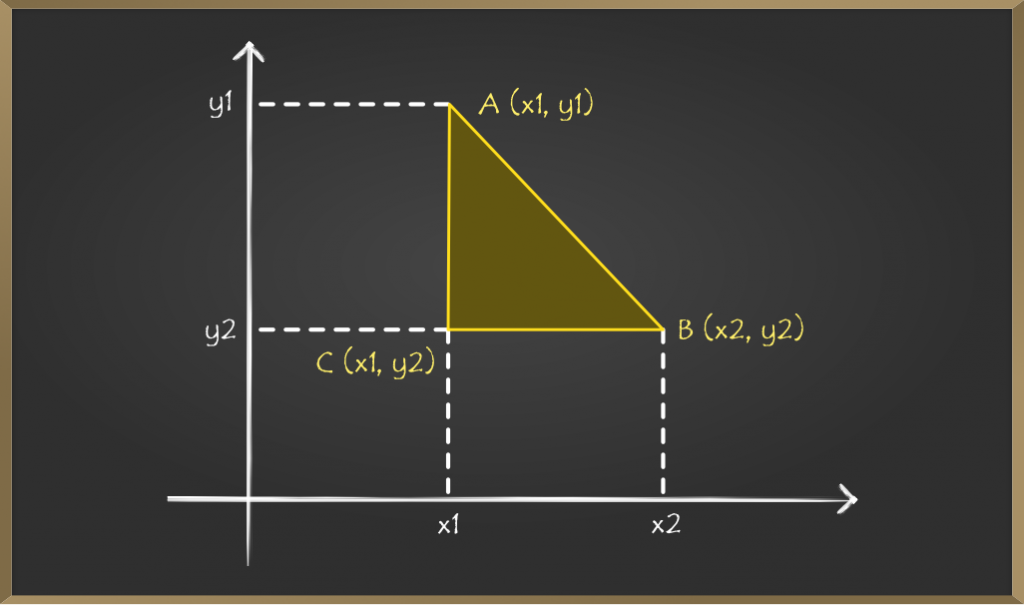
在上图中,我们必须找到两个点A(x1,y1)和B(x2,y2)。用直线将点A和B连接起来。现在从点A和点B绘制水平线,它们都在点C相交。
现在,点C的坐标将变为C(x1,y2)。
现在看起来像一个直角ACB,其中AC边垂直,CB是底边,AB是斜边。
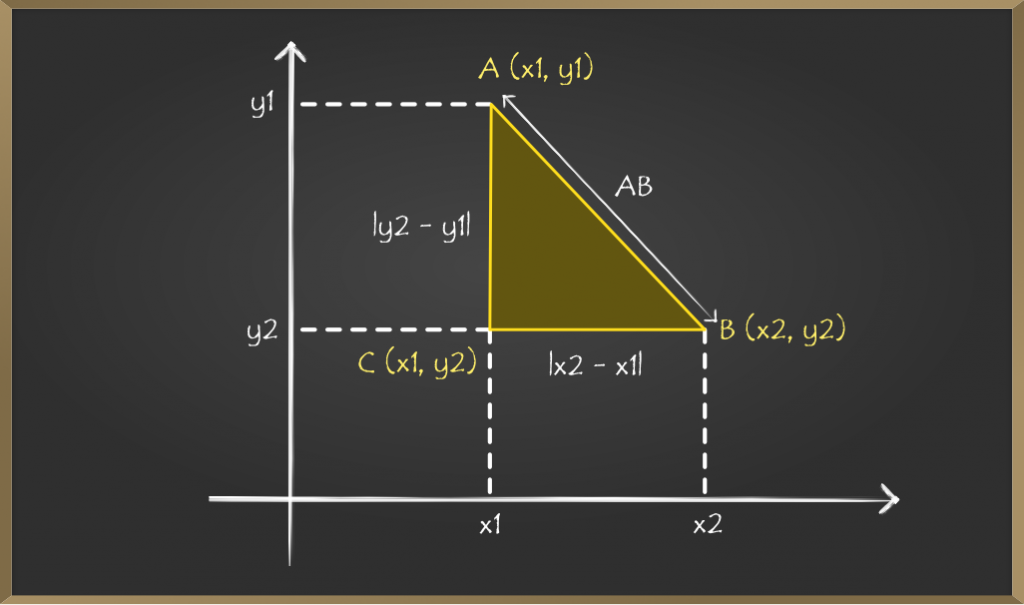
现在我们需要找到点A和C之间的距离。现在通过查看图表,它们之间的距离将是它们y坐标之间的差。
=> AC = y2 – y1 …….(1)
Similarly, the distance between points C and B will be the difference between x coordinates.
=> CB = x2 – x1 ……..(2)
∆ACB is a right-angled triangle. We need to find hypotenuse AB, by Pythagoras theorem
=> AB² = BC² + AC²
From (1) and (2),
=> AB² = (x2 – x1)² + (y2 – y1)²
Taking Square roots on both sides,
=> AB = √{(x2 – x 1)² + (y2 – y1)²}
所以距离公式是
AB =√[(x2 – x1)²+(y2 – y1)²]
距离公式的样本问题
问题1:点A的坐标为(-4,0),点B的坐标为(0,3)。找到这两个点之间的距离。
解决方案:
A的坐标为=(-4,0)
B的坐标为=(0,3)

设A和B的坐标分别为(x1,y1)和(x2,y2)
根据距离公式,
=> AB = √[(x2 – x1)² + (y2 – y1)²] = √[{0 – (-4)}²+ (3 – 0)²]
=> √(4² + 3²) = √(16 + 9) = √25
=> 5 units
Therefore the distance between points A and B is 5 units.
问题2:找到点(7,3)和(8,9)之间的距离。
解决方案:
令P的坐标=(7,3)=(x1,y1)
令Q的坐标=(8,9)=(x2,y2)

根据距离公式,
=> PQ = √[(x2 – x1)² + (y2 – y1)²]
=> PQ = √[(8 – 7)² + (9 – 3)²]
=> PQ = √(1 + 62)
=> PQ = √37 = 6.08 cm (approx)
Therefore the distance between points P and Q is 6.08 cm.
问题3:如果点(x,10)和(1,5)之间的距离为13 cm,则找到x的值。
解决方案:
令M的坐标=(x,10)=(x1,y1)
令N的坐标=(1,5)=(x2,y2)

By Distance Formula,
=> MN = √[(x2 – x1)² + (y2 – y1)²]
=> 13 = √[(1 – x)² + (5 – 10)²]
(squaring on both sides)
=> 169 = (1 – x)2 + 25
=> (1 – x)2 = 144
=> 1 – x = √144
=> x = 13 or x = -11
Here we can 2 values of x, they are 13 and -11