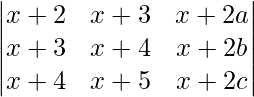问题1.证明行列式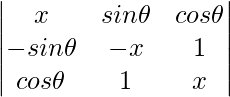 与θ无关。
与θ无关。
解决方案:
A = 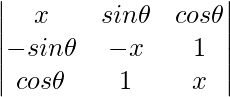
A = x(x2 – 1) – sinθ(-x sinθ – cosθ) + cosθ(-sinθ + x cosθ)
A = x3 – x + x sin2θ + sinθcosθ – sinθcosθ + x cos2θ
A = x3 – x + x(sin2θ + cos2θ)
A = x3 – x + x
A = x3(Independent of θ).
Hence, it is independent of θ
问题2。在不扩大行列式的情况下,证明
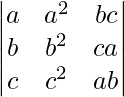 =
= 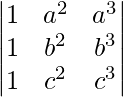
解决方案:
L.H.S. = 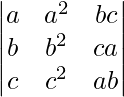
= 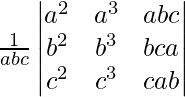
= 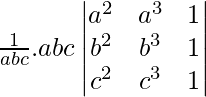
(Taking abc out from C3)
= 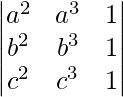
= 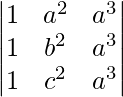
(Applying column transformation between C1 and C3 and between C2 and C3)
= R.H.S.
Hence, it is proved that 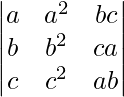 =
= 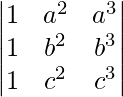
问题3.评估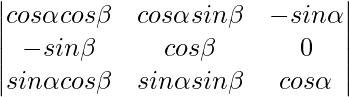
解决方案:
A = 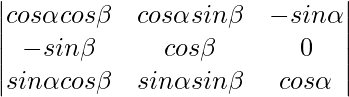
Expanding along C3
A = -sinα(-sinα sin2β – cos2β sinα) + cosα(cosα cos2β + cosα sin2β)
A = sin2α(sin2β + cos2β) + cos2α(cos2β + sin2β)
A = sin2(1) + cos2(1)
A = 1
问题4:如果a,b和c是实数,并且Δ= 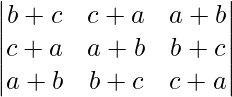 = 0
= 0
证明a + b + c = 0或a = b = c
解决方案:
Δ = 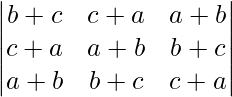
Applying R1 ⇢ R1 + R2 + R3
Δ = 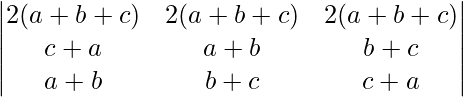
= 2(a + b + c) 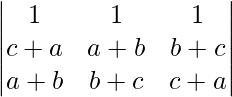
Applying C2 ⇢ C2-C1 and C3 ⇢ C3 – C1
Δ = 2(a + b + c) 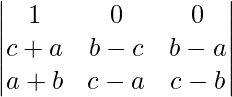
Expanding along R1
Δ = 2(a + b + c)(1)[(b – c)(c – b) – (b – a)(c – a)]
= 2(a + b + c)[-b2 – c2 + 2bc – bc + ba + ac – a2]
= 2(a + b + c)[ab + bc + ca – a2 – b2 – c2]
According to the question Δ = 0
2(a + b + c)[ab + bc + ca – a2 – b2 – c2] = 0
From above, you can see that either a + b + c =0 or ab + bc + ca – a2 – b2 – c2 = 0
Now,
ab + bc + ca – a2 – b2 – c2 = 0
-2ab – 2bc – 2ac + 2a2 + 2b2 + 2c2 = 0
(a – b)2 + (b – c)2 + (c – a)2 = 0
(a – b)2 = (b – c)2 = (c – a)2 = 0 (because (a – b)2, (b – c)2, (c – a)2 are non negative)
(a – b) = (b – c) = (c – a) = 0
a = b = c
Hence, it is proved that if Δ = 0 then either a + b + c = 0 or a = b = c.
问题5.求解方程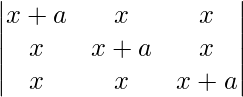 = 0,a≠0
= 0,a≠0
解决方案:
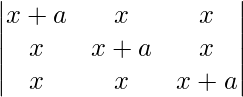 = 0
= 0
Applying R1 ⇢ R1 + R2 + R3
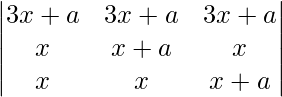 = 0
= 0
(3x + a)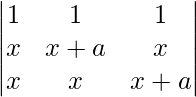 = 0
= 0
Applying C2 ⇢ C2-C1 and C3 ⇢ C3 – C1
(3x + a)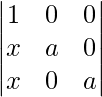 = 0
= 0
Expanding along R1
(3x + a)[a2] = 0
a2(3x + a) = 0
But a ≠ 0
Therefore,
3x + a = 0
x = a/3
问题6.证明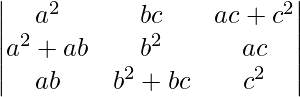 = 4a 2 b 2 c 2
= 4a 2 b 2 c 2
解决方案:
A = 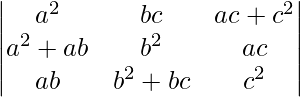
Taking out common factors a, b and c from C1, C2 and C3
A = abc 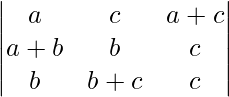
Applying R2 ⇢ R2 – R1 and R3 ⇢ R3 – R1
A = abc 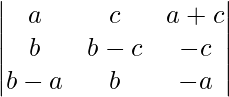
Applying R2 ⇢ R2 + R1
A = abc 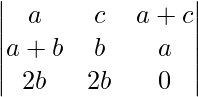
A = 2ab2c 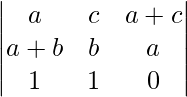
Applying C2 ⇢ C2 – C1
A = 2ab2c 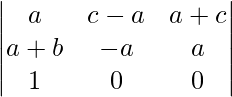
Expanding along R3
A = 2ab2c[a(c – a) + a(a + c)]
= 2ab2c[ac – a2 + a2 + ac]
= 2ab2c(2ac)
= 4a2b2c2
Hence, it is proved.
问题7.如果A -1 = 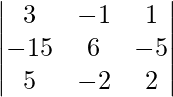 和B =
和B = 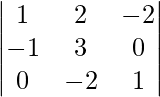 。寻找(AB) -1
。寻找(AB) -1
解决方案:
|B| = 1(3 – 0) + 1(2 – 4) = 1
B11 = 3 – 0 = 3
B12 = 1
B13 = 2 – 0 = 2
B21 = -(2 – 4) = 2
B22 = 1 – 0 = 1
B23 = 2
B31 = 0 + 6 = 6
B32 = -(0 – 2) = 2
B33 = 3 + 2 = 5
adj B = 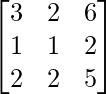
B-1 = (adj B)/|B|
B-1 = 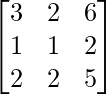
Now,
(AB)-1 = B-1A-1
(AB)-1 = 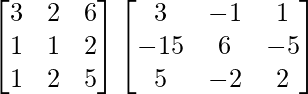
= 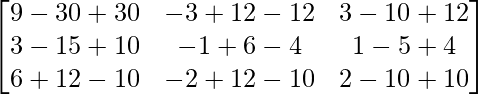
(AB)-1 = 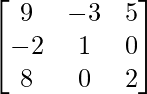
问题8.让A = 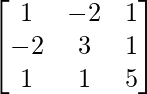 验证
验证
(i)[adj A] -1 = adj(A -1 )
(ii)(A -1 ) -1 = A
解决方案:
A = 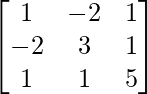
|A| = 1(15 – 1) + 2(-10 – 1) + 1(-2 – 3) = 14 – 27 = -13
A11 = 14
A12 = 11
A13 = -5
A21 = 11
A22 = 4
A23 = -3
A31 = -5
A32 = -3
A33 = -1
adj A = 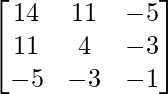
Arrr-1 = (adj A)/|A|
= 
= 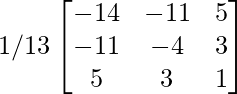
(i). |adj A| = 14(-4 – 9) – 11(-11 – 15) – 5(-33 + 20)
= 14(-13) – 11(-26) – 5(-13)
= -182 + 286 + 65 = 169
adj(adj A) = 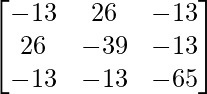
[adj A]-1 = (adj(adj A))/|adj A|
= 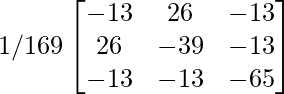
= 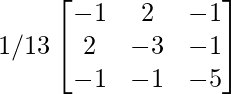
Now, A-1 = 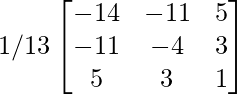
= 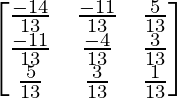
adj(A-1) = 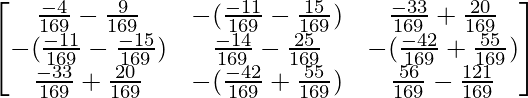
= 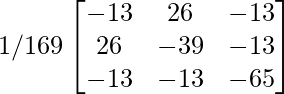
= 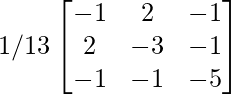
Hence, [adj A]-1 = adj(A-1)
(ii). A-1 = 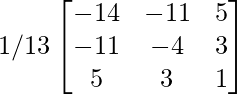
adj A-1 = 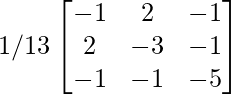
|A-1| = (1/13)3[-14 × (-13) +11 × (-26) + 5 × (-13)]
= (1/13)3 × (-169)
= -1/13
Now, (A-1)-1 = (adj A-1)/|A-1|
= 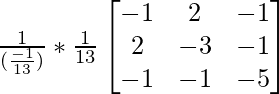
= 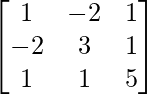
= A
Hence, it is proved that (A-1)-1 = A
问题9.评估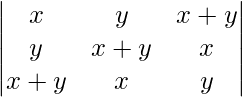
解决方案:
A = 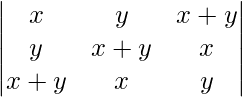
Applying R1 -> R1+R2+R3
A = 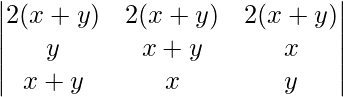
= 2(x+y)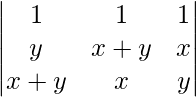
Applying C2-> C2 – C1 and C3-> C3 – C1
A = 2(x + y)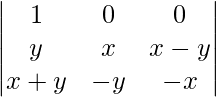
Expanding along R1
A = 2(x + y)[-x2 + y(x – y)]
= -2(x + y)(x2 + y2 – yx)
A = -2(x3 + y3)
问题10:评估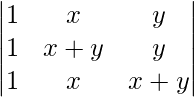
解决方案:
A = 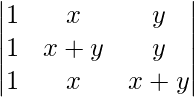
Applying R2->R2 – R1 and R3->R3 – R1
A = 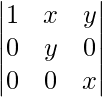
Expanding along C1
A = 1(xy – 0)
A = xy
问题11。使用行列式的性质证明:
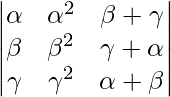 =(β-γ)(γ- α )( α -β)( α +β+γ)
=(β-γ)(γ- α )( α -β)( α +β+γ)
解决方案:
A = 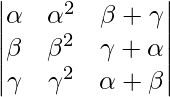
Applying R2->R2 – R1 and R3->R3 – R1
A = 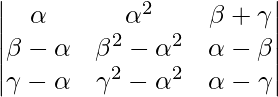
A = (γ – α)(β – α)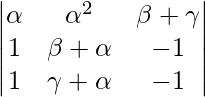
Applying R3->R3 – R2
A = (γ – α)(β – α)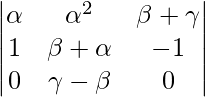
Expanding along R3
A = (γ – α)(β – α)[-(γ – β)(-α – β – γ)]
A = (γ – α)(β – α)(γ – β)(α + β + γ)
A = (β – γ)(γ – α)(α – β)(α + β + γ)
Hence, it is proved.
问题12。使用行列式的性质,证明:
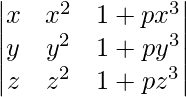 =(1 + pxyz)(x – y)(y – z)(z – x)
=(1 + pxyz)(x – y)(y – z)(z – x)
解决方案:
A = 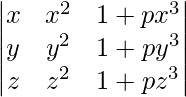
Applying R2->R2 – R1 and R3-> R3 – R1
A = 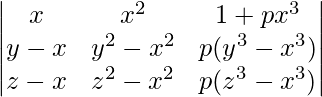
A = (y – x)(z – x)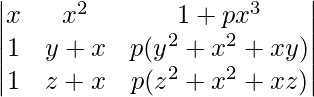
Applying R3->R3 – R2
A = (y – x)(z – x)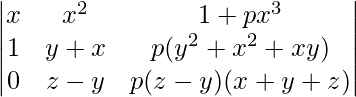
A = (y – x)(z – x)(z – y)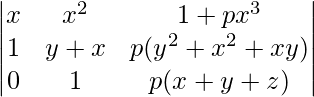
Expanding along R3
A = (x – y)(y – z)(z – x)[(-1)(p)(xy2 + x3 + x2y) + 1 + px3 + p(x + y + z)(xy)]
= (x – y)(y – z)(z – x)[-pxy2 – px3 – px2y + 1 + px3 + px2y + pxy2 + pxyz]
= (x – y)(y – z)(z – x)(1 + pxyz)
Hence it is proved.
问题13。使用行列式的性质证明
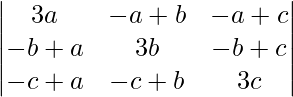 = 3(a + b + c)(ab + bc + ca)
= 3(a + b + c)(ab + bc + ca)
解决方案:
A = 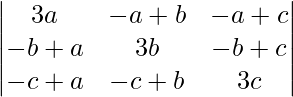
Applying C1->C1 + C2 + C3
A = 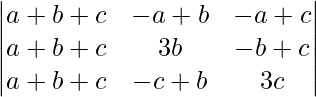
A = (a + b + c)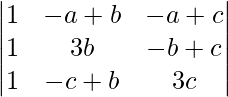
Applying R2->R2 – R1 and R3 ->R3 – R1
A = (a + b + c)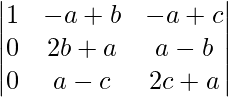
Expanding along C1
A = (a + b + c)[(2b + a)(2c + a) – (a – b)(a – c)]
= (a + b + c)[4bc + 2ab + 2ac + a2 – a2 + ac + ba – bc]
=(a + b + c)(3ab + 3bc + 3ac)
A = 3(a + b + c)(ab + bc + ca)
Hence, it is proved.
问题14.使用行列式的性质证明:
 = 1
= 1
解决方案:
A = 
Applying R2->R2 – 2R1 and R3->R3 – 3R1
A = 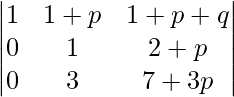
Applying R3->R3 – 3R2
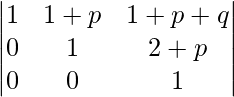
Expanding along C1
A = 1(1 – 0)
A = 1
Hence, it is proved.
问题15。利用行列式的性质证明
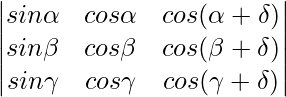 = 0
= 0
解决方案:
A = 
A = 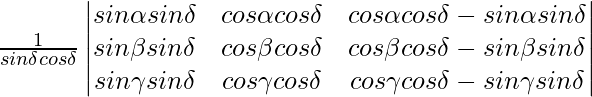
Applying C1->C1 + C3
A = 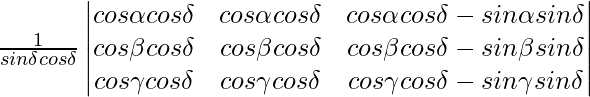
from above, you can see that two columns C1 and C2 are identical.
Hence A = 0
Hence, it is proved.
问题16.解决以下问题的系统:
2 / x + 3 / y + 10 / z = 4
4 / x – 6 / y + 5 / z = 1
6 / x + 9 / y – 20 / z = 2
解决方案:
Assume 1/x = p ; 1/y = q; 1/z = r
then. the above equations will be like
2p + 3Q + 10r = 4
4p – 6q + 5r = 1
6p + 9q – 20r = 2
This can be written in the form of AX=B
where,
A = 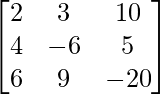
X = ![]()
B = ![]()
We have,
|A| = 2(120 – 45) – 3(-80 – 30) + 10(36 + 36)
|A| = 150 + 330 + 720
|A| = 1200 ≠ 0
Hence A is invertible matrix.
A11 = 75
A12 = 110
A13 = 72
A21 = 150
A22 = -100
A23 = 0
A31 = 75
A32 = 30
A33 = -24
A-1 = (adj A)/|A|
A-1 = 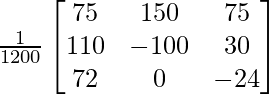
Now,
X = A-1B
![]() =
= 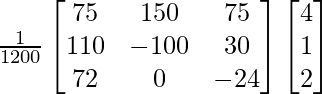
![]() =
= 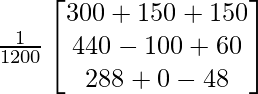
= 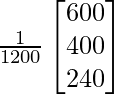
= ![]()
From above p = 1/2; q = 1/3 ; r = 1/5
So, x = 2; y = 3; z = 5
问题17.选择正确的答案。
如果a,b,c在AP中,则行列式
(A)0(B)1
(C)x(D)2倍
解决方案:
A = 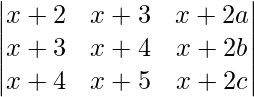
a, b and c are in A.P So, 2b = a + c
A = 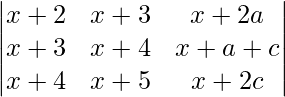
Applying R1->R1 – R2 and R3->R3 – R2
A = 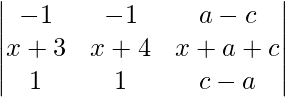
Applying R1->R1 + R3
A = 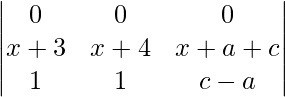
All the elements in the first row are 0.
Hence A = 0
So, the correct answer is A.
问题18.选择正确的答案。
如果x,y,z为非零实数,则矩阵A的逆= 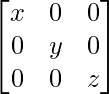 是
是
(一种) 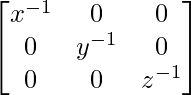
(B)xyz 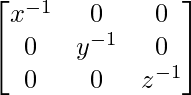
(C) 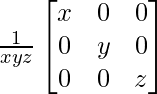
(D) 
解决方案:
A = 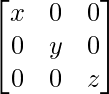
|A| = x(yz – 0) = xyz ≠ 0
Hence, the matrix is invertible
Now,
A11 = yz
A12 = 0
A13 = 0
A21 = 0
A22 = xz
A23 = 0
A31 = 0
A32 = 0
A33 = xy
adj A = 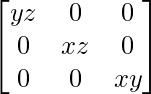
A-1 = (adj A)/|A|
A-1 = 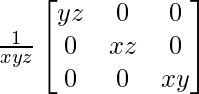
A-1 = 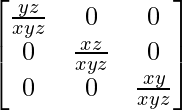
A-1 = 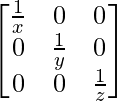
A-1 = 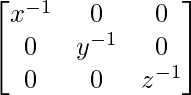
Hence, the correct answer is A.
问题19:选择正确的答案
令A = 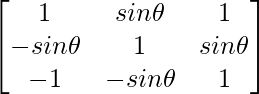 ,其中0≤θ≤2π ,则
,其中0≤θ≤2π ,则
(A)Det(A)= 0(B)Det(A)∈(2,∞)
(C)Det(A)∈(2,4)(D)Det(A)∈[2,4]
解决方案:
A = 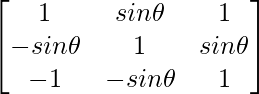
|A| = 1(1 + sin2θ) – sinθ(-sinθ + sinθ) + 1(sin2θ + 1)
|A| = 1 + sin2θ + sin2θ + 1
= 2 + 2 sin2θ
= 2(1 + sin2θ)
Now 0 ≤ θ ≤ 2π
So, 0 ≤ sinθ ≤ 1
0 ≤ sin2θ ≤ 1
0 + 1 ≤ 1 + sin2θ ≤ 1 + 1
2 ≤ 2(1 + sin2θ) ≤ 4
Det(A) ∈ [2, 4]
Hence, the correct answer is D.