二阶导数定义为给定函数的一阶导数。给定点的一阶导数为我们提供有关该点切线斜率或该点处函数的瞬时变化率的信息。二阶导数使我们想到了给定函数的图的形状。函数f(x)的二阶导数通常表示为f”(x) 。如果y = f(x),也用D 2 y或y 2或y”表示。
Let y = f(x)
Then, dy/dx = f'(x)
If f'(x) is differentiable, we may differentiate (1) again w.r.t x. Then, the left-hand side becomes d/dx(dy/dx) which is called the second order derivative of y w.r.t x.
例1:如果y = x 3 ,则求d 2 y / dx 2 。
解决方案:
Given that, y = x3
Then, first derivative will be
dy/dx = d/dx (x3) = 3x2
Again, we will differentiate further to find its
second derivative,
Therefore, d2y/dx2 = d/dx (dy/dx)
= d/dx (3x2)
= 6x
Note: d/dx (xn) = nxn – 1, where n is the power raised to x.
示例2 :如果y = Asinx + Bcosx,则找到d 2 y / dx 2 ,其中A和B是常数?
解决方案:
Given that, y = Asinx + Bcosx
Then, first derivative will be
dy/dx = d/dx (Asinx + Bcosx)
= A d/dx (sinx) + B d/dx (cosx)
= A(cosx) + B(-sinx)
= Acosx – Bsinx
Again, we will differentiate further to find its second derivative,
d2y/dx2 = d/dx (dy/dx)
= d/dx (Acosx – Bsinx)
= A d/dx (cosx) – B d/dx (sinx)
= A(-sinx) – B(cosx)
= -Asinx – Bcosx
= -(Asinx + Bcosx)
= -y
Note:
d/dx (sinx) = cosx
d/dx( cosx) = -sinx
例3:y = logx,求d 2 y / dx 2 ?
解决方案:
Given that, y = logx
Then first derivative will be,
dy/dx = d/dx (logx)
= (1 / x)
Again, we will further differentiate to find its second derivative,
d2y/dx2 = d/dx (dy/dx)
= d/dx (1 / x) (from first derivative)
= -1 / x2
示例4:y = e x sin5x,求出d 2 y / dx 2 ?
解决方案:
Given that, y = ex sin5x
Then first derivative will be,
dy/dx = d/dx (ex sin5x)
= ex d/dx (sin5x) + sin5x d/dx (ex) (multiplication rule)
= ex (cos5x . 5) + sin5x . ex
= ex (5cos5x + sin5x)
Again, we will further differentiate to find its second derivative,
d2y/dx2 = d/dx (dy/dx)
= d/dx (ex (5cos5x + sin5x))
= ex d/dx (5cos5x + sin5x) + (5cos5x + sin5x) d/dx(ex)
= ex (d/dx (5cos5x) + d/dx (sin5x)) + (5cos5x + sin5x) d/dx (ex)
= ex(5(-sin5x)5 + 5cos5x) + (5cos5x + sin5x)(ex)
= ex(-25sin5x + 5cos5x + 5cos5x + sin5x)
= ex(10cos5x – 24sin5x)
= 2ex(5cos5x – 12sin5x)
Note: Multiplication Rule of Differentiation
d(uv) / dx = (u. dv/dx) + (v. du/dx)
参数形式的函数的二阶导数
为了以参数形式计算函数的二阶导数,我们使用链式规则两次。因此,要找到二阶导数,我们可以找到相对于一阶导数的t的导数,然后除以相对于t的x的导数。假设x = x(t)和y = y(t),则其参数形式为二阶:
First Derivative: dy/dx = (dy/dt) / (dx/dt)
Second Derivative: d2y/dx2 = d/dx (dy/dx)
= d/dt (dy/dx) / (dx/dt)
Note: It is totally wrong to write the above formula as d2y/dx2 = (d2y/dt2) / (d2x/dt2)
示例:如果x = t +成本,y = sint,则求二阶导数。
解决方案:
Given that, x = t + cost and y = sint
First Derivative,
dy/dx = (dy/dt) / (dx/dt)
= (d/dt (sint)) / (d/dt (t + cost))
= (cost) / (1 – sint) —- (1)
Second Derivative,
d2y / dx2 = d/dx (dy/dx)
= d/dx (cost / 1 – sint) —- (from eq.(1))
= d/dt (cost / 1 – sint) / (dx/dt) —- (chain rule)
= ((1 – sint) (-sint) – cost(-cost)) / (1 – sint)2 / (dx/dt) —- (quotient rule)
= (-sint + sin2t + cos2t) / (1 – sint)2 / (1 – sint)
= (-sint + 1) / (1 – sint)3
= 1 / (1 – sint)2
Note:
1) Quotient Rule of Differentiation: dy/dx = v(du/dx) – u(dv/dx) / v2
2) Chain Rule: dy/dx = (dy/du) . (du/dx)
二阶导数的图形表示
用图形表示,一阶导数表示函数在一点上的斜率,而二阶导数描述斜率如何在图形中的自变量上变化。
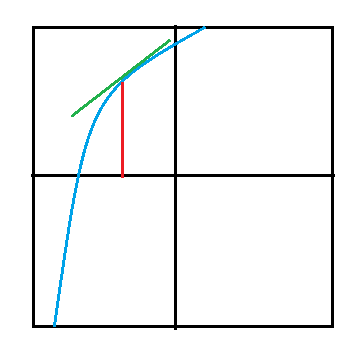
在该图中,蓝线表示斜率,即给定函数的一阶导数。例如,我们使用二阶导数检验来确定最大,最小或拐点。给定函数的二阶导数对应于图形的曲率或凹度。如果二阶导数值为正,则函数的图向上凹。如果二阶导数值为负,则函数的图将向下打开。
函数的凹入
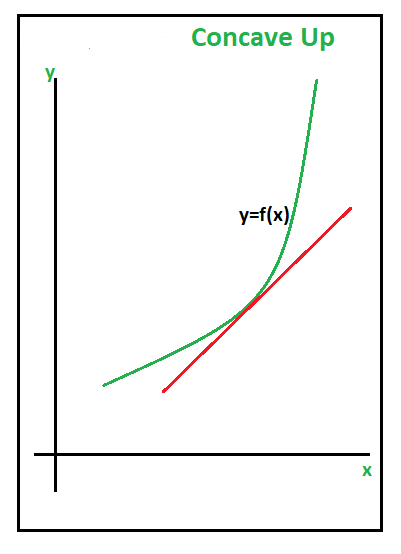
令f(x)是在适当间隔内的可微函数。然后,f(x)的图可以分类为:
上凹:如果y值从左到右以越来越快的速度增长,则曲线的一部分将上凹。
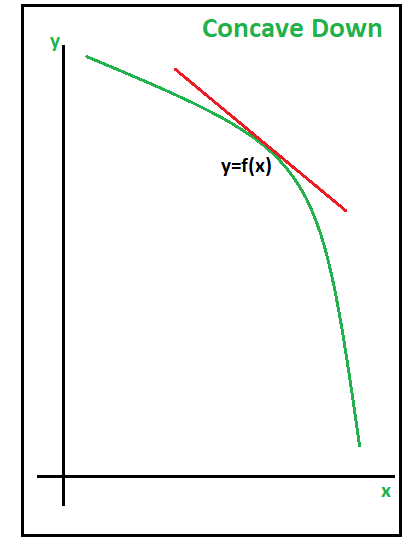
凹下凹:凹上凹的相反方向(其中y值从左到右递减)称为凹下凹。
拐点:拐点是函数改变凹度的点,即从“凹”向上变为“凹”,反之亦然。
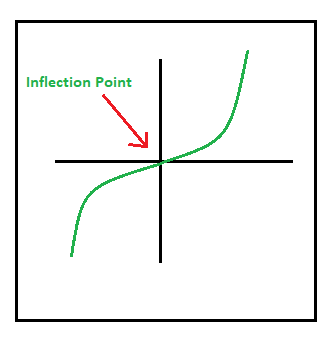
函数的二阶导数确定局部最大或最小拐点值。这些可以借助以下条件来识别:
- If f”(x) < 0, then the function f(x) has a local maximum at x.
- If f”(x) > 0, then the function f(x) has a local minimum at x.
- If f”(x) = 0, then it is not possible to conclude anything about the point x