找出练习1到10中给出的函数的二阶导数。
问题1. x 2 + 3x + 2
解决方案:
Here, y = x2+ 3x + 2
First derivative,
![]()
= 2x+ 3
Second derivative,
![]()
= ![]()
= 2
问题2. x 20
解决方案:
Here, y = x20
First derivative,
![]()
= 20x20-1
= 20x19
Second derivative,
![]()
= ![]()
= 20(19x19-1)
= 380x18
问题3. x。 cos x
解决方案:
Here, y = x . cos x
First derivative,
![]()
Using product rule
= x ![]() + cos x
+ cos x ![]()
= x (-sin x)+ cos x (1)
= – x sin x+ cos x
Second derivative,
![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
Using product rule,
= -x ![]() + sin x
+ sin x ![]() + (- sin x)
+ (- sin x)
= -x (cos x) + sin x (-1) – sin x
= – ( x cos x + 2 sin x)
问题4.日志x
解决方案:
Here, y = log x
First derivative,
![]()
= 1/x
Second derivative,
![]()
= ![]()
Using division rule,
=![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
问题5. x 3日志x
解决方案:
Here, y = x3 . log x
First derivative,
![]()
Using product rule
= x3 ![]() + log x
+ log x ![]()
= x3 (![]() ) + log x (3x2)
) + log x (3x2)
= x2 + 3x2 log x
Second derivative,
![]()
= ![]()
= ![]() +
+ ![]()
Using product rule,
= 2x + 3 (x2 ![]() – log x
– log x![]() )
)
= 2x + 3 (x2 ![]() – log x (2x))
– log x (2x))
= 2x + 3 (x – 2x . log x)
= 2x + 3x – 6x . log x
= x(5 – 6 log x)
问题6. e x罪恶5x
解决方案:
Here, y = ex sin 5x
First derivative,
![]()
Using product rule
= ex ![]() + sin 5x
+ sin 5x ![]()
= ex (5 cos(5x))+ sin 5x (ex)
= ex (5 cos(5x)+ sin 5x)
Second derivative,
![]()
=![]()
Using product rule,
= ex ![]() + (5 cos(5x)+ sin 5x)
+ (5 cos(5x)+ sin 5x) ![]()
= ex (5 (5(- sin 5x))) + 5(cos 5x) + (5 cos(5x)+ sin 5x) (ex)
= ex (- 25 sin 5x + 5cos 5x) + (5 cos(5x)+ sin 5x) (ex)
= ex (- 25 sin 5x + 5cos 5x + 5 cos(5x)+ sin 5x)
= ex (10 cos 5x – 24 sin 5x)
问题7. e 6x cos 3x
解决方案:
Here, y = e6x cos 3x
First derivative,
![]()
Using product rule
= e6x ![]() + cos 3x
+ cos 3x ![]()
= e6x (- 3 sin(3x))+ cos 3x (6e6x)
= e6x (6 cos(3x) – 3 sin (3x))
Second derivative,
![]()
= ![]()
Using product rule,
= e6x (![]() ) + (6 cos(3x) – 3 sin (3x))
) + (6 cos(3x) – 3 sin (3x)) ![]()
= e6x (6 (3 (- sin(3x)) – 3 (3 cos 3x)) + (6 cos(3x) – 3 sin (3x)) (6e6x)
= e6x (- 18sin(3x) – 9 cos 3x) + (36 cos(3x) – 18 sin (3x)) (e6x)
= e6x (27 cos(3x) – 36 sin (3x))
= 9e6x (3 cos(3x) – 4 sin (3x))
问题8.棕褐色–1 x
解决方案:
Here, y = tan–1 x
First derivative,
![]()
= ![]()
Second derivative,
![]()
= ![]()
Using division rule,
=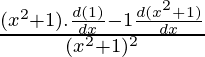
= ![]()
= ![]()
问题9.日志(log x)
解决方案:
Here, y = log (log x)
First derivative,
![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
Second derivative,
![]()
=![]()
Using division rule,
= 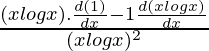
Using product rule,
= 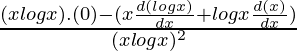
= – ![]()
= – ![]()
= – ![]()
问题10.罪过(log x)
解决方案:
Here, y = sin (log x)
First derivative,
![]()
= cos (log x) ![]()
= cos (log x) . ![]()
= ![]()
Second derivative,
![]()
= ![]()
Using division rule,
= ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
问题11.如果y = 5 cos x – 3 sin x,则证明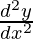 + y = 0
+ y = 0
解决方案:
Here, y = 5 cos x – 3 sin x
First derivative,
![]()
= 5 (- sin x) – 3 (cos x)
= – 5 sin(x) – 3 cos(x)
Second derivative,
![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
= -5 (cos(x)) – 3 (- sin(x))
= -(5 cos(x) – 3 sin(x))
= -y
According to the given condition,
![]() + y = -y + y
+ y = -y + y
![]() + y = 0
+ y = 0
Hence Proved!!
问题12.如果y = cos -1 x,请查找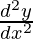 就y而言。
就y而言。
解决方案:
Here, y = cos-1 x
x = cos y
First derivative,
![]()
= – sin y
![]()
= – cosec (y)
Second derivative,
![]()
= ![]()
= – (-cosec(y) cot (y)) ![]()
= – (-cosec(y) cot (y)) (-cosec(y))
= -cosec2(y) cot (y)
Hence we get
![]() = -cosec2(y) cot (y)
= -cosec2(y) cot (y)
问题13。如果y = 3 cos(对数x)+ 4 sin(对数x),则表明x 2 y 2 + xy 1 + y = 0
解决方案:
Here, y = 3 cos (log x) + 4 sin (log x)
First derivative,
y1 = ![]()
= 3 (-sin (log x)) ![]() + 4 (cos (log(x)))
+ 4 (cos (log(x))) ![]()
= ![]() (4 cos (log(x)-3 sin (log x))
(4 cos (log(x)-3 sin (log x))
Second derivative,
y2 = ![]()
= ![]()
Using product rule.
= ![]()
![]()
= ![]() (4(-sin(log(x)))
(4(-sin(log(x)))![]() – 3 (cos(log(x)))
– 3 (cos(log(x)))![]() ) + (4 cos (log(x)-3 sin (log x)) (
) + (4 cos (log(x)-3 sin (log x)) (![]() )
)
= ![]() (-4sin(log(x))
(-4sin(log(x))![]() – 3 cos(log(x))
– 3 cos(log(x))![]() ) – (4 cos (log(x) + 3 sin (log x)) (
) – (4 cos (log(x) + 3 sin (log x)) (![]() )
)
= \frac{-1}{x^2} [-7 cos(log(x) – sin (log x)]
According to the given conditions,
xy1 = x(![]() (4 cos (log(x)-3 sin (log x)))
(4 cos (log(x)-3 sin (log x)))
xy1 = -3 sin (log x)+ 4 cos (log(x))
x2 y2 = x2 ![]()
x2 y2 =[-7 cos(log(x) – sin (log x)]
Now, rearranging
xy1 + x2 y2 + y = -3 sin (log x)+ 4 cos (log(x)) + cos(log(x)) -7 cos(log(x) – sin (log x) + 4 sin (log x)
Hence we get
xy1 + x2 y2 + y = 0
问题14.如果y = Ae mx + Be nx ,则表明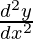 –(m + n)
–(m + n) 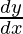 + mny = 0。
+ mny = 0。
解决方案:
Here, y = Aemx + Benx
First derivative,
![]()
= mAemx + nBenx
Second derivative,
![]()
= ![]()
= m2Aemx + n2Benx
According to the given conditions,
![]() – (m+n)
– (m+n) ![]() + mny, we get
+ mny, we get
LHS = m2Aemx + n2Benx – (m+n)(mAemx + nBenx) + mny
= m2Aemx + n2Benx – (m2Aemx + mnAemx + mnBenx + n2Benx) + mny
= -(mnAemx + mnBenx) + mny
= -mny + mny
= 0
Hence we get
![]() + mny = 0
+ mny = 0
问题15.如果y = 500e 7x + 600e – 7x ,则表明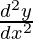 = 49岁。
= 49岁。
解决方案:
Here, y = 500e7x+ 600e– 7x
First derivative,
![]()
= 500e7x . (7)+ 600e– 7x (-7)
= 7(500e7x – 600e– 7x)
Second derivative,
![]()
= ![]()
= 7[500e7x . (7) – 600e– 7x . (-7)]
= 49[500e7x + 600e– 7x]
= 49y
Hence Proved!!
问题16。如果e y (x + 1)= 1,则表明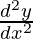 =
= 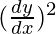
解决方案:
ey (x + 1) = 1
e-y = (x+1)
First derivative,
![]()
-e-y ![]() = 1
= 1
![]()
= ![]()
Second derivative,
![]()
= ![]()
Using division rule,
= 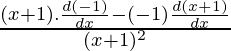
= ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
Hence we can conclude that,
![]()
问题17。如果y =(tan –1 x) 2 ,则证明(x 2 +1) 2 y 2 + 2x(x 2 +1)y 1 = 2
解决方案:
Here, y = (tan–1 x)2
![]()
= 2 . tan–1 x ![]()
(x2 + 1) ![]() = 2 tan–1 x
= 2 tan–1 x
Derivation further,
(x2 + 1)![]() +
+ ![]() (x2 + 1) =
(x2 + 1) = ![]()
(x2 + 1)![]() +
+ ![]() (2x) = 2
(2x) = 2 ![]()
Multiplying (x2 + 1),
(x2 + 1)2![]() +
+ ![]() (2x)(x2 + 1) = 2
(2x)(x2 + 1) = 2
Hence Proved,
(x2+ 1)2 y2+ 2x (x2+ 1) y1= 2