问题8.证明以下内容:
(i)sinθsin(90°–θ)–cosθcos(90°–θ)= 0
解决方案:
We have to prove that sin θ sin (90° – θ) – cosθ cos (90° – θ) = 0
Taking LHS
= sin θ sin (90° – θ) – cosθ cos (90° – θ) -(∵ sin (90° – θ) = cos θ)
= sin θ cosθ – cosθ sinθ
= 0
LHS = RHS
Hence proved
(ii) 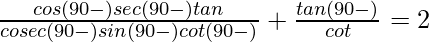
解决方案:
We have to prove that ![]()
Taking LHS
= ![]()
= 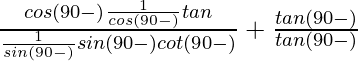
= tan θ/tan θ + cot θ/cot θ
= 1 + 1
= 2
LHS = RHS
Hence Proved
(iii) 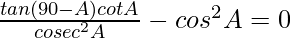
解决方案:
We have to prove that ![]()
Taking LHS
= ![]()
= ![]() -(∵ cot θ = cosθ/sinθ and cosecθ = 1/sinθ)
-(∵ cot θ = cosθ/sinθ and cosecθ = 1/sinθ)
= 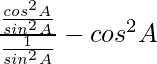
= ![]()
= cos2A – cos2A
= 0
LHS = RHS
Hence Proved
(iv) 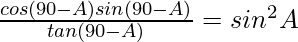
解决方案:
We have to prove that ![]()
Taking LHS
= ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
= sin2A
LHS = RHS
Hence Proved
(v)正弦(50°+θ)–余弦(40°–θ)+棕褐色1°棕褐色10°棕褐色20°棕褐色70°棕褐色80°棕褐色89°= 1
解决方案:
We have to prove that sin (50° + θ) – cos (40° – θ) + tan 1° tan 10° tan 20° tan 70° tan 80° tan 89° = 1
Taking LHS
= sin (50° + θ) – cos (40° – θ) + tan 1° tan 10° tan 20° tan 70° tan 80° tan 89°
= cos(90° – (50° + θ)) – cos (40° – θ) + tan (90° – 89°) tan (90° – 80°) tan (90° – 70°) tan 70° tan 80° tan 89°
= cos (40° – θ) – cos (40° – θ) + cot 89° cot 80° cot 70° tan 70° tan 80° tan 89°
= 0 + 1 = 1
LHS = RHS
Hence Proved
问题9.评估:
(i)2/3(cos 4 30°– sin 4 45°)– 3(sin 2 60°– sec 2 45°)+ 1 / 4cot 2 30°
解决方案:
Given: 2/3(cos430° – sin445°) – 3(sin260° – sec245°) + 1/4cot230°
= ![]()
= ![]()
= 2/3(5/16) – 3(-5/4) + 3/4
= 5/24 + 90/24 + 18/24
= 113/24
Hence, 2/3(cos430° – sin445°) – 3(sin260° – sec245°) + 1/4cot230° = 113/24
(ii)4(正弦4 30°+ cos 4 60°)– 2/3(正弦2 60°– cos 2 45°)+ 1 / 2tan 2 60°
解决方案:
Given: 4(sin430° + cos460°) – 2/3(sin260° – cos245°) + 1/2tan260°
= ![]()
= ![]()
= 4(2/16) – 2/3(1/4) + 3/2
= 1/2 – 1/6 + 3/2
= 4/2 – 1/6
= 2 – 1/6
= (12 – 1)/6
= 11/6
Hence, 4(sin430° + cos460°) – 2/3(sin260° – cos245°) + 1/2tan260° = 11/6
(iii)sin 50°/ cos 40°+ cosec 40°/秒50°– 4cos 50°cosec40°
解决方案:
Given: sin 50°/cos 40° + cosec 40° / sec 50° – 4cos 50° cosec40°
= ![]()
= sin 50°/sin 50° + cosec 40° / cosec 40° – 4cos 50° sec50°
= 1 + 1 – 4
= -2
Hence, sin 50°/cos 40° + cosec 40° / sec 50° – 4cos 50° cosec40° = -2
(iv)tan35°tan40°tan45°tan50°tan55°
解决方案:
Given: tan35°tan40°tan45°tan50°tan55°
= tan(90° – 55°)tan(90° – 50°)tan45°tan50°tan55°
= cot55°cot50°tan45°tan50°tan55°
= (1/tan55°)(1/tan50°)tan45°tan50°tan55°
= 1
Hence, tan35°tan40°tan45°tan50°tan55° = 1
(v)cosec(65°+θ)– sec(25°–θ)– tan(55°–θ)+轻便床(35°+θ)
解决方案:
Given: cosec(65° + θ) – sec(25° – θ) – tan(55° – θ) + cot(35° + θ)
= cosec(65° + θ) – cosec(90° – (25° – θ)) – tan(55° – θ) + tan(90° – (35° + θ))
= cosec(65° + θ) – cosec(90° – 25° + θ) – tan(55° – θ) + tan(90° – 35° – θ)
= cosec(65° + θ) – cosec(65° + θ) – tan(55° – θ) + tan(55° – θ)
= 0
Hence, cosec(65° + θ) – sec(25° – θ) – tan(55° – θ) + cot(35° + θ) = 0
(vi)tan7°tan23°tan60°tan67°tan83°
解决方案:
Given: tan7°tan23°tan60°tan67°tan83°
= tan(90° – 83°)tan(90° – 67°)tan60°tan67°tan83°
= cot83°cot67°tan60°tan67°tan83°
= (1/tan83°)(1/tan67°)tan60°tan67°tan83°
= tan60°
= √3
Hence, tan7°tan23°tan60°tan67°tan83° = √3
(vii) 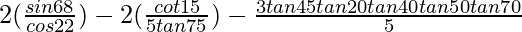
解决方案:
Given: ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
= 2 – 2/5 – 3/5
= (10 – 2 – 3)/5
= 5/5
= 1
Hence, ![]() = 1
= 1
(viii) 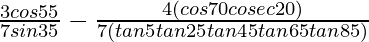
解决方案:
Given: ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
= 3/7 – 4/7
= -1/7
Hence, ![]() = -1/7
= -1/7
(ix)sin18°/ cos72°+√3(tan10°tan30°tan40°tan50°tan80°)
解决方案:
Given: sin18°/cos72° + √3(tan10°tan30°tan40°tan50°tan80°)
= sin18°/cos(90° – 18°) + √3(tan(90° – 80°)tan(90° – 50°)tan30°tan50°tan80°)
= sin18°/sin18° + √3(cot80°cot50°tan30°tan50°tan80°)
= 1 + √3tan30°
= 1 + √3(1/√3)
= 2
Hence, sin18°/cos72° + √3(tan10°tan30°tan40°tan50°tan80°) = 2
(X) 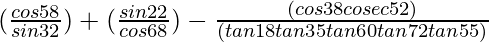
解决方案:
Given: ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
= 1 + 1 – 1/tan60°
= 2 – 1/√3
= (2√3 – 1)/√3
= (6 – √3)/3
Hence, ![]() = (6 – √3)/3
= (6 – √3)/3
问题10。如果sinθ= cos(θ-45°),其中θ和θ-45°是锐角,请找到θ的度数。
解决方案:
Given: sinθ = cos(θ − 45°), where θ and θ−45° are acute angles
= sinθ = cos(θ − 45°) -(∵ sinθ = cos(90 − θ))
= cos(90° − θ) = cos(θ − 45°)
Equating the angles
(90° − θ) = (θ − 45°)
2θ = 90° + 45° = 135°
θ = 135°/2
θ = 67![]() °
°
问题11:如果A,B,C是三角形ABC的内角,则表明
(i)罪(B + C)/ 2 = cos A / 2
解决方案:
According to question
In a triangle ABC, A, B, C are the interior angles
So, the sum of interior angles = A + B + C = 180°
B +C = 180° – A
We have
sin (B + C)/2 = cos A/2
Taking LHS
sin (B + C)/2 -(1)
Putting the value of B + C in equation(1)
= sin (180° – A)/2
= sin (90° – A/2)
= cos A/2
LHS = RHS
Hence Proved
(ii)cos(B + C)/ 2 =正弦A / 2
解决方案:
According to question
In a triangle ABC, A, B, C are the interior angles
So, the sum of interior angles = A + B + C = 180°
B + C = 180° – A
We have
cos (B + C)/2 = sin A/2
Taking LHS
cos (B + C)/2 -(1)
Putting the value of B + C in equation(1)
= cos (180° – A)/2
= cos (90° – A/2)
= sin A/2
LHS = RHS
Hence Proved
问题12.如果2θ+ 45°和30°-θ是锐角,则求出满足sin(2θ+ 45°)= cos(30°-θ)的θ的度数度量。
解决方案:
Given: 2θ + 45° and (30° − θ) are acute and sin(2θ + 45°) = cos(30° − θ)
We have,
sin(2θ + 45°) = cos(30° − θ)
sin(2θ + 45°) = sin(90° − (30° − θ)) -(∵ cosθ = sin(90° − θ))
sin(2θ + 45°) = sin(60° + θ)
Now equating the angles
2θ + 45° = 60° + θ
2θ − θ = 60° − 45°
θ = 15°
问题13.如果θ是正锐角使得secθ= cosec60°,发现2COS 2θ的值- 1。
解决方案:
Given, θ is acute and secθ = cosec60°
Find the value of 2cos2θ − 1 -(1)
cosec60° = 2/√3
or secθ = 2/√3
We know that, sec30° = 2/√3
secθ = sec30°
θ = 30°
Putting the value of θ in eq(1), we get
= 2cos230° − 1
= 2(√3/2)2 − 1
= 2(3/4) − 1
= 3/2 − 1
= 1/2
Hence, the value of 2cos2θ − 1 = 1/2
问题14.如果cos2θ=sin4θ,其中2θ和4θ是锐角,则找到θ的值。
解决方案:
Given: 2θ and 4θ are acute and cos2θ = sin4θ
So, we have,
cos2θ = sin(90° − 2θ) -(∵ sin (90° – θ) = cos θ)
Now, sin(90° − 2θ) = sin4θ
Equating the angles
90° − 2θ = 4θ
90° = 2θ + 4θ
6θ = 90°
θ = 15°
Hence, the value of θ = 15°
问题15。如果sin3θ= cos(θ-6°),其中3θ和θ-6°为锐角,则求出θ的值。
解决方案:
Given: 3θ and (θ − 6°) are acute and sin3θ = cos(θ − 6°)
So, we have,
cos(θ − 6°) = sin(90° − (θ − 6°)) = sin(96° − θ). -(∵ cosθ = sin(90° − θ))
Now, sin3θ = sin(96° − θ)
Equating the angles
3θ = 96° − θ
3θ + θ = 96°
4θ = 96°
θ = 96°/4
θ = 24°
Hence, the value of θ = 24°
问题16。如果sec4A = cosec(A – 20°),其中4A是锐角,则求出A的值。
解决方案:
Given: 4A is acute and sec4A = cosec(A − 20°)
So, we have,
sec4A = cosec(90° − 4A) -(∵ secθ = cosec(90° − θ))
Now, cosec(90° − 4A) = cosec(A − 20°)
Equating the angles
(90° − 4A) = (A − 20°)
110° = 5A
5A = 110°
A = 110°/5
A = 22°
Hence, the value of A = 22°
问题17。如果sec2A = cosec(A – 42°),其中2A是锐角,则求出A的值。
解决方案:
Given: 2A is acute and sec2A = cosec(A − 42°)
So, we have,
sec2A = cosec(90° − 2A) -(∵ secθ = cosec(90° − θ))
Now, cosec(90° − 2A) = cosec(A − 42°)
Equating the angles
(90° − 2A) = (A − 42°)
132° = 3A
3A = 132°
A = 132°/3
A = 44°
Hence, the value of A = 44°