评估以下积分:
问题1.∫(logx)/ x dx
解决方案:
Given that, I = ∫(logx)/x dx
Let us considered logx = t
Now differentiating both side we get,
d(logx) = dt
1/x dx = dt
dx = xdt
Then, put logx = t and dx = xdt, we get
I = ∫ t/x × (x)dt
= ∫ tdt
= t2/2 + c
= (logx)2/2 + c
Hence, I = (logx)2/2 + c
问题2.∫(log(1 + 1 / x))/(x(1 + x))dx
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫(log(1 + 1/x))/(x(1 + x)) dx ……(i)
Let us considered log(1 + 1/x) = t then
On differentiating both side we get,
d[log(1 + 1/x)]=dt
1/(1 + 1/x) × (-1)/x2dx = dt
1/((x + 1)/x) × (-1)/x2dx = dt
(-x)/(x2 (x + 1)) dx = -dt
dx/(x(x + 1)) = -dt
Now, on putting log(1 + 1/x) = t and dx/(x(x + 1)) = -dt in equation (i), we get
I = ∫t × -dt
= -t2/2 + c
= -1/2 [log(1 + 1/x)]2 + c
Hence, I = -1/2 [log(1 + 1/x)]2 + c
问题3.∫(((1 +√x) 2 )/√xdx
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫((1 + √x)2)/√x dx
Let us considered (1 + √x) = t then,
On differentiating both side we get,
d(1 + √x) = dt
1/(2√x) dx = dt
dx = dt × 2√x
Now on putting (1 + √x) = t and dx = dt × 2√x, we get
I = ∫t2/√x × dt × 2√x
= 2∫t2dt
= 2 × t3/3 + c
= 2/3[1 + √x]3 + c
Hence, I = 2/3(1 + √x)3 + c
问题4.∫√(1 + e x )e x d
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫√(1 + ex) ex dx ……(i)
Let us considered 1 + ex = t then,
On differentiating both side we get,
d(1 + ex) = dt
ex dx = dt
dx = dt/ex
Now on putting 1 + ex = t and dx = dt/ex in equation (i), we get
I = ∫√t × ex × dt/ex
= ∫ t1/2 dt
= 2/3t3/2 + c
= 2/3 (1 + ex)3/2+c
问题5.∫∛(cos 2 x)sinxdx
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫∛(cos2x) sinx dx ……(i)
Let us considered cosx = t then,
On differentiating both side we get,
d(cosx) = dt
-sinxdx = dt
dx = -dt/(sinx))
Now on putting cosx = t and dx = -dt/(sinx) in equation (i), we get
I = ∫∛(t2) sinx × (-dt)/(sinx)
= -∫t2/3 sinx dt/(sinx)
= -∫ t2/3 dt
= -3/5 × t5/3
Hence, I = -3/5(cosx)5/3 + c
问题6.∫E的x /(1 + E X)2 DX
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫ex/(1 + ex)2 dx …….(i)
Let us considered 1 + ex = t then,
On differentiating both side we get,
d(1 + ex) = dt
ex dx = dt
dx = dt/ex
Now on putting 1 + ex = t and dx = dt/ex in equation (i), we get
I = ∫ex/t2 × dt/ex
= ∫dt/t2
= ∫t-2 dt
= -t-1 + c
= -1/t + c
= -1/(1 + ex) + c
Hence, I = -1/(1 + ex) + c
问题7.∫cot3x余割2xDX
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫cot3x cosec2x dx …….(i)
Let us considered cotx = t then,
On differentiating both side we get,
d(cotx) = dt
-cosec2x dx = dt
dx = -dt/cosec2x
Now on putting cotx = t and dx = -dt/(cosec2x) in equation (i), we get
I = ∫ t3 cosec2x × (-dt)/(cosec2x)
= -∫ t3 dt
= -t4/4 + c
= -(cot4x)/4 + c
Hence, I = -(cot4x)/4 + c
问题8。 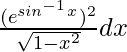
解决方案:
Given that I =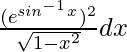 [Tex] [/Tex] …….(i)
[Tex] [/Tex] …….(i)
Let us considered sin-1x = t then,
On differentiating both side we get,
d(sin-1x) = dt
1/√(1 – x2)dx = dt
dx = √(1 – x2) dt)
Now on putting sin-1x = t and dx = √(1 – x2) dt in equation (i), we get
I = ∫ (et)2/√(1 – x2) × √(1 – x2) dt
= ∫e2t dt
= e2t/2 + c
= ![]() + c
+ c
Hence, I = ![]() + c
+ c
问题9.∫(1 +sinx)/√(x-cosx)dx
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫(1 + sinx)/√(x – cosx) dx ……..(i)
Let us considered x – cosx = t, then
On differentiating both side we get,
d(x – cosx) = dt
[1 – (-sinx)]dx = dt
(1 + sinx)dx = dt
Now on putting x – cosx = t and (1 + sinx)dx = dt in equation (i), we get
I = ∫ dt/√t
= ∫ t-1/2 dt
= 2t1/2 + c
= 2(x – cosx)1/2 + c
Hence, I = 2√(x – cosx) + c
问题10。∫1/(√(1 – x 2 )(sin -1 x) 2 )dx
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫1/(√(1 – x2) (sin-1x)2) dx …..(i)
Let us considered sin-1x = t then,
On differentiating both side we get,
d(sin-1x) = dt
1/√(1 – x2 ) dx = dt
Now on putting sin-1x = t and 1/√(1 – x2) dx = dt in equation (i), we get
I = ∫dt/t2
= ∫t-2 dt
= -t-1 + c
= (-1)/t + c
= (-1)/(sin-1x) + c
Hence, I = (-1)/(sin-1x) + c
问题11.∫(cotx)/√(sinx)dx
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫(cotx)/√(sinx) dx …….(i)
Let us considered sinx = t then,
On differentiating both side we get,
d(sinx) = dt
cosxdx = dt
Now, I = ∫(cotx)/√(sinx) dx
= ∫(cosx)/(sinx√(sinx)) dx
= ∫ cosx/(sinx)3/2dx
= ∫ cosx/(sinx)3/2 dx …….(ii)
Now on putting sinx = t and cosxdx = dt in equation (ii), we get
I = ∫ dt/t3/2
= ∫ t-3/2 dt
= -2t-1/2 + c
= -2/√t + c
= -2/√(sinx) + c
I = -2/√sinx + c
问题12.∫(tanx)/√(cosx)dx
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫(tanx)/√(cosx) dx
I = ∫sinx/cosx√(cosx) dx
= ∫ sinx/(cosx)3/2 dx
= ∫sinx/(cosx)3/2 dx ……..(i)
Let us considered cosx = t then,
On differentiating both side we get,
d(cosx) = dt
-sinxdx = dt
sinxdx = -dt
Now on putting cosx = t and sinxdx = -dt in equation (i), we get
I = ∫(-dt)/t-3/2
= -∫t-3/2 dt
= -[-2t-1/2] + c
= 2/t1/2 + c
= 2/√(cosx) + c)
Hence, I = 2/√(cosx) + c
问题13∫cos3×/√(sinx)DX
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫cos3x/√(sinx) dx
= ∫(cos2xcosx)/√(sinx) dx
= ∫((1 – sin2x)cosx)/√(sinx) dx
= ∫((1 – sin2x))/√(sinx) cosxdx ……(i)
Let us considered sinx = t then,
On differentiating both side we get,
d(sinx) = dt
cosxdx = dt
Now on putting sinx = t and cosxdx = dt in equation (i), we get
I = ∫(1 – t2)/√t dt
= ∫(t-1/2-t2 x t-1/2)dt
=∫(t-1/2 – t3/2)dt
= 2t1/2 – 2/5 t5/2 + c
= 2(sinx)1/2 – 2/5(sinx)5/2 + c
Hence, I = 2√(sinx) – 2/5(sinx)5/2 + c
问题14.∫(sin 3 x)/√(cosx)dx
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫(sin3x)/√(cosx) dx
= ∫(sin2xsinx)/√(cosx) dx
=∫((1 – cos2x))/√(cosx) sinxdx …….(i)
Let us considered cosx = t then,
On differentiating both side we get,
d(cosx) = dt
-sinxdx = dt
sinxdx = -dt
Now on putting cosx = t and sinxdx = -dt in equation (i), we get
I = ∫((1 – t2))/√t × -dt
= ∫(t2 – 1)/√t dt
= ∫(t2/t1/2 – 1/t1/2)dx
= ∫(t2-1/2 – t-1/2)dt
= ∫(t3/2 – t1/2)dt
= 2/5 t5/2 – 2t1/2 + c
= 2/5 cos5/2x – 2cos1/2x + c
Hence, I = 2/5 cos5/2x – 2√(cosx) + c
问题15.∫1/(√(tan -1 x)(1 + x 2 ))dx
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫1/(√(tan-1x) (1 + x2)) dx …..(i)
Let us considered tan-1x = t, then
On differentiating both side we get,
d(tan-1x) = dt
1/(1 + x2) dx = dt
Now on putting tan-1x = t and 1/(1 + x2) dx = dt in equation (i), we get
I = ∫1/√t dt
= ∫t-1/2 dt
= 2t1/2 + c
= 2√tan-1x + c
Hence, I = 2√tan-1x + c
问题16.∫√(tanx)/(sinxcosx)dx
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫√(tanx)/(sinxcosx) dx
= ∫(√(tanx)×cosx)/(sinxcosx×cosx) dx
= ∫√(tanx)/(tanxcos2x) dx
= ∫(sec2xdx)/√(tanx) dx
Let us considered tanx = t, then
On differentiating both side we get,
sec2xdx = dt
Now
I = ∫ dt/√t
= 2√t + c
Hence, I = 2√tanx + c
问题17.1 / x×(logx) 2 dx
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫1/x × (logx)2 dx …..(i)
Let us considered logx = t then,
On differentiating both side we get,
d(logx) = dt
1/x dx = dt
Now on putting logx = t and 1/x dx = dt in equation (i), we get
I = ∫t2 dt
= t3/3 + c
= (logx)3/3 + c
Hence, I = (logx)3/3 + c
问题18∫sin5×cosxDX
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫sin5x cosx dx ……(i)
Let us considered sinx = t then,
On differentiating both side we get,
d(sinx) = dt
cosxdx = dt
Now on putting sinx = t and cosxdx = dt in equation (i), we get
I = ∫ t5 dt
= t6/6 + c
= (sin6x)/6 + c
Hencec, I = 1/6 (sin6x) + c
问题19∫tan3/2x秒2xDX
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫tan3/2xsec2xdx ……(i)
Let us considered tanx = t then,
On differentiating both side we get,
d(tanx) = dt
sec2xdx = dt
Now on putting tanx = t and sec2xdx = dt in equation (i), we get
I = ∫ t3/2 dt
= 2/5 t5/2 + c
= 2/5(tanx)5/2 + c
Hence, I = 2/5 tan5/2x + c
问题20.∫(x 3 )/(x 2 +1) 2 dx
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫(x3)/(x2 + 1)2dx …….(i)
Let us considered 1 + x2 = t then,
On differentiating both side we get,
d(1 + x2) = dt
2xdx = dt
xdx = dt/2
Now on putting 1 + x2 = t and xdx = dt/2 in equation (i),we get
I = ∫x2/t3 × dt/2
= 1/2∫(t – 1)/t3 dt [1 + x2 = t]
= 1/2∫[(t/t3 – 1/t3)dt]
= 1/2∫(t-2 – t-3)dt
= 1/2 [-1t-1 – t-2/(-2)] + c
= 1/2 [-1/t + 1/(2t2)] + c
= -1/2t + 1/(4t2) + c
= -1/2(1 + x2) + 1/(4(1 + x2)2) + c
= (-2(1 + x2) + 1)/(4(1 + x2)2) + c
= (-2 – 2x2 + 1)/(4(1 + x2)2) + c
= (-2x2 – 1)/(4(1 + x2)2) + c
= -(1 + 2x2 )/(4(x2 + 1)2) + c
Henec, I = -(1 + 2x2)/(4(x2 + 1)2) + c
问题21.∫(4x + 2)√(x 2 + x + 1)dx
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫(4x + 2)√(x2 + x + 1) dx
Let us considered x2 + x + 1 = t then,
On differentiating both side we get,
(2x + 1)dx = dt
Now,
I = ∫ (4x + 2)√(x2 + x + 1) dx
= ∫2√t dt
= 2∫√t dt
= 2t3/2/(3/2) + c
Hence, I = 4/3 (x2 + x + 1)3/2 + c
问题22.∫(4x + 3)/√(2x 2 + 3x + 1)dx
解决方案:
Given that l = ∫(4x + 3)/√(2x2 + 3x + 1) dx ……(i)
Let us considered 2x2 + 3x + 1 = t then,
On differentiating both side we get,
d(2x2 + 3x + 1) = dt
(4x + 3)dx = dt
Now on putting 2x2 + 3x + 1 = t and (4x + 3)dx = dt in equation (i), we get
I = ∫dt/√t
= ∫t-1/2 dt
= 2t1/2 + c
= 2√t + c
Hence, I = 2√(2x2 + 3x + 1) + c
问题23.∫1/(1 +√x)dx
解决方案:
Given that I = ∫1/(1 + √x) dx …….(i)
Let us considered x = t2 then,
On differentiating both side we get,
dx = d(t2)
dx = 2tdt
Now on putting x = t2 and dx = 2tdt in equation (i), we get
I = ∫2t/(1 + √(t2)) dt
= ∫2t/(1 + t) dt
= 2∫t/(1 + t) dt
= 2∫(1 + t – 1)/(1 + t) dt
= 2⌋[(1 + t)/(1 + t) – 1/(1 + t)]dt
= 2∫dt – 2∫1/(1 + t) dt
= 2t – 2log|(1 + t)| + c
= 2√x – 2log|(1 + √x)| + c
Hence, I = 2√x – 2log|(1 + √x)| + c
问题24。 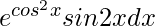
解决方案:
Given that I = ![]() …….(i)
…….(i)
Let us considered cos2x = t then,
On differentiating both side we get,
d(cos2x) = dt
-2cosx sinx dx = dt
-sin2x dx = dt
sin2x dx = -dt
Now on putting cos2x = t and sin2x dx = -dt in equation (i), we get
I = ∫et(-dt)
= -et + c
= –![]() + c
+ c
Hence, I = –![]() + c
+ c