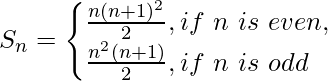第 11 课 RD Sharma 解决方案 - 第 12 章数学归纳 - 练习 12.2 |设置 3
问题 33. 证明 n 11 /11 + n 5 /5 + n 3 /3 – 62/165n 对于所有 n ∈ N 都是正确的。
解决方案:
Let, P(n) = n11/11 + n5/5 + n3/3 – 62/165n
Step 1:
Now, let us check P(n) for n = 1.
So, P(1) = 1/11 + 1/5 + 1/3 – 62/165 = 1
So, P(1) is true.
Step 2:
Let us consider P (n) be the true for n = m,
Let, P(m) = m11/11 + m5/5 + m3/3 – 62/165m
So, m11/11 + m5/5 + m3/3 – 62/165m = λ, where λ ∈ N is a positive integer.
Step 3:
Now, we have to prove for P(m + 1) is true.
P(m + 1) = (m + 1)11/11 + (m + 1)5/5 + (m + 1)3/3 – 62/165(m + 1)
= 1/11(m11 + 11m10 + 55m9 + 165m8 + 330m7 + 462m6 + 462m5 + 330m4 +
165m3 + 55m2 + 11m + 1) + 1/5(m5 + 5m4 + 10m3 + 10m2 + 5m + 1) +
1/3(m3 + 3m2 + 3m + 1) + 62/165(m + 1)
= λ + m6 + 3m5 + 5m4 + 5m3 + 3m2 + m + m4 + 2m3 + 2m2 + m + m2 + m + m + 1
As λ is positive, so it is a positive integer.
So, P (n) is true for n = m + 1
i.e., P (n) is true for all n ∈ N
Hence, by principle of Mathematical Induction (PMI), P (n) is true for all n ∈ N.
问题 34. 证明 (1/2)tan(x/2) + (1/4)tan(x/4) +…..+ (1/2 n )tan(x/2 n ) = (1/ 2 n )cot(x/2 n ) – 所有 n ∈ N 和 0< x < π/2 的 cotx。
解决方案:
Let, P(n) = (1/2)tan(x/2) + (1/4)tan(x/4) +…..+ (1/2n)tan(x/2n) = (1/2n)cot(x/2n) – cotx, for all n ∈ N and 0< x < π/2.
Step 1:
Now, let us check P(n) for n = 1.
LHS = 1/2 tan(x/2)
RHS = (1/2)cot(x/2) – cot(x) = 1/(2tan(x/2)) – 1 tan(x)
= 1/(2tan(x/2)) – 1/(2tan(x/2))/(1 – tan2(x/2))
= 1/(2tan(x/2)) – (1 – tan2(x/2))/(2tan(x/2))
=(1/2)tan(x/2)
So, P(1) is true.
Step 2:
Let us consider P (n) be the true for n = m,
P(m) = (1/2)tan(x/2) + (1/4)tan(x/4) +…..+ (1/2m)tan(x/2m) = (1/2m)cot(x/2m) – cotx
Step 3:
Now, we have to prove for P(m + 1) is true.
P(m + 1) = (1/2)tan(x/2) + (1/4)tan(x/4) +…..+ (1/2m)tan(x/2m) + (1/2(m + 1))tan(x/2(m + 1)) = (1/2(m + 1))cot(x/2(m + 1)) – cotx
So, = (1/2m)cot(x/2m) – cotx + (1/2(m+1))cot(x/2(m+1))
= (1/2m)cot (x/2m) + (1/2(m+1))tan(x/2(m+1)) – cotx
= 1/(2mtan(2x/2(m+1)) + (1/2(m+1))tan(x/2(m+1)) – cotx
= [(1 – tan2(x/2(m+1)))/2(m+1).tan(x/2(m+1))] + (1/2(m+1))tan(x/2(m+1)) – cotx
= (1/2(m+1))cot(x/2(m+1)) – cotx
Now,
(1/2)tan(x/2) + (1/4)tan(x/4)+…..+ (1/2m)tan(x/2m) + (1/2(m+1))tan(x/2(m+1)) = (1/2(m+1))cot(x/2(m+1)) – cotx
So, P (n) is true for n = m + 1
i.e., P (n) is true for all n ∈ N
Hence, by principle of Mathematical Induction (PMI), P (n) is true for all n ∈ N.
问题 35. 证明 (1 – 1/2 2 )(1 – 1/3 2 )(1 – 1/4 2 )……(1 – 1/n 2 ) = (n + 1)/2n 对于所有 n ∈ N。
解决方案:
Let, P(n) = (1 – 1/22)(1 – 1/32)(1 – 1/42)……(1 – 1/n2) = (n + 1)/2n
Step 1:
Now, let us check P(n) for n = 2.
P(2) = 1 – 1/22 = (2 + 1)/2.2
or, 3/4 = 3/4
So, P(2) is true.
Step 2:
Let us consider P (n) be the true for n = k, So, P(k) is
P(k) = (1 – 1/22)(1 – 1/32)(1 – 1/42)……(1 – 1/k2) = (k + 1)/2k
Step 3:
Now, we have to prove for P(k + 1) is true. i.e.
P(k + 1) = (1 – 1/22)(1 – 1/32)(1 – 1/42)……(1 – 1/(k + 1)2) = (k + 2)/2k
Now, (1 – 1/22)(1 – 1/32)(1 – 1/42)……(1 – 1/k2)(1 – 1/(k + 1)2)
Now, from step 2, we get
So, (1 – 1/(k + 1)2)((k + 1)/2k)
or, ((k + 1)/2k)((k2 + 1 + 2k – 1)/(k + 1)2)
or, k(k + 2)/2k(k + 1)
or, (k + 2)/2(k + 1)
So, P (n) is true for n = k + 1
i.e., P (n) is true for all n ∈ N
Hence, by principle of Mathematical Induction (PMI), P (n) is true for all n ∈ N.
问题 36. 证明 (2n)!/2 2n (n!) 2 ≤ 1/√(3n + 1) 对所有 n ∈ N 成立。
解决方案:
Let, P(n) = (2n)!/22n(n!)2 ≤ 1/√(3n + 1)
Step 1:
Now, let us check P(n) for n = 1.
P(1) = 1/2 ≤ 1/√3 + 1 = 1/2
So, P(1) is true.
Step 2:
Let us consider P (n) be the true for n = m.
P(m) = (2m)!/22m(m!)2 ≤ 1/√(3m + 1)
Step 3:
Now, we have to prove for P(m + 1) is true. i.e.
P(m + 1) = (2m + 2)!/22m+2(m!)2 ≤ 1/√(3m + 4)
Now,
P(m + 1) = ((2m + 1)(2m + 1)(2m)!)/(2m2.22(m + 1)2(m!)2)
or, (2m + 2)!/2{2m + 2}((m + 1)!)2 = ((2m)!/22m) × (2m + 1)(m + 2)/22(m + 1)2
or, (2m + 2)!/2{2m + 2}((m + 1)!)2 ≤ (2m + 1)/2(m + 1)√(3m + 1)
or, (2m + 2)!/2{2m + 2}((m + 1)!)2 ≤ √((2m + 1)2/4(m + 1)2(3m + 1))
(2m + 2)!/2{2m + 2}((m + 1)!)2 ≤ √((2m + 1)2/4(m + 1)2(3m + 1))
or, (2m + 2)!/2{2m + 2}((m + 1)!)2 ≤ √(12m3 + 28m2 + 19m + 4)/(12m3 + 28m2 + 20m + 4)(3m + 4)
now, (12m3 + 28m2 + 19m + 4)/(12m3 + 28m2 + 20m + 4) < 1
so, (2m + 2)!/2{2m + 2}((m + 1)!)2 ≤ 1/√(3m + 4)
So, P (n) is true for n = m + 1
i.e., P (n) is true for all n ∈ N
Hence, by principle of Mathematical Induction (PMI), P (n) is true for all n ∈ N.
问题 37. 证明 1 + 1/4 + 1/9 + 1/16 + .....+ 1/n 2 < 2 – 1/n 对于所有 n > 2,n ∈ N。
解决方案:
Let P(n) = 1 + 1/4 + 1/9 + 1/16 + …..+ 1/n2 < 2 – 1/n for all n > 2, n ∈ N
Step 1:
Now, let us check P(n) for n = 2.
P(2) = 1/22 < 2 – 1/2
So, P(1) is true.
Step 2:
Let us consider P (n) be the true for n = m.
P(m) = 1 + 1/4 + 1/9 + 1/16 +…..+ 1/m2 < 2 – 1/m
Step 3:
Now, we have to prove for P(m + 1) is true. i.e.,
From step 2 we have, 1 + 1/4 + 1/9 + 1/16 +…..+ 1/m2 < 2 – 1/m
Now, adding 1/(m + 1)2 to both the sides, we get
= 1 + 1/4 + 1/9 + 1/16 +…..+ 1/m2 + 1/(m + 1)2 < 2 – 1/m + 1/(m + 1)2
or, (m + 1)2 > m + 1
or, 1/(m + 1)2 < 1/(m + 1)
or, 1/m – 1/(m + 1)2 < 1/(m + 1)
So, P(m + 1) < 2 – 1/(m + 1)
So, P (n) is true for n = m + 1
i.e., P (n) is true for all n ∈ N
Hence, by principle of Mathematical Induction (PMI), P (n) is true for all n ∈ N.
问题 38. 证明 x 2n-1 + y 2n-1可以被 x + y 整除。
解决方案:
Let, P(n) be x2n-1 + y2n-1
Step 1:
Now, let us check P(n) for n = 1.
P(1) = x + y
So, P(1) is divisible by x + y.
So, P(1) is true.
Step 2:
Let us consider P (n) be the true for n = m.
P(m) = x2m-1 + y2m-1= λ(x + y) ……….. (i)
Step 3:
Now, we have to prove for P(m + 1) is true.
i.e. , P(m + 1) = x2m+1 + y2m+1
= x2m+1 + y2m+1 – x2m-1. y2 + x2m-1 . y2
= x2m-1(x2 – y2) + y2(x2m-1+y2m-1)
= (x + y)(x2m-1 (x – y) + λy2)
So, P (n) is true for n = m + 1
i.e., P (n) is true for all n ∈ N
Hence, by principle of Mathematical Induction (PMI), P (n) is true for all n ∈ N.
问题 39. 证明 sinx + sin3x + …+ sin(2n – 1)x = sin 2 nx/sinx 对于所有 n ∈ N 都是正确的。
解决方案:
Let, P(n) = sinx + sin3x + …+ sin(2n – 1)x = sin2nx/sinx
Step 1:
Now, let us check P(n) for n = 1.
P(1) = sin x = sin2 x / sin x = sin x
So, P(1) is true.
Step 2:
Let us consider P (n) be the true for n = m.
P(m) = sinx + sin3x + …+ sin(2m – 1)x = sin2mx/sinx
Step 3:
Now, we have to prove for P(m + 1) is true.
i.e.,
P(m + 1) = sinx + sin3x +…+ sin(2m – 1)x + sin(2m + 1)x = (sin2mx/sinx) + sin(2m+1)x
now,
P(m + 1) = {(sin2mx + sinx[sin(mx) + cos(m + 1)x + sin(m + 1)x + cos(mx)])}/sinx
= {(sin2mx + 2sinx.cosx.cos(mx) – sin2x.sin2mx + cos2mx.sin2x)}/sinx
= {(sin2mx(1 – sin2x) + 2sinx.cosx.cos(mx) + cos2mx.sin2x)}/sinx
= {(sin2mx.cos2x + 2sinx.cosx.cos(mx) + cos2mx.sin2x)}/sinx
= {(sin(mx).cosx + cos(mx).sinx)2}/sinx
= {(sin(m + 1)x)2}/sinx
So, P (n) is true for n = m + 1
i.e., P (n) is true for all n ∈ N
Hence, by principle of Mathematical Induction (PMI), P (n) is true for all n ∈ N.
问题 40. 证明![由 QuickLaTeX.com 渲染 cosα + cos(α +β) +cos(α +2β)+....+cos(α +(n-1)β)=\frac{(cos[α +(\frac{n-1}{2})β] sin(\frac{nβ}{2}))}{sin(\frac{β}{2})}](https://mangodoc.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/geek8geeks/Class_11_RD_Sharma_Solutions_%E2%80%93_Chapter_12_Mathematical_Induction_%E2%80%93_Exercise_12.2_%7C_Set_3_0.jpg) 对所有 n ∈ N 都成立。
对所有 n ∈ N 都成立。
解决方案:
Let, P(n) = ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com cosα + cos(α +β) +cos(α +2β)+....+cos(α +(n-1)β)=\frac{(cos[α +(\frac{n-1}{2})β] sin(\frac{nβ}{2}))}{sin(\frac{β}{2})}](https://mangodoc.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/geek8geeks/Class_11_RD_Sharma_Solutions_%E2%80%93_Chapter_12_Mathematical_Induction_%E2%80%93_Exercise_12.2_%7C_Set_3_1.jpg)
Step 1:
Now, let us check P(n) for n = 1.
L.H.S = cos [α + (1 – 1)β] = cos α
R.H.S =![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{(cos[α +(\frac{1-1}{2})β] sin(\frac{β}{2}))}{sin(\frac{β}{2})} = cosα](https://mangodoc.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/geek8geeks/Class_11_RD_Sharma_Solutions_%E2%80%93_Chapter_12_Mathematical_Induction_%E2%80%93_Exercise_12.2_%7C_Set_3_2.jpg)
So, P(1) is true as LHS and RHS are equal.
Step 2:
Let us consider P (n) be the true for n = k.
P(k) = ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com cosα + cos(α +β) +cos(α +2β)+....+cos(α +(k-1)β)=\frac{(cos[α +(\frac{k-1}{2})β] sin(\frac{kβ}{2}))}{sin(\frac{β}{2})}](https://mangodoc.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/geek8geeks/Class_11_RD_Sharma_Solutions_%E2%80%93_Chapter_12_Mathematical_Induction_%E2%80%93_Exercise_12.2_%7C_Set_3_3.jpg)
Step 3:
Now, we have to prove for P(k + 1) is true.
So, adding cos(α + kβ) both sides of P(k), we get
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com P(k+1)= cosα + cos(α +β) +cos(α +2β)+....+cos(α +(k-1)β) +cos(α +kβ)=\frac{(cos[α +(\frac{k-1}{2})β] sin(\frac{kβ}{2}))}{sin(\frac{β}{2})}+cos(α +kβ)](https://mangodoc.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/geek8geeks/Class_11_RD_Sharma_Solutions_%E2%80%93_Chapter_12_Mathematical_Induction_%E2%80%93_Exercise_12.2_%7C_Set_3_4.jpg)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com =\frac{(cos[α +(\frac{k-1}{2})β] sin(\frac{kβ}{2})+cos(α +kβ)sin(\frac{β}{2})}{sin(\frac{β}{2})}](https://mangodoc.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/geek8geeks/Class_11_RD_Sharma_Solutions_%E2%80%93_Chapter_12_Mathematical_Induction_%E2%80%93_Exercise_12.2_%7C_Set_3_5.jpg)
![]()
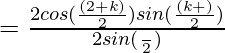
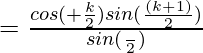
Now,
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com RHS= \frac{(cos[α +(\frac{kβ}{2})] sin(\frac{(k+1)β}{2}))}{sin(\frac{β}{2})}](https://mangodoc.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/geek8geeks/Class_11_RD_Sharma_Solutions_%E2%80%93_Chapter_12_Mathematical_Induction_%E2%80%93_Exercise_12.2_%7C_Set_3_9.jpg)
So, P (n) is true for n = k + 1
i.e., P (n) is true for all n ∈ N
Hence, by principle of Mathematical Induction (PMI), P (n) is true for all n ∈ N.
问题 41. 证明 1/(n+1) + 1/(n+2) +…..+ 1/2n > 13/24 对于所有自然数,n > 1。
解决方案:-
Let,P(n) = 1/(n+1) + 1/(n+2) +…..+ 1/2n > 13/24
Step 1:
Now, let us check P(n) for n = 2.
P(2) = 1/(2 + 1) + 1/(2 + 2) = 1/3 + 1/4 = 7/12 > 13/24
So, P(2) is true.
Step 2:
Let us consider P (n) be the true for n = k, So, P(k) is
P(k) = 1/(k + 1) + 1/(k + 2) +…..+ 1/2k > 13/24
Step 3:
Now, we have to prove for P(k + 1) is true. When P(k) is true.
So, P(k + 1) = 1/(k + 2) + 1/(k + 3) +…..+ 1/2k + 1/2(k + 1)
Here, as LHS = RHS
So, P (n) is true for n = k + 1
i.e., P (n) is true for all n ∈ N
Hence, by principle of Mathematical Induction (PMI), P (n) is true for all n ∈ N.
问题 42. 给定 a 1 = 1/2(a 0 + A/a 0 ),a 2 = 1/2(a 1 + A/a 1 ) 和 a n+1 = 1/2(a n + A/ a n ), a, A > 0
证明: 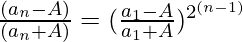
解决方案:
Let, P(n) = ![]()
Step 1:
Now, let us check P(n) for n=1.
LHS = (a1 – √A) / (a1 + √A)
RHS = ![]()
= (a1 – √A) / (a1 + √A)
So, P(1) is true.
Step 2:
Let us consider P (n) be the true for n = k, So, P(k) is
So, P(k) = ![]()
Step 3:
Now, we have to prove for P(k + 1) is true. When P(k) is true.
So, P(k + 1) = LHS = (ak+1 – √A) / (ak+1 + √A)
= (1/2(ak + A/ak) – √A) / (1/2(ak + A/ak) + √A)
= (1/2(ak2+ A – 2ak√A)/ak ) / (1/2(ak2+ A + 2ak√A)/ak )
= (ak+1 – √A)2 / (ak+1 + √A)2
= ![]()
= ![]()
here, as LHS = RHS
So, P (n) is true for n = k + 1
i.e., P (n) is true for all n ∈ N
Hence, by principle of Mathematical Induction (PMI), P (n) is true for all n ∈ N.
问题 43. 设 P(n) 为陈述:2 n ≥ 3n。如果 P(r) 为真,则证明 P(r + 1) 为真,你是否得出结论 P(n) 对所有 n ∈ N 都为真?
解决方案:
Let P(n) = 2n ≥ 3n
Step 1:
Now, let us check P(n) for n = 1.
L.H.S = 2
R.H.S = 3
As L.H.S < R.H.S
So, P(1) is true.
Step 2:
Let us consider P (n) be the true for n = r, So, P(r) is 2r ≥ 3r
Step 3:
Now, we have to prove for P(k + 1) is true. When P(k) is true.
So, P(k + 1) = 2r+1 = 2.2r
For, x > 3, 2x > x + 3
So, 2.2r > 2r+3 for r > 1
or,2r+1 > 2r+3 for r > 1
or, 2r+1 > 3r +3 for r > 1
or, 2r+1 > 3(r + 1) for r >1
So, P (n) is true for n = r + 1
i.e., P (n) is true for all n ∈ N
Hence, by principle of Mathematical Induction (PMI), P (n) is true for all n ∈ N.
问题 44. 用数学归纳法证明级数 1 2 + 2 × 2 2 + 3 2 + 2 × 4 2 + 5 2 + 2 × 6 2 + 7 2 +… 的 n 项之和 Sn 是由
解决方案:
Let, P(n) = Sn = 12 + 2 × 22 + 32 + 2 × 42 + 52 + 2 × 62 + 72 +… = 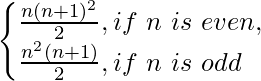
Step 1:
Now, let us check P(n) for n = 1.
LHS = 1 = RHS
So, P(1) is true.
Step 2:
Let us consider P (n) be the true for n = k, So, P(k) is
P(k) = 12 + 2.22 + 32 + 2.42 + 52 = 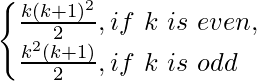
Step 3:
Now, we have to prove for P(k + 1) is true. When P(k) is true.
Case1: When k is odd, then (k + 1) is even
P(k + 1) = LHS = 12 + 2.22 + 32 + 2.42 + 52…. k2 + 2.(k + 1)2
= k2(k + 1)/2 + 2.(k + 1)2
= {(k2(k + 1) + 4(k + 1)2)}/2
= (k + 1)(k + 2)2/2
now, RHS = (k + 1)(k + 1 + 1)2/2
= (k + 1)(k + 2)2/2
So, it is true for n = k + 1, when k is odd.
Case 2: When k is even, then (k + 1) is odd
P(k + 1) = LHS = 12 + 2.22 + 32 + 2.42 + 52….+ 2. k2 + (k + 1)2
= k(k + 1)2/2 + (k + 1)2
= (k(k + 1)2 + 2.(k + 1)2)/2
= (k + 1)2(k + 2)/2
RHS = (k + 1)2(k + 1 + 1)/2
= (k + 1)2(k + 2)/2
now, LHS = RHS.
So, it is true for n=k+1, when k is even.
So, P (n) is true for n = k + 1
i.e., P (n) is true for all n ∈ N
Hence, by principle of Mathematical Induction (PMI), P (n) is true for all n ∈ N.
问题 45. 证明对于所有 n ∈ N,包含 n 个不同元素的集合的子集数为 2 n 。
解决方案:
Let, P(n): The number of subsets of a set containing n distinct elements = 2n, for all n ∈ N.
Step 1:
Now, let us check P(n) for n = 1.
LHS = As, the subsets of the set containing only 1 element are:
Φ and the set itself
i.e. the number of subsets of a set containing only element=2
R.H.S = 21 = 2
now, LHS = RHS
So, P(1) is true.
Step 2:
Let us consider P (n) be the true for n = k,
So, P(k) is The number of subsets of a set containing k distinct elements = 2k
Step 3:
Now, we have to prove for P(k + 1) is true. When P(k) is true.
P(k + 1) = Let A = {a1, a2, a3, a4,..…, ak, b} so that A has (k + 1) elements.
Now, the subset t of A can be divided into two collections such that
First contains subsets of A which don’t have b in them and
The second contains subsets of A which do have b in them.
So, First collection: {}, {a1}, {a1, a2}, {a1, a2, a3},…,{a1, a2, a3, a4,…, ak} and
and the second collection: {b}, {a1, b}, {a1, a2, b}, {a1, a2, a3, b},…,{a1, a2, a3, a4,…,ak, b}
It can be clearly seen that:
The number of subsets of A in first collection
= The number of subsets of set with k elements i.e. {a1, a2, a3, a4,…, ak} = 2k
Also, it follows that the second collection must have
the same number of the subsets as that of the first = 2k
So the total number of subsets of A = 2k + 2k = 2k+1
So, P (n) is true for n = k + 1
i.e., P (n) is true for all n ∈ N
Hence, by principle of Mathematical Induction (PMI), P (n) is true for all n ∈ N.
问题 46. 序列 a 1 , a 2 , a 3 ,….. 定义为对于所有自然数 k ≥ 2 的 a 1 = 3 和 a k = 7a k-1 。证明 a n = 3.7 n- 1对于所有 n ∈ N。
解决方案:
Let P(n) be an = 3.7n-1 for all n ∈ N
Step 1:
Now, let us check P(n) for n = 1.
so, a1 = 3.71-1 = 3
So, P(1) is true.
Step 2:
Let us consider P (n) be the true for n = k,
P(k) = ak = 3.7k-1
Step 3:
Now, we have to prove for P(k + 1) is true. When P(k) is true.
P(k + 1) = ak+1 = 7.ak
= 7.3.7k-1
= 3.7k-1+1
= 3.7(k+1)-1
So, P (n) is true for n = k + 1
i.e., P (n) is true for all n ∈ N
Hence, by principle of Mathematical Induction (PMI), P (n) is true for all n ∈ N.
问题 47. 序列 x 1 , x 2 , x 3 ,….. 定义为 x 1 = 2 和 x k = x k-1 /k 对于所有自然数 k, k ≥ 2。证明 x n = 2/n!对于所有 n ∈ N。
解决方案:
Let, P(n) be xn = 2/n! for all n ∈ N.
Step 1:
Now, let us check P(n) for n = 1.
P(1) = x1 = 2/1! = 2
So, P(1) is true.
Step 2:
Let us consider P (n) be the true for n = k,
P(k) = xk = 2/k!
Step 3:
Now, we have to prove for P(k + 1) is true. When P(k) is true.
so, xk+1 = 2/(k + 1)!
or, 2/(k + 1).k!
or, 2/(k + 1)!
So, P (n) is true for n = k + 1
i.e., P (n) is true for all n ∈ N
Hence, by principle of Mathematical Induction (PMI), P (n) is true for all n ∈ N.
问题 48. 一个序列 x 0 , x 1 , x 2 , x 3 , ……。是通过让 x 0 = 5 和 x k = 4 + x k -1对于所有自然数 k 来定义的。使用数学归纳法证明对于所有 n ∈ N,x n = 5 + 4 n 。
解决方案:-
Let, P(n) = xn = 5 + 4n for all n ∈ N
Step 1:
Now, let us check P(n) for n = 0.
P(0) = 5 + 4(0) = 5
So, P(0) is true.
Step 2:
Let us consider P (n) be the true for n = k,
P(k) = xk = 5 + 4k
Step 3:
Now, we have to prove for P(k + 1) is true. When P(k) is true.
so, P(k + 1) = xk+1 = 4 + xk+1 -1
= 4 + xk
= 4 + 5 + 4k
= 5 + 4(k + 1)
So, P (n) is true for n = k + 1
i.e., P (n) is true for all n ∈ N
Hence, by principle of Mathematical Induction (PMI), P (n) is true for all n ∈ N.
问题 49. 利用数学归纳原理证明
√n < 1/√1 + 1/√2+ 1/√3 +…..+1/√n 对于所有自然数 n ≥2。
解决方案:
Let, P(n) = √n < 1/√1 + 1/√2+ 1/√3 +…..+1/√n for all n ≥ 2.
Step 1:
Now, let us check P(n) for n=2.
P(2) = √2 < 1 + 1/√2
or, 1.41 < 1 + 0.707 = 1.707
So, P(2) is true.
Step 2:
Let us consider P (n) be the true for n = k,
P(k) = √k < 1/√1 + 1/√2+ 1/√3 +…..+1/√k
Step 3:
Now, we have to prove for P(k+1) is true. When P(k) is true.
Now, LHS = √(k + 1)
Now, RHS = 1/√1 + 1/√2+ 1/√3 +…..+1/√k + 1/√(k + 1)
or, k/√{(k + 1)} < √k
or, k + 1/√{(k + 1)} – 1/√(k + 1) < √k
or, √(k + 1) – 1/√(k + 1)< √k
or, √(k + 1) < √k + 1/√(k + 1)
so, LHS < RHS.
So, P (n) is true for n = k + 1
i.e., P (n) is true for all n ≥ 2
Hence, by principle of Mathematical Induction (PMI), P (n) is true for all n ≥ 2.
问题 50. 代数的分配定律指出,对于所有实数 a 1和 a 2 ,我们有 c (a 1 + a 2 ) = ca 1 + ca 2 。用这个定律和数学归纳法证明,对于所有自然数,n ≥ 2,如果 c, a 1 , a 2 ,...,a n是任意实数,则 c (a 1 +a 2 +...+a n ) = ca 1 +ca 2 +…+ca n 。
解决方案:
Let, P(n) = c (a1+a2+…+an) = ca1+ca2+…+can, for all natural numbers, n ≥ 2.
Step 1:
Now, let us check P(n) for n=2.
LHS = c(a1 + a2)
RHS = c a1 + ca2
So, P(2) is true.
Step 2:
Let us consider P (n) be the true for n = k,
P(k) = c(a1+a2+…+ak) = ca1+ca2+…+cak
Step 3:
Now, we have to prove for P(k+1) is true. When P(k) is true.
LHS = c(a1+a2+…+ak + ak+1)
= c[(a1+a2+…+ak) + ak+1]
= c(a1+a2+…+ak) + cak+1
= ca1+ca2+…+cak + cak+1
= RHS
So, P (n) is true for n = k + 1
i.e., P (n) is true for all n ≥ 2
Hence, by principle of Mathematical Induction (PMI), P (n) is true for all n ≥ 2.