上一章已经研究了三角学的概念和不同比例。这里有一些三角学的基本应用需要讨论。众所周知,三角学是世界范围内研究的古老主题之一。三角学在天文学中有很多用途,可以用来计算行星与恒星之间的距离。在日常生活中,可以使用三角法以一种简单的方式来计算距离。在进入主要应用程序之前,首先应清除基本术语,例如仰角,视线,俯角等。
通常,高度是在垂直方向上从某一点偏离而在水平方向上测量的。通过下面提供的每个主题,您将对这些术语更加清楚。
仰角
考虑一个人在看灯塔的顶部,如下图所示:
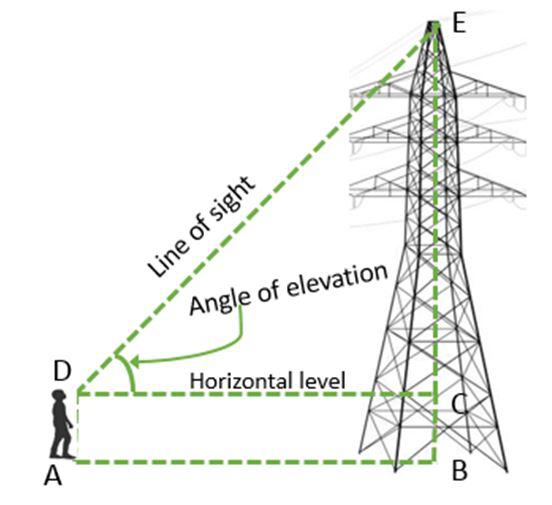
图1
在该图中,从男孩的眼睛到塔顶的线DE称为视线。
视线与男孩眼睛水平线之间的角度ΔCDA或∠D称为仰角。
当我们测量仰角时,观察者应抬起头并朝水平面上方看。
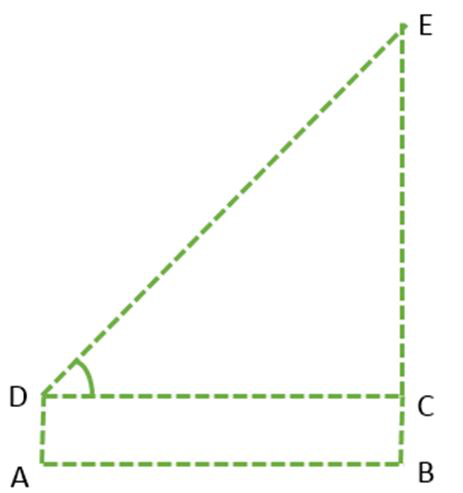
图2
如果要在不实际测量塔架的情况下计算塔架的高度,那么需要什么以及需要多少信息?需要以下细节来找出塔的高度而不进行测量;
- 塔与男孩站立的点之间的距离,AB或CD。
- 塔顶的仰角∠EDC。
- 男孩DA的身高。
在ΔCDE中,已知的∠D与侧面CE相反,而已知侧面CD。那么这里的三角比可以用来应用所有这三个量吗?确定tan D或cot D的比率,因为它们的比率涉及CD和CE。
在计算塔或任何其他物体的长度时,应记住男孩的长度,以将由三角比得出的结果相加。通过以下示例,此概念将更加清楚。
俯角
现在考虑给定图4中的情况,一个人正从阳台望着球。它的视线在水平线以下。视线与水平线之间的角度称为俯角。
因此,该点在物体上的俯角是水平点与视线在水平点以下时的夹角。

图4
在上图中,C点的人正朝B点的球看。CB是视线,AC是阳台的高度。
在ΔBCD中, ∠BCD是点B的下倾角度。这是阳台AC的高度= BD,球到建筑物的地面脚的距离AB = CD。根据给定的数据,可以使用三角比,因为它可能涉及已知量和未知量。
样本问题
问题1:一根杆子垂直站立在飞机上。从平面上距杆底脚12 m的点开始,杆顶顶部的仰角为30°。确定杆的高度。
解决方案:
First, draw a simple diagram of the given problem as below:
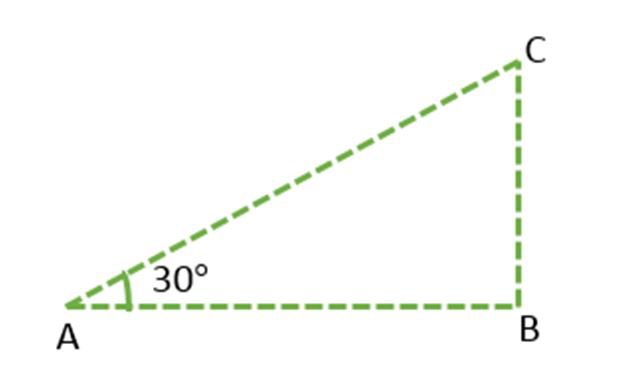
Figure 3
In this figure, BC represents the height of the electric pole and ∠CAB or ∠A represents the angle of the elevation of the top of the tower. In ΔABC, ∠CAB is the right angle and AB = 12 m. In ΔABC, CB is needed to be determined i.e. the height of the pole.
To solve the given problem use trigonometry ratio tan A or cot A as they involve given sides in ratios.
Now,
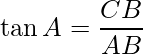
i.e.
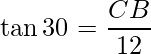
or
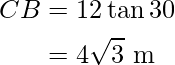
Hence, the height of the poll is 4√3.
问题2:一个男孩从某个角度开始为两朵云服务。云的仰角为30°和45°。如果从地面到云的高度相同,并且云之间的距离为300 m,则求出云的高度。
Solution:
First, draw a simple diagram of the given problem as below.

In this figure, CE and BD represents the height of the clouds and ∠DAB and ∠EAC represents the angle of the elevation of the clouds at point A. In ΔABD, ∠DBA is the right angle, if the height of cloud BD is h then using trigonometry ratio tan A
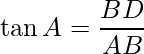
i.e.
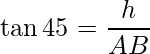
or
AB = h (Since, tan 45° = 1)
In ΔACE, ∠ACE is the right angle, if the height of cloud CE is h then using trigonometry ratio as:
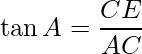
i.e.
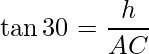
or
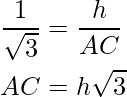
i.e.
AC = h√3
From the above figure 4,
AC = AB + BC
Given: BC = 300.
Therefore,
h√3 = h + 300
i.e.
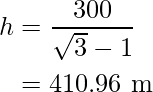
Hence, the height of the cloud is 410.96 m.
问题3:坐在树上的那只鸟与地面的某个点(与树脚相距60 m)的仰角为60°。找到树的高度。 (取√3= 1.73)。
Solution: First draw a simple diagram of the given problem as below:
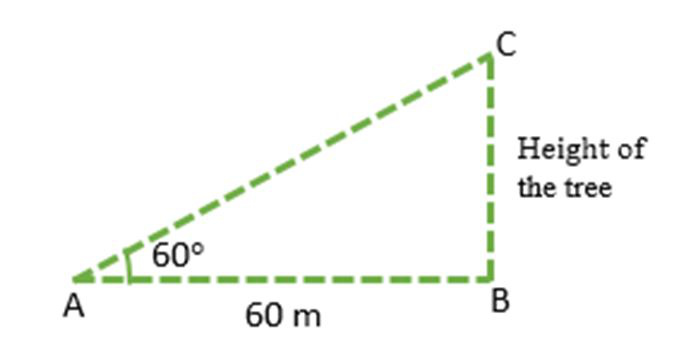
In above figure, AB represents the distance between the ground point and foot of the tree, i.e. 60 m. BC is the height of the tree, let’s assume h.
In ΔABC, ∠ABC is the right angle and the angle of the elevation is ∠B i.e. 60°.
Using trigonometry ratio tan A,
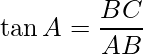
or
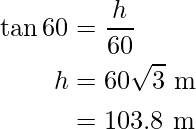
Hence, the height of the tree is 103.8 m.
问题4:停在公园中的自行车从45 m高的建筑物的顶部向下倾斜的角度为30°。自行车到建筑物底部的距离(以米为单位)是多少?
Solution:
Below is a simple diagram of the given problem.
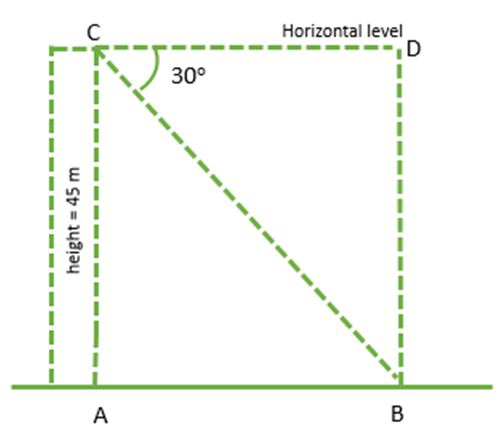
In above figure, AB represents the distance between the base of the building and the bike. AC is the height of the building, i.e. 45 m.
In ΔBCD, ∠BCD is the right angle and the angle of the depression is ∠C i.e. 30°. Using trigonometry ratio tan C in ΔBCD.
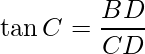
Here AC = BD and AB = CD.
i.e.

Hence, the distance between the base of building and the bike is 77.85 m.
问题5:电工需要修理电气故障以解决村庄的电源问题。存在故障的电极的高度为7 m。他想从极点顶部到达1.5 m以下的点以修复该断层。如果梯子相对于水平方向倾斜60°,他应使用多长的梯子才能到达所需位置?还发现他应该将梯子放到离杆脚多远的位置(取√3= 1.73)。
Solution:
First, Draw a basic diagram of the given problem as below:
In this figure, BC is the ladder, AD is the total length of the pole, Point C is the where electrician wants to reach.

As given CD = 1.5 m and AD = 7 m.
Therefore,
AC = AD – CD
i.e.
AC = 7 – 1.5 m
= 5.5 m
In ΔABC, ∠B is 60° and ∠A is right angle,
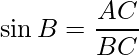
or
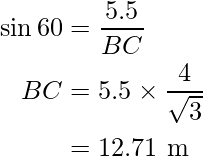
And, in ΔABC,
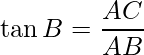
or
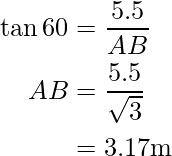
Hence, the length of the ladder BC is 12.71 m and the distance between ladder and foot of the pole AB is 3.17 m.
问题6:从某个点(在湖水表面某处)起的云的仰角为30°。从同一点湖水中的云的阴影的俯角为60°。如果云的高度为75 m,则找到阴影的深度。 (取√3= 1.73)。
Solution:
First, draw a basic diagram of the given problem as below:
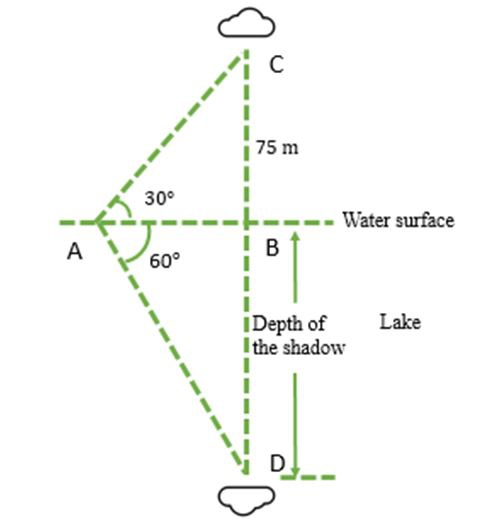
In this figure, AB is the water surface of the lake. Points C and D represent the cloud and its shadow respectively. ∠ABC and ∠ABD are the right angles. BC is the height of the cloud, i.e. 75 m and BD is the depth of the shadow. ∠BAC and ∠BAD are the angle of elevation and the angle of the depression, i.e. 30° and 60°.
In ΔABC,
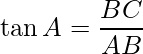
i.e.
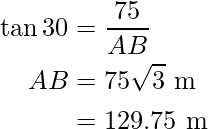
Now in ΔABD,
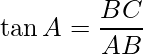
or
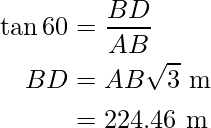
Hence, the depth of the shadow is 224.46 m.
问题7:考虑下图:
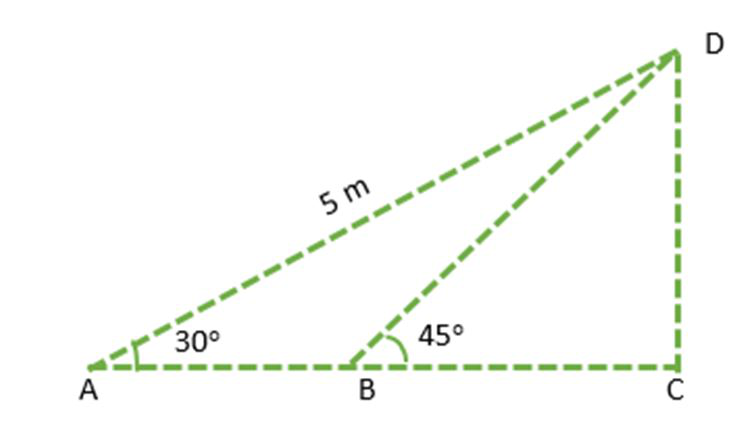
如果√ACB是直角,则找到AB和CD(取√3= 1.73)。
Solution:
In ΔACD, use the trigonometry ratio sin A,
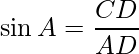
i.e.
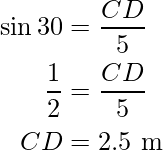
And,
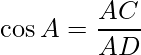
i.e.
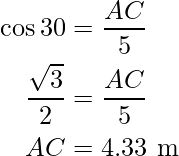
In ΔBCD, use the trigonometry ratio ![]() ,
,
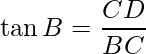
i.e.
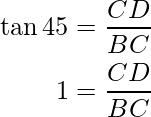
BC = CD = 2.5 m
From the given figure:
i.e.
AC = AB + BC
or
AB = 4.33 m – 2.5 m
=1.83 m
Hence, AB = 1.83 m and CD = 2.5 m.
问题8:一个1.5 m高的男孩正朝着两座建筑物看。两座建筑物的高度均为12 m。建筑物顶部的仰角分别为45°和60°。找出两座建筑物之间的距离以及男孩到附近建筑物的距离。
Solution:
A simple diagram of the given problem is drawn below
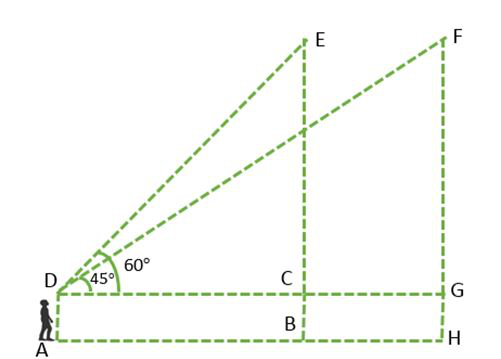
Figure 6
In the above figure, CB and GH represent the two buildings, CG is the distance between the two buildings, CD and GD is the distance between the boy and foot of the buildings of EB and FH respectively.
In ΔCDE and ΔFDG,
EC = FG = EB – AD (Since, AD = CB = GH)
i.e.
EC = FG = 12 m – 1.5 m
or
EC = FG = 10.5 m
In ΔCDE, ∠CDE is equal to ![]() and ∠DCE is the right angle.
and ∠DCE is the right angle.
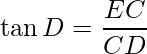
i.e.
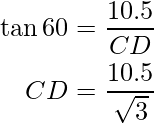
or
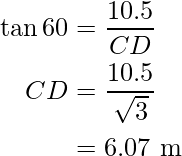
In ΔFDG, ∠FDG is ![]() and ∠FGD is right angle.
and ∠FGD is right angle.
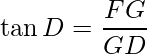
i.e.
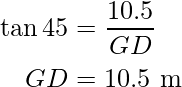
The distance between the buildings is:
CG = GD – CD
= 10.5 m – 6.07 m
= 4.43 m
Hence, the distance between the buildings CG is 4.43 m and the distance between the boy and the foot of the near building CD is 6.07 m.