第 12 类 RD Sharma 解决方案 - 第 31 章概率 - 练习 31.7 |设置 2
问题 14. 一个产品由三台机器 A、B和 C 制造。在特定时期内制造的产品总数中,50% 在机器 A 上制造,30% 在带上制造,20% 在 C 上制造。 A 生产的产品和 B 生产的 2% 的产品有缺陷,C 生产的产品中有 3% 有缺陷。所有物品都存放在一个仓库中。随机抽取一件商品,发现有瑕疵。它在机器 A 上制造的概率是多少?
解决方案:
Let us assume that E be the event of getting a defective item.
So, we have
P(A) = 50 % = 1/2
P(B) = 30 % = 3/10
P(C) = 20 % = 1/5
Also we have,
P(E/A) = 2 % = 1/50
P(E/B) = 2 % = 1/50
P(E/C) = 3 % = 3/100
Now,
P(the defective item drawn was manufactured on machine A) = ![]()
= 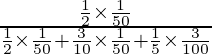
= 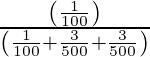
= 
= ![]()
= 500/1100
= 5/11
问题 15. 有三个硬币。一种是双头硬币(两面都有一个头),另一种是正面朝上的硬币,有 75% 的时间出现正面,第三种也是 40% 的时候出现背面的有偏见的硬币。随机选择三枚硬币中的一枚并投掷,并显示正面。它是两面硬币的概率是多少?
解决方案:
Let us assume
A = the event of choosing two-headed coin,
B = the event of choosing a biased coin that comes up head 75 % of the times
C = the event of choosing a biased coin that comes up tail 40 % of the times
E = the event of getting a head.
Now,
P(A) = 1/3
P(B) = 1/3
P(B) = 1/3
Also we have,
P(E/A) = 1
P(E/B) = 75 % = 75/100 = 3/4
P(E/C) = 60 % = 60/100 = 3/5
By using Bayes’ theorem, the required probability is
P(the head shown was of two-headed coin) = P (A/E)
= ![]()
= 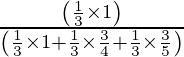
= 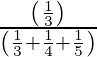
= 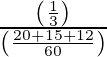
= ![]()
= 20/47
问题 16. 在一家工厂中,机器 A 生产总产量的 30%,机器 B 生产 25%,机器 C 生产剩余的产量。如果机器 A、B 和 C 生产的缺陷品分别为 1%、1.2%、2%。三台机器一起工作,一天可以生产 10000 件商品。从一天的输出中随机抽取一件物品,发现有缺陷。找出它是由机器 B 生产的概率?
解决方案:
Let us assume that the events are
A = the item is defective
E1 = machine A is chosen
E2 = machine B is chosen
E3 = machine C is chosen
So,
P(E1) = 30/100
P(E2) = 25/100
P(E3) = 45/100
Now,
P(A/E1) = 1/100
P(A/E2) = 1.2/1000
P(A/E3) = 2/100
By using Bayes’ theorem, the required probability is
P(E1/A) =
= 
= ![]()
= 30/150
= 1/5
= 0.2
问题 17. 一家公司有两个工厂生产自行车。第一个工厂生产 60% 的自行车,第二个工厂生产 40%。 80% 的自行车在第一工厂被评为标准质量,在第二工厂被评为标准质量的 90%。随机捡起一辆自行车,发现其质量符合标准。找出它来自第二个工厂的概率。
解决方案:
Let us assume that the events are
A = the cycle is of standard quality
E1 = plant I is chosen
E2 = plant II is chosen.
So,
P(E1) = 60/100
P(E2) = 40/100
Now,
P(A/E1) = 80/100
P(A/E2) = 90/100
By using Bayes’ theorem, the required probability is
P(E2/A) =
= 
= ![]()
= 36/84
= 3/7
问题 18. 三个瓮 A、B 和 C 包含 6 个红色和 4 个白色; 2红6白;和 1 个红球和 5 个白球。随机选择一个骨灰盒并抽出一个球。如果发现抽出的球是红色的,则求该球是从 A 罐中抽出的概率。
解决方案:
Let us assume that the events are
A = the ball is red
E1 = urn A is chosen
E2 = urn B is chosen
E2 = urn C is chosen.
So, P(E1) = 1/3
P(E2) = 1/3
P(E3) = 1/3
Now,
P(A/E1) = 6/10 = 3/5
P(A/E2) = 2/8 = 1/4
P(A/E3) = 1/6
By using Bayes’ theorem, the required probability is
P(E1/A) =
= 
= 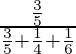
= 36/61
问题 19. 在 400 人的一组中,160 人是吸烟者和非素食者,100 人是吸烟者和素食者,其余的是非吸烟者和素食者。患上特殊胸部疾病的概率分别为 35%、20% 和 10%。从该组中随机选择一个人,并发现该人患有该疾病。被选中的人是吸烟者和非素食者的概率是多少?
解决方案:
Let us assume that the events are
A = the person suffers from the disease
E1 = a smoker and a non-vegetarian
E2 = a smoker and a vegetarian
E3 = a non-smoker and a vegetarian
So, P(E1) = 160/400
P(E2) = 100/400
P(E3) = 140/400
Now,
P(A/E1) = 35/100
P(A/E2) = 20/100
P(A/E3) = 10/100
By using Bayes’ theorem, the required probability is
P(E1/A) =
= 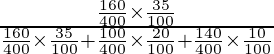
= ![]()
= 560/900
= 28/45
问题 20。一家工厂有三台机器 A、B 和 C,每天生产 100、200 和 300 件特定类型的物品。这些机器分别产生 2%、3% 和 5% 的缺陷品。某天生产结束,随机捡到一件物品,发现有瑕疵。求它是由机器 A 生产的概率。
解决方案:
Let us assume that the events are
A = the item is defective
E1 = machine A is chosen
E2 = machine B is chosen
E3 = machine C is chosen
So, P(E1) = 100/600
P(E2) = 200/600
P(E3) = 300/600
Now,
P(A/E1) = 2/100
P(A/E2) = 3/100
P(A/E3) = 5/100
By using Bayes’ theorem, the required probability is
P(E1/A) =
= 
= ![]()
= 2/23
问题 21. 一个袋子里有 1 个白球和 6 个红球,第二个袋子里有 4 个白球和 3 个红球。随机拿起其中一个袋子,从中随机抽出一个球,发现是白色的。找出抽出的球来自第一个袋子的概率。
解决方案:
Let us assume the events are
A = the ball is white
E1 = bag I is chosen
E2 = bag II is chosen
So, P(E1) = 1/2
P(E2) = 1/2
Now,
P(A/E1) = 1/7
P(A/E2) = 4/7
By using Bayes’ theorem, the required probability is
P(E1/A) = ![]()
= 
= ![]()
= 1/5
问题22:某高校有4%的男生和1%的女生身高超过1.75米。此外,大学里60%的学生是女生。从学院随机抽取的一名学生被发现身高超过1.75米。求所选学生是女孩的概率。
解决方案:
Let us assume the events are
A = The height of the student is more than 1.75 m
E1 = The selected student is a girl
E2 = The selected student is a boy
So,
P(E1) = 60/100
P(E2) = 40/100
Now,
P(A/E1) = 1/100
P(A/E1) = 4/100
By using Bayes’ theorem, the required probability is
P(E1/A) = ![]()
= 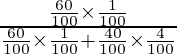
= ![]()
= 6/22
= 3/11
问题 23. 对于 A、B 和 C,被选为公司经理的机会分别为 4:1:2。他们对营销策略进行彻底改变的概率分别为 0.3、0.8 和 0.5。如果确实发生了变化,请找出它是由于 B 或 C 的任命引起的概率。
解决方案:
Let us assume the events are
A = The change takes place
E1 = A is selected
E2 = B is selected
E3 = C is selected
So,
P(E1) = 4/7
P(E2) = 1/7
P(E3) = 2/7
Now,
P(A/E1) = 0.3
P(A/E2) = 0.8
P(A/E3) = 0.5
By using Bayes’ theorem, the required probability is
P(E1/A) =
= 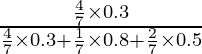
= ![]()
= 1.2/3
= 2/5
1 – P(E1/A) = 1 – 2/5 = 3/5
问题 24. A、B 和 C 三个人申请私人公司的经理职位。他们选择(A、B 和 C)的机会比例为 1 : 2 : 4。A、B 和 C 可以引入变化以提高公司利润的概率分别为 0.8、0.5 和 0.3 .如果没有发生变化,求出它是由于 C 的任命引起的概率。
解决方案:
Let us assume the events are
E1 = The selection of A as manager
E2 = The selection of B as manager
E3 = The selection of C as manager
So,
P(E1) = The probability of selection of A = 1/7
P(E2) = The probability of selection of B = 2/7
P(E3) = The probability of selection of C = 4/7
Let us assume that A be the event representing the change not taking place.
P(A/E1) = Probability that A does not introduce change = 0.2
P(A/E2) = Probability that B does not introduce change = 0.5
P(A/E3) = Probability that C does not introduce change = 0.7
So, the required probability = P(A/E3)
By using Bayes’ theorem, the required probability is
P(A/E3) = ![]()
= 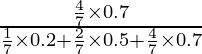
= ![]()
= 2.8/4
= 0.7
问题 25。一家保险公司为 2000 辆踏板车和 3000 辆摩托车投保。涉及踏板车的事故概率为 0.01,而摩托车事故的概率为 0.02。被保险车辆发生事故。求事故车辆是摩托车的概率。
解决方案:
Let us assume the events are
A = The vehicle meets the accident
E1 = is a scooter
E2 = is a motorcycle
So,
P(E1) = 2000/5000 = 0.4
P(E2) = 3000/5000 = 0.6
Now,
P(A/E1) = 0.01
P(A/E2) = 0.02
By using Bayes’ theorem, the required probability is
P(E2/A) =
= ![]()
= ![]()
= 0.012/0.016
= 3/4
问题 26. 在大学的学生中,已知有 60% 住在宿舍,40% 不住在宿舍。去年的结果显示,30% 住在宿舍的学生在年度考试中获得 A 级,20% 不在宿舍的学生获得 A 级。年底时,从学院中随机选择一名学生,他的成绩为A。被选中的学生是房东的概率是多少?
解决方案:
Let us assume the events are
A = The selected student attains grade A
E1 = resides in a hostel
E2 = does not reside in a hostel
So, P(E1) = 60/100
P(E2) = 40/100
Now,
P(A/E1) = 30/100
P(A/E2) = 20/100
By using Bayes’ theorem, the required probability is
P(E1/A) = ![]()
= 
= ![]()
= 9/13